Table of Contents
Key Takeaways:
- Choose CCSP if:
- You want multi-cloud career flexibility.
- You are interested in governance and risk roles.
- You aim for architecture or leadership positions.
- Choose AWS Security if:
- You work mainly in AWS environments.
- You handle IAM, encryption, and monitoring tools.
- You prefer deep technical specialization.
Cloud security careers are growing rapidly today. Many professionals seek the right certification. The debate around CCSP vs AWS Security is common. Both certifications promise strong career growth. But they serve different learning goals. Choosing wisely can shape your future. Understanding their differences is very important. Let us explore them clearly.
Each certification offers unique advantages. Your choice depends on career direction. Some prefer broad cloud security knowledge. Others want deep AWS expertise. Experience level also plays a role. Industry demand should guide your decision. Salary expectations may influence you too. Clear understanding helps avoid confusion. This guide will simplify your decision.
Enroll in Entri’s AI-Powered Cybersecurity course now!
What Is CCSP Certification?
The CCSP certification focuses on cloud security expertise. It stands for Certified Cloud Security Professional. It is offered by ISC2. This certification validates advanced cloud security knowledge. It targets experienced IT and security professionals. CCSP emphasizes practical and strategic security skills. It applies across different cloud environments. It supports secure cloud adoption globally.
Overview of CCSP
CCSP is a globally respected credential. It concentrates on cloud security frameworks. It covers architecture, governance, and compliance. CCSP also addresses risk management practices. The certification suits mid and senior professionals. It proves deep understanding of cloud risks. It demonstrates leadership in cloud security roles.
Key Highlights
- Vendor neutral cloud security certification
- Focuses on advanced security principles
- Recognized worldwide by employers
- Designed for experienced professionals
Who Should Pursue CCSP?
CCSP is not entry level. It requires professional experience. It suits security architects and engineers. CCSP benefits consultants and security managers. CCSP helps professionals handling cloud governance. It supports those managing compliance programs. It strengthens leadership career paths.
Ideal Roles
- Cloud Security Architect
- Information Security Manager
- Security Consultant
- Cloud Risk Analyst
Experience Requirements
CCSP has strict eligibility criteria. Candidates need professional experience. Experience must include information technology. Security domain experience is also required. Cloud related work experience is valuable. Experience can be cumulative. It must meet defined standards.
Experience Breakdown
- Minimum five years IT experience
- Three years in information security
- One year in cloud security domain
Candidates lacking full experience may qualify later. They can become Associate of ISC2. Full certification requires verified experience.
Domains Covered in CCSP
CCSP covers multiple cloud security domains. Each domain builds specialized knowledge. These domains follow structured guidelines. They align with industry standards. They focus on real world scenarios. Knowledge areas remain broad and detailed.
Major Domains
- Cloud Concepts and Architecture
- Cloud Data Security
- Cloud Platform and Infrastructure Security
- Cloud Application Security
- Cloud Security Operations
- Legal Risk and Compliance
Each domain requires conceptual clarity. Practical understanding is also necessary. Questions test analytical thinking skills. Memorization alone is insufficient.
Core Skills Developed
CCSP builds strategic security skills. It improves cloud architecture knowledge. It enhances risk assessment capabilities. CCSP strengthens compliance understanding. It supports data protection planning. It improves incident response strategies.
Skill Areas
- Cloud governance planning
- Risk identification methods
- Security control implementation
- Data lifecycle management
- Regulatory compliance mapping
These skills support leadership roles. They enable secure decision making. They strengthen enterprise security posture.
Exam Structure
The CCSP exam tests advanced knowledge. It uses multiple choice questions. Questions assess scenario based reasoning. The exam duration is limited. Time management is important.
| Exam Component | Details |
|---|---|
| Question Type | Multiple choice |
| Number of Questions | Around 125 |
| Duration | About four hours |
| Passing Score | Fixed scaled score |
The exam demands conceptual clarity. Practical experience improves success chances. Preparation requires structured study planning.
Certification Validity
CCSP certification remains valid with maintenance. Professionals must earn continuing education credits. These credits maintain certification status. Annual fees are also required. Continuous learning remains essential.
Maintenance Requirements
- Earn continuing professional education credits
- Pay annual maintenance fee
- Follow ethical guidelines
This ensures updated knowledge. It promotes lifelong learning culture.
Global Recognition
CCSP is recognized worldwide. Employers trust this credential. It meets international security standards. It aligns with global compliance needs. Many industries value this certification. It supports cross border career growth.
Industries Valuing CCSP
- Banking and financial services
- Healthcare organizations
- Government institutions
- Technology companies
- Consulting firms
Global demand for cloud security grows. Certified professionals gain competitive advantage.
Benefits of CCSP Certification
CCSP enhances professional credibility. It strengthens career progression opportunities. CCSP increases employer confidence. CCSP supports higher responsibility roles. It improves risk management expertise.
Professional Advantages
- Strong global recognition
- Vendor neutral credibility
- Advanced security leadership validation
- Broader career mobility
The certification builds long term value. It reflects dedication to security excellence.
Learning Approach for CCSP
Preparation requires structured study plans. Official study guides are helpful. Practice exams improve readiness. Hands on experience strengthens understanding. Domain wise preparation works best.
Study Strategy
- Review official exam outline
- Study domain concepts deeply
- Practice scenario based questions
- Revise compliance frameworks
Consistent preparation improves confidence. Real world experience supports exam success.
Summary of CCSP Features
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Type | Vendor neutral certification |
| Focus | Advanced cloud security |
| Level | Professional and advanced |
| Recognition | Global industry acceptance |
| Maintenance | Continuing education required |
CCSP represents comprehensive cloud security knowledge. It combines governance and technical skills. It prepares professionals for leadership roles. CCSP supports secure cloud transformation initiatives. It stands as a respected security credential worldwide.
What Is AWS Security Certification?
AWS Security Certification focuses on securing AWS environments. It validates expertise in AWS cloud security. The certification is offered by Amazon Web Services. It is officially named AWS Certified Security – Specialty. This credential targets professionals securing AWS workloads. It proves advanced technical security skills. This certification demonstrates deep AWS service knowledge. It is designed for experienced cloud practitioners.
Overview of AWS Security Certification
This certification is vendor specific. It focuses only on AWS cloud services. This certification tests practical and technical expertise. It evaluates real world security scenarios. This certification also emphasizes implementation and monitoring skills. It suits professionals managing AWS infrastructure. It supports organizations using AWS heavily.
Key Highlights
- Vendor specific AWS security certification
- Focuses on technical implementation skills
- Recognized in AWS centric companies
- Designed for experienced cloud engineers
Who Should Pursue AWS Security Certification?
This certification suits technical professionals. It benefits AWS security engineers. It helps cloud administrators and architects. This certification supports DevOps professionals in AWS. It strengthens roles managing AWS compliance. It suits professionals handling AWS workloads daily.
Ideal Roles
- AWS Security Engineer
- Cloud Security Specialist
- DevSecOps Engineer
- Cloud Infrastructure Architect
It is not ideal for beginners. It requires prior AWS knowledge. Practical AWS experience is highly recommended.
Recommended Experience
There is no strict mandatory requirement. However practical experience is essential. Candidates should understand AWS core services. Security best practices knowledge is important. Hands on configuration experience is beneficial.
Suggested Background
- Two years AWS experience
- Experience securing AWS workloads
- Knowledge of AWS networking
- Familiarity with encryption services
Strong AWS fundamentals improve exam success. Practical labs support better understanding.
Domains Covered in AWS Security Certification
The certification covers focused security domains. Each domain relates to AWS services. Topics emphasize real configuration tasks. Knowledge must be practical and specific. The exam checks applied security skills.
Major Domains
- Incident Response in AWS
- Logging and Monitoring
- Infrastructure Security
- Identity and Access Management
- Data Protection
- Governance and Compliance
Each domain involves AWS tools. Candidates must understand service integration. Real world troubleshooting knowledge is helpful.
Core Skills Developed
This certification builds AWS security expertise. It strengthens identity management skills. It improves encryption implementation knowledge. This certification enhances monitoring and logging capabilities. It supports secure architecture design.
Skill Areas
- IAM policy configuration
- Key management service usage
- Secure VPC architecture design
- Threat detection using monitoring tools
- Compliance control implementation
These skills are practical and technical. They apply directly to AWS projects. They improve operational cloud security.
Important AWS Services Covered
The exam focuses on AWS security tools. Candidates must understand specific services. Configuration knowledge is essential. Monitoring setup skills are important.
Common Services Tested
- AWS Identity and Access Management
- AWS Key Management Service
- AWS CloudTrail
- AWS Config
- AWS GuardDuty
- AWS Security Hub
Understanding service integration is critical. Knowledge of best practices is required. Hands on labs strengthen confidence.
Exam Structure
The AWS Security exam is scenario based. It includes multiple choice questions. Questions test problem solving skills. Time management is necessary.
| Exam Component | Details |
|---|---|
| Question Type | Multiple choice |
| Number of Questions | Around 65 |
| Duration | About 170 minutes |
| Passing Score | Scaled passing score |
Questions focus on AWS use cases. Memorization alone is insufficient. Practical understanding ensures better performance.
Certification Validity
The certification remains valid for limited years. Recertification is required periodically. Professionals must retake the exam. This ensures updated AWS knowledge. Cloud services change frequently.
Maintenance Requirements
- Recertify every three years
- Stay updated with AWS changes
- Continue hands on practice
Continuous learning is essential. AWS services evolve rapidly.
Industry Recognition
This certification holds strong market value. It is respected in AWS environments. Many companies rely on AWS infrastructure. Skilled AWS security professionals remain in demand. Employers prefer certified AWS specialists.
Industries Valuing AWS Security
- Technology startups
- E commerce platforms
- Financial services companies
- SaaS product firms
- Cloud consulting agencies
Demand grows with cloud adoption. Organizations prioritize AWS expertise.
Benefits of AWS Security Certification
This certification boosts technical credibility. It strengthens AWS specialization. It improves job opportunities in AWS roles. This certification supports career advancement in cloud security. It enhances practical security implementation skills.
Professional Advantages
- Strong AWS specific credibility
- Technical skill validation
- Higher demand in AWS roles
- Competitive salary potential
It demonstrates hands on cloud expertise. It reflects commitment to AWS mastery.
Learning Approach for AWS Security
Preparation requires practical labs. Official AWS documentation is helpful. Practice exams improve readiness. Real world AWS projects enhance understanding. Structured domain wise study works best.
Study Strategy
- Review AWS exam guide
- Practice IAM configurations
- Test monitoring service setups
- Study encryption methods
- Analyze scenario based questions
Hands on experience is critical. Regular revision strengthens knowledge retention.
Summary of AWS Security Certification Features
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Type | Vendor specific certification |
| Focus | AWS cloud security |
| Level | Specialty advanced certification |
| Recognition | High in AWS ecosystems |
| Renewal | Recertification required periodically |
AWS Security Certification validates deep AWS expertise. It emphasizes technical security implementation. It prepares professionals for AWS focused roles. AWS strengthens operational cloud defense capabilities. It remains valuable in AWS driven industries.
Enroll in Entri’s AI-Powered Cybersecurity course now!
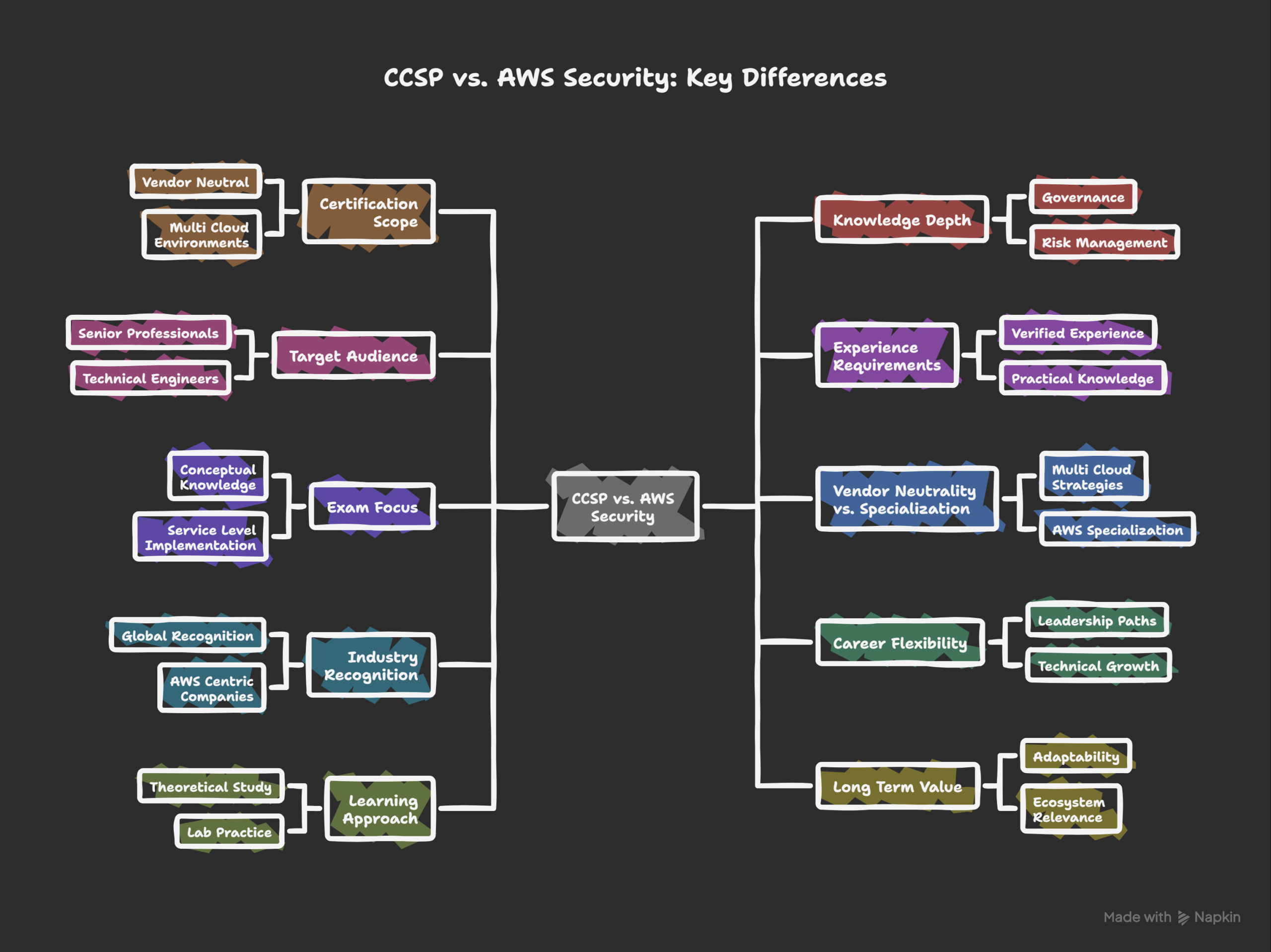
Key Differences Between CCSP and AWS Security
Choosing between these certifications requires clarity. Both validate cloud security expertise. However their scope differs significantly. Focus areas are not identical. Career outcomes may also vary. Understanding differences supports informed decisions. Each certification serves distinct professional goals. Careful comparison prevents confusion.
1. Certification Scope
Scope defines knowledge coverage. Certified Cloud Security Professional offers broad cloud security coverage. Coverage spans multiple cloud platforms. The credential remains vendor neutral. Security principles apply universally.
AWS Certified Security – Specialty concentrates only on AWS environments. The certification remains platform specific. Knowledge depth centers on AWS services. Other providers receive no focus. The approach stays AWS aligned.
Scope Comparison Table
| Aspect | CCSP | AWS Security |
|---|---|---|
| Coverage | Multi cloud environments | AWS only |
| Approach | Vendor neutral | Vendor specific |
| Flexibility | Cross platform applicability | AWS ecosystem focused |
CCSP supports broader cloud ecosystems. AWS Security supports focused AWS specialization.
2. Knowledge Depth
Both certifications demand strong expertise. Depth varies in structure and emphasis. CCSP emphasizes conceptual clarity. Governance and architecture frameworks receive attention. Policy and compliance knowledge remains essential.
AWS Security emphasizes technical implementation. Service level configuration forms the core. Monitoring and encryption tools receive detailed focus. Real AWS scenarios dominate questions.
Depth Focus
CCSP Focus Areas
- Governance and risk management
- Cloud architecture principles
- Legal and compliance frameworks
- Data lifecycle management
AWS Security Focus Areas
- IAM policy configuration
- Key management service usage
- Logging and monitoring setup
- Incident response in AWS
CCSP builds strategic understanding. AWS Security builds technical mastery.
3. Target Audience
Audience suitability differs clearly. CCSP suits senior professionals. Architects and managers benefit significantly. Consultants and compliance leaders find strong value.
AWS Security suits technical engineers. Administrators and DevSecOps professionals gain relevance. Daily AWS practitioners align closely.
Role Alignment Table
| Role Type | CCSP Suitable | AWS Security Suitable |
|---|---|---|
| Security Architect | Yes | Yes |
| Cloud Security Engineer | Yes | Yes |
| Compliance Manager | Yes | Limited |
| AWS Administrator | Limited | Yes |
CCSP aligns with leadership progression. AWS Security aligns with operational specialization.
4. Experience Requirements
Experience expectations vary substantially. CCSP requires verified professional background. Security domain exposure remains mandatory. Cloud related experience strengthens eligibility.
AWS Security recommends practical exposure. Strict formal verification does not apply. Hands on AWS familiarity remains crucial. Real project experience improves confidence.
Experience Comparison
- CCSP demands structured eligibility verification
- AWS Security suggests practical AWS experience
- CCSP targets experienced professionals
- AWS Security targets skilled practitioners
Formal criteria distinguish CCSP clearly.
5. Exam Structure
Exam formats reflect different priorities. CCSP includes longer duration assessment. Broad knowledge areas receive testing. Scenario based reasoning dominates evaluation.
AWS Security presents shorter examination format. AWS specific use cases drive questions. Configuration decisions form core challenges. Strong service knowledge ensures better outcomes.
Exam Comparison Table
| Component | CCSP | AWS Security |
|---|---|---|
| Focus | Conceptual and strategic | Technical and service specific |
| Question Style | Scenario based analysis | Service based implementation |
| Preparation Style | Theory plus experience | Hands on labs essential |
Preparation strategy must match exam design.
6. Vendor Neutrality vs Specialization
Vendor neutrality supports flexibility. CCSP applies across major cloud providers. Hybrid and multi cloud strategies gain advantage. Career mobility increases across environments.
AWS Security emphasizes specialization depth. Expertise centers on AWS ecosystem. Multi cloud exposure remains limited. Organizations using AWS heavily prefer such focus.
Comparison Points
- CCSP provides cross platform adaptability
- AWS Security provides AWS specialization
- CCSP fits hybrid cloud strategies
- AWS Security fits AWS only strategies
Career direction influences this distinction strongly.
7. Industry Recognition
Both credentials carry industry value. CCSP enjoys global recognition. Enterprises focusing on governance appreciate the credential. Compliance driven sectors value broad expertise.
AWS Security holds strong credibility within AWS environments. Companies operating primarily on AWS prioritize such specialization. Technical teams recognize practical skill validation.
Industry Fit
| Industry Type | CCSP Advantage | AWS Security Advantage |
|---|---|---|
| Government | Strong | Moderate |
| Consulting | Strong | Strong |
| AWS Focused Firms | Moderate | Strong |
| Multi Cloud Enterprises | Strong | Limited |
Recognition depends largely on organizational structure.
8. Career Flexibility
Career mobility differs significantly. CCSP supports transition across cloud providers. Consulting and advisory paths gain advantage. Strategic leadership roles become accessible.
AWS Security strengthens AWS centric pathways. Deep platform expertise increases technical authority. Transition beyond AWS may require additional certifications.
Career Path Comparison
- CCSP enables strategic cloud leadership
- AWS Security enables AWS technical specialization
- CCSP supports consulting mobility
- AWS Security supports AWS engineering depth
Long term vision shapes preference.
9. Learning Approach
Learning style expectations vary widely. CCSP preparation demands framework understanding. Governance models require careful study. Risk management concepts require clarity.
AWS Security preparation demands lab practice. Service configuration exercises become essential. Monitoring and encryption setup require hands on repetition.
Study Method Comparison
| Study Aspect | CCSP | AWS Security |
|---|---|---|
| Theory Emphasis | High | Moderate |
| Practical Labs | Moderate | High |
| Governance Focus | Strong | Limited |
| Service Configuration | General | Detailed |
Study approach must align with certification goals.
10. Long Term Value
Long term relevance depends on strategy. CCSP maintains value across providers. Vendor neutrality ensures adaptability. Changing cloud trends remain manageable.
AWS Security maintains relevance within AWS ecosystems. Platform growth directly influences value. Deep specialization ensures technical credibility.
Both certifications provide meaningful benefits. Differences revolve around scope and focus. Strategic comparison clarifies suitability. Career objectives should guide the final decision.
Which Certification Should You Choose?
Choosing the right certification requires clarity. Career direction plays a major role. Current job responsibilities also influence decisions. Long term goals must remain central. Cloud environment exposure matters significantly. Skill level determines suitable difficulty. Careful evaluation prevents wrong choices. A strategic approach ensures better outcomes.
1. Choose Based on Career Goals
Career goals define certification relevance. Professionals seeking leadership roles may prefer Certified Cloud Security Professional. Strategic governance knowledge supports senior positions. Architecture and compliance expertise strengthen management pathways.
Professionals seeking technical specialization may prefer AWS Certified Security – Specialty. Deep AWS expertise benefits engineering roles. Platform specific mastery enhances operational responsibilities.
Career Goal Alignment
- Leadership and consulting roles → CCSP
- Architecture and governance focus → CCSP
- AWS engineering roles → AWS Security
- DevSecOps in AWS → AWS Security
Long term ambition should guide selection.
2. Consider Current Work Environment
Workplace environment influences certification value. Multi cloud organizations benefit from vendor neutral knowledge. Broad security frameworks support hybrid strategies.
AWS dominant organizations value platform expertise. Technical teams require strong AWS configuration skills. Daily AWS exposure favors specialization.
Environment Comparison Table
| Work Environment | Recommended Certification |
|---|---|
| Multi cloud setup | CCSP |
| AWS only environment | AWS Security |
| Hybrid cloud strategy | CCSP |
| AWS focused projects | AWS Security |
Organizational focus determines certification impact.
3. Evaluate Experience Level
Experience level must align with certification demands. CCSP requires verified professional background. Security domain knowledge remains essential. Senior professionals match eligibility criteria.
AWS Security recommends hands on AWS experience. Strict formal verification does not apply. Technical practitioners with lab exposure perform well.
Experience Based Choice
- Senior security professionals → CCSP
- Governance specialists → CCSP
- AWS administrators → AWS Security
- DevOps engineers in AWS → AWS Security
Matching experience prevents preparation challenges.
4. Assess Learning Preference
Learning style varies among professionals. Conceptual and framework based learners may prefer CCSP. Policy and governance study requires analytical thinking.
Hands on learners may prefer AWS Security. Lab practice strengthens AWS service understanding. Configuration tasks demand practical engagement.
Study Approach Comparison
| Learning Style | Suitable Certification |
|---|---|
| Theory focused | CCSP |
| Governance oriented | CCSP |
| Hands on technical | AWS Security |
| Lab intensive practice | AWS Security |
Preparation comfort influences exam success.
5. Consider Career Flexibility
Career flexibility supports long term growth. CCSP enables cross platform mobility. Vendor neutrality increases adaptability. Consulting opportunities expand significantly.
AWS Security strengthens deep specialization. Technical authority grows within AWS ecosystems. Platform centric careers gain momentum.
Mobility Consideration
- Multi cloud aspirations → CCSP
- Consulting ambitions → CCSP
- AWS deep specialization → AWS Security
- Platform loyalty to AWS → AWS Security
Future transitions must remain possible.
6. Salary and Market Demand
Market demand affects certification value. Broad governance expertise supports enterprise roles. Multi cloud organizations seek strategic security leaders.
AWS adoption continues to expand globally. Organizations require skilled AWS security engineers. Technical specialization commands competitive compensation.
Salary levels depend on experience. Industry and region also influence earnings. Certification strengthens credibility and negotiation power.
7. Time and Preparation Commitment
Preparation intensity varies significantly. CCSP requires structured theoretical study. Domain wise revision becomes essential. Compliance frameworks demand clarity.
AWS Security requires lab based preparation. Practice environments improve retention. Service configuration exercises strengthen readiness.
Preparation Comparison Table
| Preparation Aspect | CCSP | AWS Security |
|---|---|---|
| Conceptual Study | High | Moderate |
| Practical Labs | Moderate | High |
| Governance Review | Strong | Limited |
| Technical Configuration | Moderate | Strong |
Available time should influence decision.
8. Long Term Vision
Long term vision defines strategic value. CCSP supports evolving cloud landscapes. Vendor neutral knowledge remains adaptable. Broader leadership pathways become accessible.
AWS Security supports AWS ecosystem dominance. Deep technical expertise ensures operational excellence. Platform growth strengthens specialization value.
Strategic Direction
- Enterprise leadership track → CCSP
- Compliance and governance track → CCSP
- AWS technical expert track → AWS Security
- DevSecOps AWS specialization → AWS Security
Vision clarity ensures meaningful certification investment.
9. When Both Certifications Make Sense
Some professionals may pursue both credentials. Strategic foundation through CCSP builds broad understanding. AWS Security then deepens platform expertise.
Sequential planning strengthens career impact. Broad knowledge combined with specialization enhances credibility. However timing must align with experience.
Final Consideration
No universal answer exists. Personal goals determine suitability. Professional environment shapes relevance. Experience level influences preparation comfort. Learning preference affects exam performance. Strategic clarity ensures long term benefit. Careful evaluation leads to confident decisions.
Career Opportunities and Salary Impact
Cloud security demand continues growing globally. Organizations prioritize secure cloud adoption strategies. Skilled professionals remain highly valuable. Certifications strengthen professional credibility significantly. Career advancement becomes more structured. Salary growth potential increases with specialization. Market demand influences compensation trends. Strategic certification choice impacts long term earnings.
Career Opportunities with CCSP
Certified Cloud Security Professional supports strategic security roles. Leadership pathways become more accessible. Governance focused organizations value such expertise. Multi cloud environments prefer vendor neutral knowledge.
Professionals often move into senior positions. Architecture responsibilities increase gradually. Advisory and consulting opportunities expand significantly. Enterprise risk management roles become attainable.
Common Job Roles
- Cloud Security Architect
- Information Security Manager
- Cloud Security Consultant
- Risk and Compliance Manager
- Security Governance Lead
These roles involve strategic planning. Policy design responsibilities increase. Cross functional collaboration becomes essential. Decision making authority expands over time.
Industries Hiring CCSP Professionals
Large enterprises value broad expertise. Government sectors emphasize compliance knowledge. Financial institutions prioritize risk management skills. Healthcare organizations require strong data protection planning. Consulting firms seek advisory capabilities.
Industry Demand Table
| Industry | Demand Level |
|---|---|
| Banking and Finance | High |
| Government | High |
| Healthcare | Strong |
| IT Consulting | Strong |
| Enterprise Technology | High |
Vendor neutrality increases mobility across industries.
Salary Impact of CCSP
Salary levels depend on experience. Senior roles command higher compensation. Leadership responsibilities influence earnings. Geographic location affects pay structure. Industry type also impacts salary range.
Mid level professionals see steady growth. Senior architects earn significantly higher packages. Consulting roles often include performance incentives. Governance specialists gain long term stability.
Higher responsibility correlates with increased salary. Certification enhances negotiation strength. Employer confidence improves with recognized credentials.
Career Opportunities with AWS Security
AWS Certified Security – Specialty strengthens AWS specific careers. Technical expertise becomes more visible. Platform focused organizations value deep specialization. Engineering pathways expand within AWS ecosystems.
Operational security roles become attainable. DevSecOps opportunities increase steadily. Cloud infrastructure security positions grow rapidly. Technical leadership roles emerge gradually.
Common Job Roles
- AWS Security Engineer
- Cloud Security Specialist
- DevSecOps Engineer
- AWS Cloud Architect
- Security Operations Analyst
These roles emphasize implementation. Configuration responsibilities remain central. Monitoring and response duties increase. Technical troubleshooting becomes frequent.
Industries Hiring AWS Security Professionals
Startups using AWS prefer specialized experts. SaaS companies rely heavily on AWS infrastructure. E commerce platforms demand strong AWS security. Cloud consulting firms require certified specialists. Technology driven firms prioritize platform expertise.
Industry Demand Table
| Industry | Demand Level |
|---|---|
| SaaS Companies | High |
| E commerce | High |
| Technology Startups | Strong |
| Cloud Consulting | Strong |
| Digital Enterprises | High |
AWS market expansion increases demand steadily.
Salary Impact of AWS Security
Technical specialization influences compensation strongly. Hands on expertise commands competitive salaries. Project critical roles often receive premium pay. High demand improves bargaining power.
Mid level engineers experience noticeable growth. Senior AWS architects earn substantial packages. DevSecOps professionals often receive performance bonuses. Specialized skills reduce job replacement risk.
Compensation varies by region. Experience remains a key factor. Technical depth increases earning potential. Continuous skill upgrades sustain salary growth.
Comparative Salary Outlook
Both certifications improve earning potential. Role type influences income range. Leadership roles offer structured progression. Technical specialization offers rapid growth.
| Factor | CCSP | AWS Security |
|---|---|---|
| Leadership Roles | Strong advantage | Moderate |
| Technical Engineering | Moderate | Strong advantage |
| Multi cloud Mobility | High | Limited |
| AWS Platform Demand | Moderate | High |
Strategic roles often bring long term stability. Technical specialization offers immediate demand.
Long Term Career Growth
Cloud security continues evolving rapidly. Regulatory requirements increase complexity. Organizations invest heavily in secure infrastructure. Certified professionals remain competitive.
Broad expertise supports executive pathways. Deep specialization supports technical mastery. Continuous learning remains essential. Market relevance depends on adaptability.
Both certifications create strong career foundations. Final impact depends on professional direction. Experience combined with certification maximizes salary growth. Strategic planning ensures sustainable success.
Final Verdict
Both certifications offer strong professional value. The right choice depends on career direction. Certified Cloud Security Professional suits professionals seeking broad, vendor neutral expertise. Leadership, governance, and multi cloud roles align well. Strategic thinkers may benefit more from this path. In contrast, AWS Certified Security – Specialty favors deep technical specialization. AWS focused engineers gain strong advantages here. Platform specific mastery strengthens operational credibility.
No single certification fits everyone. Work environment should guide the decision. Long term goals must remain central. Experience level also influences suitability. Multi cloud aspirations support choosing CCSP. AWS centric careers support choosing AWS Security. Both paths enhance credibility and salary potential. Careful evaluation ensures a confident final decision.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the main difference between CCSP and AWS Security certification?
The primary difference lies in scope and focus. Certified Cloud Security Professional is vendor neutral and covers broad cloud security principles. The certification applies across multiple cloud platforms. In contrast, AWS Certified Security – Specialty focuses only on AWS services. AWS Security emphasizes technical implementation within the AWS ecosystem. CCSP emphasizes governance, risk, and architecture. The choice depends on whether broad strategy or AWS specialization matters more.
Is CCSP harder than AWS Security certification?
Difficulty depends on professional background. CCSP requires strong conceptual understanding and verified experience. Governance, compliance, and architecture topics demand analytical thinking. AWS Security focuses on technical configuration knowledge. Candidates with hands on AWS experience may find AWS Security manageable. Professionals with leadership exposure may find CCSP more aligned. Preparation style also affects perceived difficulty. Both certifications require structured study and practice.
Which certification is better for beginners in cloud security?
Neither certification targets beginners directly. CCSP requires professional experience verification. AWS Security expects practical AWS exposure. Entry level professionals should first build foundational knowledge. Gaining cloud experience strengthens eligibility. After experience development, selecting based on career goals becomes easier. Early specialization without experience may create challenges. Practical exposure remains essential before attempting either certification.
Does CCSP cover AWS security concepts?
CCSP covers cloud security concepts broadly. AWS may be referenced as an example platform. However deep AWS configuration details are not included. The focus remains on universal principles. Governance and risk frameworks receive more attention. Professionals seeking service level AWS knowledge may need additional study. CCSP builds strategic understanding rather than tool specific mastery.
Does AWS Security certification have global recognition?
AWS Security holds strong recognition worldwide. Many organizations rely on AWS infrastructure. Certified professionals gain credibility within AWS environments. Technology companies especially value this certification. However recognition remains strongest in AWS centric roles. Multi cloud enterprises may prefer broader certifications. Industry context influences recognition impact significantly.
Can professionals pursue both CCSP and AWS Security?
Yes, pursuing both certifications can be strategic. CCSP builds broad cloud security foundations. AWS Security deepens platform specific expertise. Combining both enhances professional credibility. Strategic planning ensures proper timing. Experience should align with certification level. Sequential preparation often produces better results. Dual credentials strengthen both leadership and technical pathways.
How long does preparation take for each certification?
Preparation time varies by background knowledge. CCSP may require several months of structured study. Domain wise revision becomes necessary. AWS Security preparation often includes lab practice. Hands on AWS experience shortens preparation time. Candidates new to AWS may need additional practice. Consistency and real world exposure improve readiness.
Which certification offers better salary growth?
Salary growth depends on role and experience. CCSP often supports senior leadership positions. Governance roles may offer structured long term growth. AWS Security supports high demand technical roles. Specialized engineers may earn competitive packages quickly. Industry and region also influence salary levels. Certification enhances negotiation power but does not replace experience.
Which certification provides better career flexibility?
CCSP provides broader flexibility. Vendor neutrality supports movement across platforms. Consulting and advisory roles benefit from such adaptability. AWS Security provides strong specialization depth. However specialization may limit cross platform mobility. Professionals planning multi cloud careers may prefer broader credentials. Long term goals should guide flexibility decisions.
How should someone decide between CCSP and AWS Security?
Decision making should start with career vision. Current job responsibilities must be evaluated carefully. Work environment also influences certification relevance. Leadership aspirations align more with CCSP. Technical AWS specialization aligns more with AWS Security. Experience level must match eligibility expectations. Careful assessment ensures meaningful certification investment.