Table of Contents
Preparations for an Electrical Engineer interview are just over the basics. Employers seek candidates who can apply technical knowledge to problems in the real world by clearly communicating their views. Whether you are a recent graduate or an experienced professional, it is necessary to be ready for many questions from circuit theory and power system to safety standards and troubleshooting. Interviews often test your ability to think seriously under pressure. To help you succeed, we have gathered the latest and most asked questions about electrical engineer with clear, practical answers. This guide is designed to promote your self -confidence, accelerate your understanding and help help stand competitive labor market. Let’s get started!
Get hands-on with our MEP Quantity Surveyor course – sign up for a free demo!
Electrical Engineer Core Technical Questions
1. Mention the difference between a generator and a transformer?
Answer: A generator converts mechanical energy to electrical energy, while a transformer transforms electrical energy between the circuit through electromagnetic induction, without changing the total effect.
2. Define the concept of power factor and why it is important.
Answer: The power factor is the ratio of real power for clear power in an alternating current circuit. A high strength factor means more efficient use of power. Low power factor leads to energy loss and high use tax.
3. What are the different types of circuit breakers?
Answer: General types include short -circuit breakers (MCB), Molded Case Circuit Breakers (MCCB), Air Circuit Breakers (ACB) and Vacuum Circuit Breakers (VCB), each customized each separate voltage and power reviews.
4. How do you calculate the current-carrying capacity of a conductor?
Answer: It is based on the content of the conductor, cross -sectional area, environmental temperature and insulation type. Standard tables in electrical codes provide values or you can use the formula: I = √3 × V × PF / (√(R² + X²)) for 3-phase systems.
5. Difference between a star and delta connection?
Answer: In a star connection, one end of each step is connected; In the delta, the ends are connected in a loop. The star provides a neutral point and is used for long distance transmission. Delta is used where high early torque is needed.
6. Explain synchronous motor, and how is it different from an induction motor?
Answer: A synchronous motor load moves at constant speed anyway, synchronized with supply frequency. Induction motors depend on slides and do not drive exactly with synchronous speed.
7. Define harmonics in electrical systems?
Answer: Hormonics are voltage or power waves on the multiples with basic frequency, usually caused by non-ledging loads. They reduce efficiency, cause heating and interfere with the equipment.
8. Explain the working principle of a relay?
Answer: A relay is operated as an electromachanic switch. When a small control current flows through the coil, it produces a magnetic field that opens or closes the contacts to control a large load.
9. Define the purpose of earthing in electrical systems?
Answer: Earthing provides a safe passage for error streams, prevents electric shock and protects the equipment from damage by exposing conductive parts due to the ground.
10. How does a capacitor work in an AC circuit?
Answer: In the AC circuit, the creation of a phase change between capacitor store and the release of energy, voltage and power. They are usually used to improve power factor and filtration.
Electrical Engineer Circuit and Machine-Based Questions
1. Explain the working principle of a DC motor?
Answer: A DC engine works according to the principle that a current-bearing conductor is located in a magnetic field that experiences a force. This power creates rotational speed. The direction of rotation is given by the left handled flaming rule.
2. Explain the difference between an open circuit and a short circuit?
Answer: An open circuit has a broken orbit, so there is no current flow. A short circuit occurs when the current takes an unexpected low -resistance path, causing excessive power flow and potential damage.
3. Define the equivalent circuit of a transformer?
Answer: The equivalent circuit represents transformers using resistance and reactions to magnetize the wallpaper, the leak flow and the current. This helps to analyze the performance under different load conditions.
4. How does an induction motor start and what are the starting methods?
Answer: An induction motor starts when a rotating magnetic field induces the current in the rotor. Regular early methods include direct-on-line (DOL), Star Delta and Auto transformer start, selected based on motor sizes and load types.
5. Define the function of a capacitor in an AC circuit?
Answer: An AC power circuit releases a capacitor and energy in the store, improves the power factor, reduces damage and filters voltage spikes or noise.
6. Explain the differences between a series and parallel RLC circuit?
Answer: In the RLC circuit in a sequence, the additives divide the identical modern, and the overall impedance is the sum of personal impedance. In a parallel RLC circuit, additives share voltage, and the total modern is the sum of character department currents. Their resonance conduct additionally varies.
Master MEP Design with Industry-Leading Training!
Gain in-depth knowledge of Mechanical, Electrical, and Plumbing (MEP) Design with expert-led courses. Learn HVAC, fire safety, sustainable building strategies, and BIM applications to excel in the construction industry.
Know MoreElectrical Engineer Control Systems & Instrumentation Questions
1. Differences between open-loop and closed-loop control systems?
Answer:
-
Open-loop control system: The output is not fed back to the input for comparison. The system operates based on predefined instructions without adjusting for output variations.
-
Closed-loop control system: The output is continuously measured and fed back to the input to compare and correct the systeghrefm’s behavior, maintaining the desired output despite disturbances.
2. What is transfer function in control systems.
Answer: The transfer feature is the ratio of the Laplace remodel of the output to the Laplace rework of the enter, assuming all preliminary situations are 0. It mathematically represents the connection between enter and output of a linear time-invariant machine.
3. Define, what is a PID controller and what are its components?
Answer: A PID controller is a comments controller used in control structures to keep the desired output by minimizing the mistake. It consists of 3 components:
-
Proportional (P): Produces output proportional to the current error.
-
Integral (I): Produces output based on the accumulation of past errors.
-
Derivative (D): Produces output based on the rate of change of the error, predicting future errors.
4. Explain instrumentation in control systems?
Answer: Instrumentation refers to devices and systems used for measures, monitoring and control in a control system. This includes sensors, turns, control and actuators to maintain the performance of the system.
5. What is the significance of feedback in control systems?
Answer: Feedback in control systems is used to compare with the desired output of the actual output and to adjust the input accordingly. This helps to reduce errors, improve stability and increase accuracy and performance of the system. Feedback is an important component of the control system for close looping and ensures that the system can effectively respond to changes and disruptions.
Get hands-on with our MEP Quantity Surveyor course – sign up for a free demo!
Electrical Engineer Practical/ Workplace-Related Questions
1. How do you check a pressure sensor in an industrial control system?
Answer: The calibration involves comparing the output from the sensor to a known standard or reference pressure. Stages include:
-
Isolate the sensor from the process.
-
Apply known pressure values using a calibration device (like a dead-weight tester or pressure calibrator).
-
Record the sensor output at each applied pressure.
-
Adjust the sensor or controller settings to align sensor output with the standard values.
-
Document the calibration results for quality control.
2. What steps will you take if a temperature does irregular readings on the control panel?
Answer:
- Check wiring and connections for loose or damaged cables.
- Follow the sensor (eg thermocapal or RTD) for physical damage or contamination.
- Check power supply voltage and signal integrity.
- Test the transmitter output with a known temperature source or simulator.
- Ommer if necessary the transmitter or replace defective components.
- Review environmental conditions (intervention, excessive temperature) that can affect reading.
3. In a PID controlled system, how do you decide when to tune the controller parameters at the workplace?
Answer:
-
When the system shows instability (oscillations) or slow response.
-
After hardware changes, like replacing sensors or valves.
-
If there are changes in process dynamics or load conditions.
-
During routine maintenance or after calibration to improve performance.
-
Using step response tests or auto-tuning tools to adjust Proportional, Integral, and Derivative gains for optimal control.
4. What would you do if a control valve is not responding to signals from the controller?
Answer: First, check the controller output to ensure it is sending the correct signal (typically 4-20 mA). Then, inspect the wiring and connections to the valve actuator for any damage or disconnection. If the signal is correct, verify the valve actuator’s power supply and air pressure (if pneumatic). Manually stroke the valve to see if it moves freely. If not, the valve might be stuck due to mechanical failure or debris. Finally, check for configuration issues in the controller or signal converter settings.
5. How do you ensure the reliability of instrumentation systems in a plant?
Answer: Regular preventive maintenance and calibration are key. Always use certified instruments and follow manufacturer guidelines. Keep records of calibrations, inspections, and replacements. Use redundancy for critical sensors (e.g., dual temperature sensors) and monitor signals for drift or noise. Train staff to recognize early signs of faults and establish alert thresholds in the control system to catch abnormal behavior early.
HR & Behavioral Questions
1. Tell me about a challenging problem you faced in a control system project and how you solved it.
Answer: In a project, the temperature control loop was unstable due to ups and downs in entry signals. I checked systematically the sensor calibration and wires, and then analyzed PID settings. After setting the control parameters and replacing a deficient sensor, stabilized the system and met the process requirements.
2. How do you prioritize your tasks when working on multiple instrumentation maintenance jobs?
Answer: I prioritize tasks on the basis of safety, impact on production and urgency. Important systems affecting safety or production continuity come first. I communicate with my team and observers to ensure adjustment and efficient resource allocation, instant repair with preventive maintenance can be balanced.
3. Describe a time when you had to work as part of a team to complete an instrumentation project. How did you contribute?
Answer: Recently in a project, our team set up a new flow control system. I collaborated with electrical and mechanical engineers to choose appropriate sensors, assisted cord and calibration and shared knowledge of system integration. My active communication and troubleshooting helped to complete the project within time and budget.
4. How do you handle stressful situations when a critical instrument fails during production?
Answer: I remain calm and follow the troubleshooting protocol established to identify the problem quickly. I clearly communicate with operations and management to inform them. If necessary, I continue or ask for extra support to reduce shutdown to ensure safety and effective solution.
-
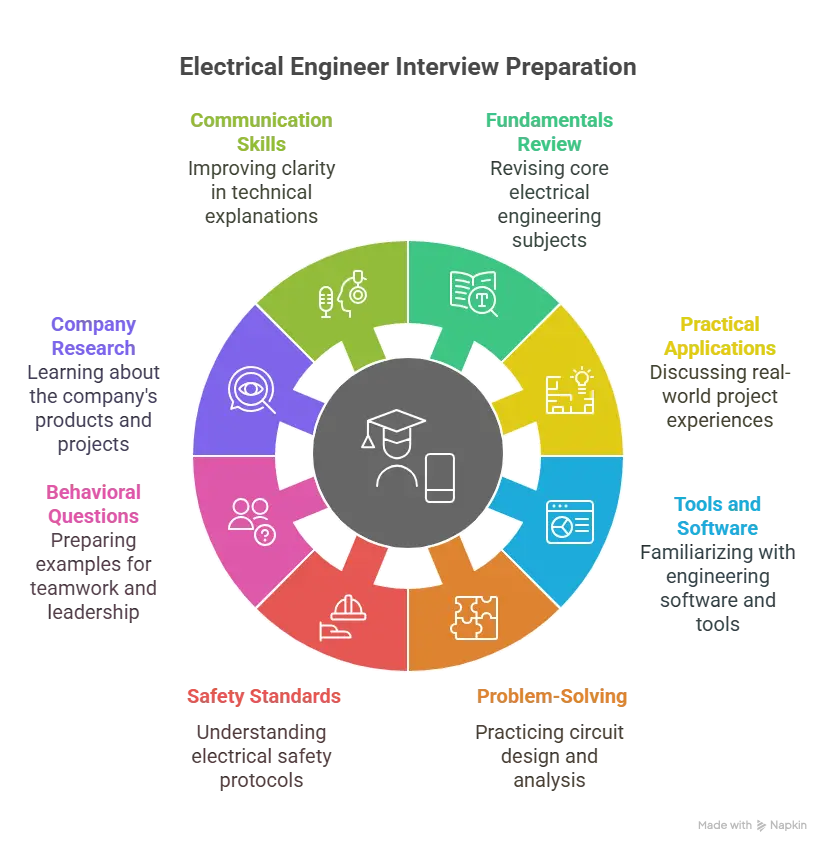
Brush up on fundamentals: Review core themes such as circuit theory, control system, power electronics, signals and systems and instruments.
-
Understand practical applications: Be prepared to discuss how you have used theory in real projects, internships or laboratories.
-
Familiarize with tools and software: Learn General Engineering Tools such as MatLab, AutoCAD, PLC Programming or Simulating Software.
-
Prepare for problem-solving questions: Electrical engineers Exercise circuit design, troubleshooting and analysis problems quickly and accurately solve the interview.
-
Review safety standards: Be aware of electrical safety protocols and industry standards such as IEEE or NEC.
-
Work on behavioral questions: Use star method to prepare a clear example of teamwork, management and adaptability.
-
Research the company: Understand your products, projects and technologies to tailor your answers and questions.
-
Practice communication skills: Clear, short explanations help you stand out, especially for technical subjects.
Get hands-on with our MEP Quantity Surveyor course – sign up for a free demo!
Conclusion
Preparing for Electrical Engineer interview requires balanced attention to technical knowledge, practical skills and effective communication. By changing the main concepts, understanding industry equipment and practicing the problem solution in the real world, you can safely demonstrate your expertise. In addition, performing professionalism, adaptability and a strong work ethic under practical questions can leave a permanent impression. With proper preparation and mentality, you will be well placed to succeed in your interview and take the next step in your engineering career.
| Related Links | |
Master MEP Design with Industry-Leading Training!
Gain in-depth knowledge of Mechanical, Electrical, and Plumbing (MEP) Design with expert-led courses. Learn HVAC, fire safety, sustainable building strategies, and BIM applications to excel in the construction industry.
Know MoreFrequently Asked Questions
Who should read this blog on electrical engineer interview questions?
This blog is perfect for freshers, experienced engineers, and job seekers preparing for interviews in electrical companies, core industries, or PSU roles. It covers both basic and advanced questions that can be asked in real interviews.
What kind of questions are included in the blog?
The blog includes questions from topics like circuit theory, power systems, control systems, machines, electronics, instrumentation, and practical troubleshooting. It also covers real-world workplace scenarios and commonly asked HR questions.
Are the answers provided in technical language or simple terms?
The answers are written in simple, easy-to-understand language. Even complex technical concepts are explained clearly to help both beginners and experienced candidates prepare confidently.
Can I use this blog for PSU or government exam interviews?
Yes. Many of the questions are relevant for PSU interviews like BHEL, NTPC, ONGC, and state electricity boards. The concepts covered are part of core electrical engineering and can help with both technical and personal interviews.
Are there any practical or real-time workplace questions included?
Yes. The blog includes practical questions like how to troubleshoot sensors, calibrate instruments, or tune a PID controller. These are commonly asked in job interviews for plant engineers and maintenance roles.
How can I best prepare using this blog?
Read each question carefully, understand the explanation, and try to relate it to your projects or internship experience. Practice answering out loud and revise topics like machines, transformers, and control systems regularly.