Table of Contents
Introduction
Picture this: You’re in a boardroom as a cyber breach unfolds, regulators knocking at the door, and executives scrambling— that’s the high-pressure world a GRC Analyst steps into every day, turning chaos into controlled strategy. With organizations worldwide grappling with evolving threats under GDPR, SOX, and India’s DPDP Act, demand for these pros has spiked over 30% in the last year, offering entry-level salaries of ₹8-15 LPA in India’s tech hotspots like Bangalore and Hyderabad. Securing a GRC role demands more than expertise; it’s about shining in interviews where you dissect risks, champion compliance, and showcase real impact.
This blog equips you with 80+ handpicked interview questions—from behavioral questions to technical challenges on NIST frameworks and tools like RSA Archer or MetricStream—plus model answers, insider tips, and practical scenarios. This interview prep guide is ideal for freshers chasing cybersecurity certs or mid-level talent aiming for MNCs in Europe or the Gulf. These insights will transform interview jitters into your secret weapon.
Enroll in Entri’s AI-Powered Cybersecurity course now!
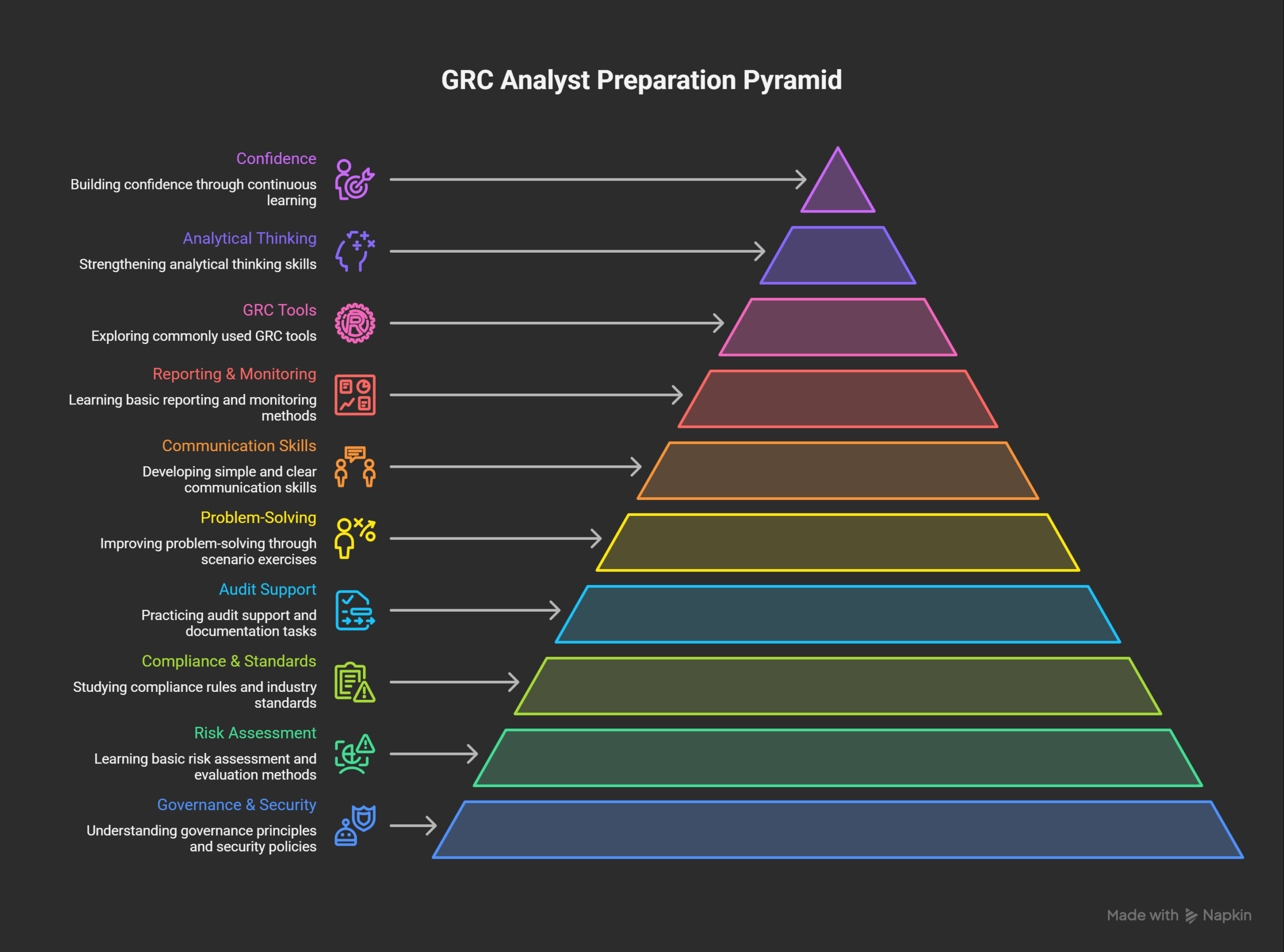
Key Preparation Focus Areas
- Understanding governance principles and security policies
- Learning basic risk assessment and evaluation methods
- Studying compliance rules and industry standards
- Practicing audit support and documentation tasks
- Improving problem-solving through scenario exercises
- Developing simple and clear communication skills
- Learning basic reporting and monitoring methods
- Exploring commonly used GRC tools
- Strengthening analytical thinking skills
- Building confidence through continuous learning
This approach supports long-term cybersecurity career success.
Enroll in Entri’s AI-Powered Cybersecurity course now!
What is GRC in Cybersecurity?
In cybersecurity it means Governance, Risk, and Compliance. This helps organizations manage security in a easy way. It connects business goals with daily security operations. GRC improves clarity, control, and accountability. This approach strengthens protection against common cyber threats. It also supports long-term organizational safety and stability.
Key benefits of GRC include:
- Better security planning and management
- Clear rules and responsibilities
- Strong connection between business and security
- Improved visibility and control
Governance focuses on leadership, policies, and accountability. It defines roles, duties, and security expectations. Clear policies guide safe working practices. Strong leadership supports consistent rule enforcement. Proper planning improves security readiness.
Governance includes:
- Security policies and procedures
- Leadership direction and oversight
- Role definition and responsibility
- Security planning and review
Risk management identifies threats and system weaknesses. It evaluates possible impact and damage. Risk analysis supports proper decision-making. Control measures reduce chances of security incidents. Regular monitoring keeps risks under control.
Risk management involves:
- Threat identification
- Risk evaluation
- Risk reduction actions
- Continuous monitoring
Compliance ensures rules, laws, and standards are followed. It protects organizations from legal and financial penalties. Strong compliance builds customer trust. Regular audits check control effectiveness. Clear records support transparency.
Compliance includes:
- Regulatory tracking
- Audit preparation
- Control reviews
- Compliance reporting
GRC brings governance, risk, and compliance together. This approach strengthens security and operational stability.
Frequently Asked Questions
Who can apply for a GRC analyst role?
Fresh graduates from IT, cybersecurity, or computer science backgrounds can apply for GRC roles. Candidates with basic knowledge of security principles also qualify for entry-level positions. Students interested in compliance, risk management, and auditing can pursue this career path. Professional certifications improve job readiness and selection chances. Strong communication and documentation skills further increase hiring opportunities.
What qualifications are required to become a GRC analyst?
A bachelor’s degree in IT, cybersecurity, or computer science is commonly required. Basic understanding of governance, risk, and compliance concepts is essential for beginners. Knowledge of security frameworks improves interview performance and job readiness. Certifications like ISO 27001, CISA, or Security+ add professional value. Internships and hands-on training further strengthen career prospects.
Is coding required for a GRC analyst job?
Coding skills are not mandatory for GRC analyst positions. Basic technical understanding helps interpret security systems and reports. Familiarity with dashboards and automation tools improves operational efficiency. Knowledge of workflows supports compliance tracking and documentation. Analytical thinking remains more important than programming expertise.
What certifications help in building a GRC career?
ISO 27001 certification builds strong compliance and audit understanding. CISA strengthens governance and information system auditing knowledge. CRISC improves enterprise risk management capabilities. Security+ develops cybersecurity foundation and technical awareness. These certifications enhance credibility and professional recognition.
What tools should freshers learn for GRC roles?
RSA Archer provides strong enterprise GRC workflow experience. ServiceNow GRC supports automated risk and compliance management processes. Spreadsheet tools assist in documentation and reporting activities. Risk assessment templates improve analysis and evaluation skills. Dashboard tools enhance reporting clarity and visualization.
What career growth opportunities exist in GRC?
GRC analysts can advance into senior analyst and consultant positions. Experience enables movement into audit management and risk leadership roles. Advanced certifications support promotion into managerial responsibilities. Cross-domain exposure allows transition into cybersecurity leadership positions. Continuous learning ensures long-term professional advancement.
What skills are important for GRC analysts?
Analytical thinking supports accurate risk evaluation and reporting. Communication skills improve collaboration across technical and business teams. Documentation abilities ensure audit readiness and compliance tracking. Problem-solving skills strengthen incident response and corrective planning. Organizational skills improve workflow management and reporting accuracy.
How should freshers prepare for GRC analyst interviews?
Freshers should learn basic governance, risk, and compliance concepts thoroughly. Studying security frameworks builds strong conceptual clarity. Practicing scenario-based questions improves practical problem-solving skills. Learning GRC tools enhances operational readiness and confidence. Mock interviews help reduce nervousness and improve communication quality.
What industries hire GRC analysts?
Banking organizations require strict compliance and risk management controls. Healthcare sectors demand data protection and regulatory adherence. IT companies need strong governance and cybersecurity oversight. Government institutions require audit and regulatory compliance operations. E-commerce businesses need secure data management frameworks.
Is GRC a good long-term career option?
GRC offers strong demand across global cybersecurity job markets. Growing regulations increase long-term employment stability. Diverse industry roles provide steady career growth opportunities. Continuous learning ensures skill relevance and professional development. High-responsibility roles deliver meaningful career satisfaction.