Table of Contents
Behind every well-functioning hospital has two important pillars administration and operation management. While the goal is to ensure smooth distribution of healthcare, their roles, responsibilities and impact differ significantly. The hospital administration focuses on strategic management, compliance and general management, while operational management is zeroes on efficiency, resource allocation and daily processes. Understanding the difference between the two not only helps health professionals define clear responsibility, but also improves better patient care, coordination and organizational development of employees.
Explore Your Future in Hospital Administration! Enroll now
Introduction
The Hospital Administration acts as the backbone of health institutions, which leads to management, policy design, financial management and compliance with regulations. Administrators are responsible for shaping the hospital’s long-term vision, and ensuring that it operates within the legal framework, maintains high quality standards and receives permanent growth. Their role is more strategic, focusing on management, budget plan and decisions that lead the organization’s overall direction.
However, the operation management, belongs to the practical side of running the hospital effectively. This highlights process adjustment, resource allocation, patient records management and the coordination between different departments. The operations managers focus on improving efficiency, reducing congestion and ensuring that patients receive timely and effective care. While the administration looks at the overall view, operations management ensures that the daily activities of the hospital originally match their long-term goals.
What is Hospital Administration?
1: What is the primary role of a hospital administrator?
The hospital administration refers leadership and management activities that ensure that the hospital goes smoothly, safely and efficiently. This is a process of supervising the overall functions of a healthcare, including planning, organization, direction and controlling resources to distribute high quality medical services to patients.
The role of the hospital administration is widespread and strategic. Administrators are responsible for making important decisions on compliance with budget, guidelines, staffing and health services. They act as a bridge between medical staffs, support teams and governing bodies to ensure that the hospital provides the best possible care despite being financially stable and legally obedient.
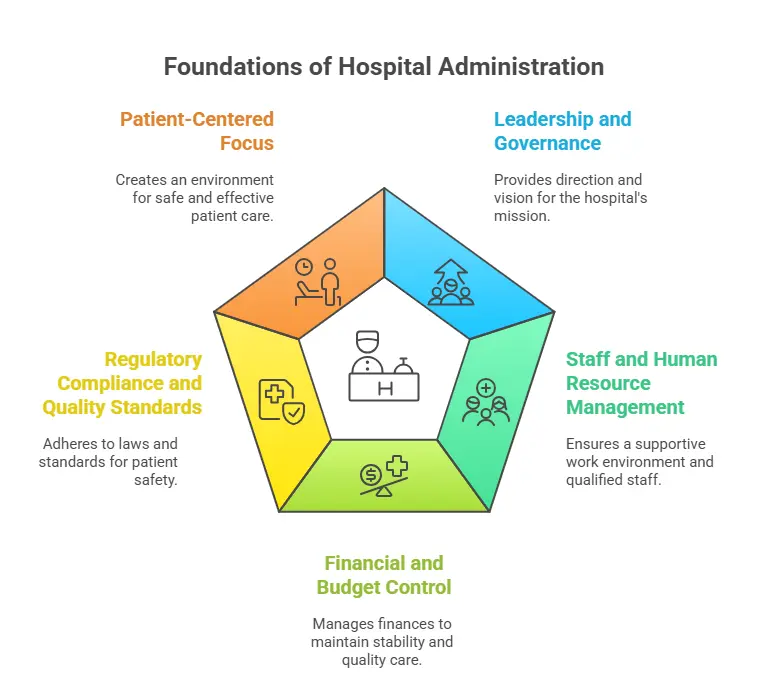
1. Leadership and Governance
Hospital administrators provide direction and vision for health facilities. They develop guidelines, set goals and ensure that the hospital moves in the right direction. Their management helps to coordinate employees, resources and systems with the hospital’s mission.
2. Staff and Human Resource Management
Administrators are responsible for hiring qualified employees, training employees and creating a supportive work environment. They also handle staff conditions, staffing level and workplace policies to ensure even collaboration between doctors, nurses and support teams.
3. Financial and Budget Control
One of the greatest responsibilities in the hospital administration is to manage finance. This involves planning budget, checking expenses and securing the hospital to ensure that it remains financially stable. Administrators should balance the cost efficiency while maintaining high quality patient care.
4. Regulatory Compliance and Quality Standards
Hospitals should follow strict laws and regulations for the healthcare system. Administrators ensure that the convenience meets security standards, maintains licenses and follows medical guidelines. It helps protect patients and keep the hospital legally obedient.
5. Patient-Centered Focus
Although administrators cannot treat patients directly, their decisions have a direct effect on patient care. By ensuring the right staffing, the availability of equipment and effective systems, they create an environment where patients receive safe, timely and effective treatment.
Hospital Administration Course with Assured Career Growth
Hospital Administration Course by Entri App: Master essential healthcare management skills, gain certification, and secure top roles in leading hospitals
Join Now!What is Operations Management in Healthcare?
Operation management in the healthcare system refers to the practice of planning, organizing and controlling the daily activity of hospitals and medical facilities. It focuses on making the delivery of health services more efficient, cost effective and patient-centered. Unlike the hospital administration, which belongs to the overall strategy and management, the operation management ensures that the daily processes in the hospital run smoothly and correspond to long-term goals.
This ensures that patients receive timely treatment, employees work in an organized environment, and resources are used with care. While the hospital administration determines the vision, operations management brings that vision to life by running everything evenly at ground level.
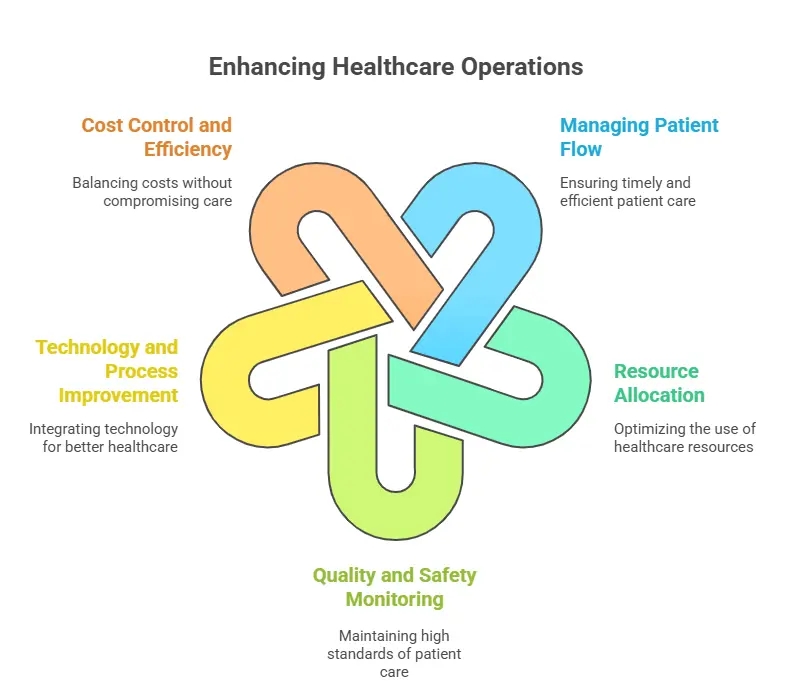
1. Managing Patient Flow
One of the greatest responsibilities for the operations management of health services is to ensure that patients recieve care at the right time without unnecessary delays. This involves dealing with appointments, reducing the waiting time and improving the process of accepting patients, treating and discharging patients. Effective treatment of patient leads to high satisfaction and better health results.
2. Resource Allocation
Operations managers ensure that assets including staff, equipments and all facilities are used efficiently. For example, they make sure that the operating rooms are properly decided, the medical supply is stocked on time, and the shifts of each staff are planned to satisfy the patient’s demand. Proper resource allocation reduces unwanted things and improves service quality.
3. Quality and Safety Monitoring
Health services management also focuses on maintaining high standards for quality and patient safety. This includes the following protocols, reduces medical errors and ensures compliance with health services rules. By tracking the overall performance and implementing safety measures, the operations managers assist to build trust and reliability in patient care.
4. Technology and Process Improvement
Modern health care is dependent on technology, and operations management plays a major role in integrating new systems. This includes electronic health records, telemedicine platforms and automatic planning tools. By using new technologies, hospitals can improve efficiency, reduce costs and provide more accurate care quickly.
5. Cost Control and Efficiency
The healthcare system is expensive, and operations management helps to balance the costs without compromising on care of the patient. Managers analyze workflows, cut unnecessary steps and find ways to distribute services more efficiently. This ensures that hospitals remain financially stable by providing high quality care.
Skills Required
Both hospital administrators and operations manager play an important role in keeping health facilities effective, safe and patient. While their responsibilities are different, they share some common skill sets with unique abilities that help them to succeed.
1. Leadership and Decision-Making
The administrators and operations manager must be strong leaders. They guide the teams, make important decisions and solve conflicts. Operations management helps them to motivate employees, build self-confidence and create a positive atmosphere in the workplace where everyone works towards similar goals.
2. Communication Skills
Clear communication is necessary in the healthcare system. These professionals should explain guidelines, share updates and coordinate between doctors, nurses and assistant employees. Good communication also involves listening to response and addressing concerns about improving hospital operations.
3. Problem-Solving and Critical Thinking
Hospitals face daily challenges such as a lack of staffing, delay in patient flow or budget issues. Administrators and operation managers require problem-solving skills to analyze conditions, identify solutions and quickly make smart decisions.
4. Organizational and Time Management
The functions of the healthcare system are composed, many departments work together. Strong organizational skills programs help manage resources and workflows. Time management ensures that significant functions are completed without any delay, especially in a rapidly growing environment.
5. Financial and Analytical Skills
Hospital administrators often handle budget and the patients records, while operation managers focus on cost efficiency and improve the entire process. Both roles require financial understanding and capability to evaluate data to make informed decisions.
6. Knowledge of the Healthcare Regulations
Since each hospitals must follow strict laws and standards, both roles require knowledge of healthcare policy, safety protocols and permission requirements. This ensures the patient’s safety and protects the hospital from any legal issues.
7. Adaptability to the Technology Skills
With new techniques such as electronic health records and telemedicine, adaptability is important in these days. Both administrators and operation managers must be familiar to using digital tools to improve efficiency and become effective.
Educational Qualifications
Both hospital administrators and operations managers require a strong educational basis in health and management. While the study pathway often overlap, each role may require slightly different qualifications.
Hospital Administration
- Undergraduate Degree – Most hospital administrators start with a bachelor’s degree in the healthcare system, public health, business administration or related fields. It provides basic knowledge of the healthcare system, governance and organizational behavior.
- Postgraduate Degree – Master of Healthcare Administration (MHA) or Master of Business Administration (MBA) with health focus is often preferred for management positions. These advanced degrees prepare professionals for decision-making, policy development and high-level management.
- Certifications – Additional Certificates such as Certified Healthcare Administrator (CHA) or American College of Healthcare Executives (FACHE) can increase the possibilities and reliability of their career.
Operations Management in Healthcare
- Undergraduate Degree – Bachelor’s degree in Health Service Management, Business Management, Operations Management or Industrial Engineering is usually needed. It helps to understand system management, logistics and organizational processes.
- Postgraduate Degree – Several operations managers, along with a Master of Healthcare Administration (MHA), MBA in Operations Management, or Master of Public Health (MPH). These programs highlight improving process, efficiency and leadership.
- Certifications – Special certifications such as Certified Professional in Healthcare Quality (CPHQ), Lean Six Sigma, or Project Management Professional (PMP). They convey specialization in improving processes and maintaining quality standards.
Explore Your Future in Hospital Administration! Enroll now
Hospital Administration Course with Assured Career Growth
Hospital Administration Course by Entri App: Master essential healthcare management skills, gain certification, and secure top roles in leading hospitals
Join Now!Career Scope & Opportunities
The health care system is one of the fastest growing industries around the world, and with that, the demand for skilled hospital administrators and operating managers continues to increase. Both career paths provide a chance to create real effects on stability, development and patient care and hospital performance.
Hospital Administration: Career Scope
Hospital administrators are responsible for the direction of general management and health facilities. With increasing difficulty of the healthcare system, their role is more important. They can work in hospitals, nursing homes, rehabilitation centers, clinics and government health departments.
Opportunities in such role are:
- Hospital Administrator/ Director – overseeing the entire hospital and setting policies.
- Healthcare Executive – managing strategic initiatives and compliance.
- Department Head – leading specific departments like finance, HR, or patient services.
- Public Health Administrator – working with government or NGOs to improve healthcare access.
With advanced degrees and certificates, administrators can also advance in advisory roles, and advise hospitals to improve efficiency, policy and quality.
Operations Management: Career Scope
The operations managers focus on improving the efficiency of health services. They are necessary to ensure that hospitals go smoothly on a daily basis. Their skill sets are highly valued in every hospitals, private health centres, pharmaceutical companies, insurance companies and even healthcare startups.
Opportunities in such role are:
- Operations Manager / Director – overseeing hospital operations, patient flow, and logistics.
- Healthcare Quality Manager – ensuring safety and quality standards are met.
- Process Improvement Specialist – applying Lean Six Sigma and other methods to reduce waste.
- Project Manager in Healthcare – handling system upgrades, digital health adoption, or expansion projects.
Operations management can also be experts on professional supply chain management, telecommunications operations or IT systems for healthcare, and open doors for different and sought-after career tracks.
Future Opportunities
The future looks bright for both fields. With the increasing patient’s demand, technological innovations and a strong focus on quality care, hospital administration and operations management will continue to see great demand. According to industry reports, the health management roles are expected to grow much faster than the average of other companies.
Roles & Responsibilities Compared
While each health facility management and operations management aim to enhance the healthcare distribution, their roles and duties are specific in scope, awareness and execution. Understanding these differences enables to clarify how every characteristic contributes to the achievement of a health facility.
Hospital Administration: Roles & Responsibilities
Hospital administrators are responsible for the overall management and management of a health service. Their role is more strategic and politics, focused on “big picture” instead of daily tasks.
Key Responsibilities:
- Leadership & Governance – Establishment of vision, assignments and long term goals for management and management of hospital. Administrators ensure that all departments secure hospital goals.
- Policy Development – To create and implement guidelines for patient care, employees and operational standards.
- Financial Management – To maintain the budget, approve expenses and ensure that the hospital remains financial stability.
- Regulatory Compliance – Safe hospitals follows health laws, safety standards and recognition requirements.
- Human Resource Management – Employment of employees, administer employees’ benefits and maintain a positive culture in the workplace.
- Public Relations & Community Engagement – Representing hospitals in society, building partnerships and improving the hospital’s reputation.
Operations Management: Roles & Responsibilities
The operations focus on the daily processes in the hospital. Their responsibility is to ensure that the convenience goes effectively, patients are treated with timely treatment, and resources are used effectively.
Key Responsibilities:
- Process Management – To reduce the patient’s waiting time and improve workflows for admission, treatment and discharge to improve satisfaction.
- Resource Allocation – Guide of equipment, supply and staff plan to meet the patient’s needs without waste.
- Quality & Safety Assurance – Implementation of quality improvement programs, monitor patient safety and addressing operational challenges.
- Technology Integration – Overseeing for the use of new technology for healthcare, electronic records and digital tools for better efficiency.
- Cost Efficiency – Identification of waste areas to optimize hospital operations and apply methods such as Lean or Six Sigma.
- Interdepartmental Coordination – Secure collaboration between different hospital units such as emergency, surgery, pharmacy and diagnosis.
Key Differences
- Scope: Administrators focus on long-term strategy and management, while the operations managers handle daily processes.
- Decision-making: Administrators make policy and economic decisions; Operations managers make practical adjustments.
- Impact: Administrators affect the reputation, development and compliance with the hospital. The operators affect the patient’s experience, efficiency and quality of service directly.
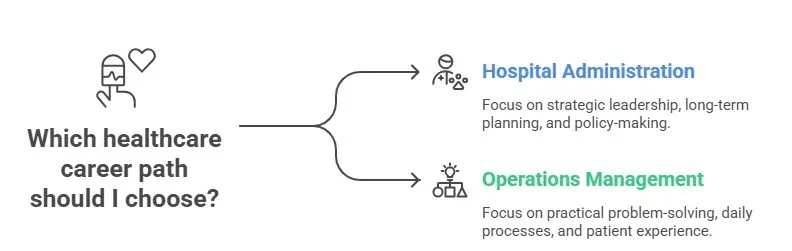
Which Career Should You Choose?
The healthcare system is one of the fastest growing industries, and both hospital administration and operations management are exciting career paths with good opportunities. Although both roles are important for the success of hospital or health services, the right choice depends on you on your interests, skills and career goals.
Hospital Administration: The Path of Strategic Leadership
The hospital administration is best suited for those who want to become leaders at the executive level. Administrators focus on big picture, they set long-term goals, make financial decisions and ensure that the hospital complies with health services and standards. Their work is less about the daily details and more about leading the entire organization in the right direction.
- Leadership and Vision – To shape the guidelines of leading teams and hospitals.
- Decision-Making – Handling budgets, staffing, and organizational development.
- Public Relations – Which represents the hospital jointly and building partnerships.
- Policy & Compliance – Ensure legal, moral and quality standards are completed.
Career progression in this field can lead to roles asHospital Director, Healthcare Executive, Chief Executive Officer (CEO), or Public Health Administrator. These posts not only give you the power to shape a hospital, but also a large healthcare system.
Operations Management: The Path of Practical Problem-Solving
Operation management is perfect for those who like problems-solving and organizational development. The operations managers focus on daily processes, and ensure that patients are treated effectively, the staff plans runs smoothly, and the resources are used with care. Their work affects the patient’s experience directly every day.
- Process correction – analysis of workflows and make them more effective.
- Coordination – Work with doctors, nurses and support staff to improve the patient’s flow.
- Technology integration – Use hospital software and digital tools to customize performance.
- Cost and resource management – reduce waste while maintaining quality care.
Career growth in this field may lead to posts as Operations Director, Healthcare Quality Manager, Process Improvement Specialist, or Healthcare Project Manager. These roles are very advantageous because you can see the immediate effect of your work on patients and staff.
How to Decide?
When choosing between the hospital administration and the operations management, you can ask these important questions:
- Do I like strategic management and policy design (choosing administration), or do I like to organize procedures and solve daily challenges (Select Operations Management)?
- Am I more interested in long-term plan (administration) or daily execution (operation)?
- Do I want to influence health services for big-picture or focus on improving the patient’s experiences directly?
Explore Your Future in Hospital Administration! Enroll now
Conclusion
Hospital administration and operating management are two pillars that work effectively for health organizations. While administration focuses on management, management and long-term strategy, operations management ensures daily processes, resource adjustment and patient-focused efficiency evenly. Both roles are different, but still complement – administrators determine vision, and the operators make that vision come true.
For anyone who considers a career in healthcare, the alternative between these two paths depends on personal strength and interests. If you like strategic management and policy design, the hospital administration may be your calling. If you enjoy problems solving, coordination and improvement in the process, operations management may be ideal fit.
Finally, both careers are rewarded and offer strong growth opportunities, and most importantly play an important role in improving the patient’s care. Together, hospital administrators and operation managers make the backbone of a healthcare system that is effective, durable and able to meet patients growing needs worldwide.
Hospital Administration Course with Assured Career Growth
Hospital Administration Course by Entri App: Master essential healthcare management skills, gain certification, and secure top roles in leading hospitals
Join Now!Frequently Asked Questions
What is the main difference between hospital administration and operations management?
Hospital administration focuses on leadership, governance, and long-term planning for the entire healthcare facility. Operations management, on the other hand, deals with the daily processes—such as patient flow, staff scheduling, and resource allocation—to ensure the hospital runs efficiently.
Do hospital administrators work directly with patients?
Generally, no. Hospital administrators work behind the scenes, managing policies, finances, staffing, and compliance. While their decisions directly affect patient care, they usually do not provide hands-on treatment like doctors or nurses.
What are the typical responsibilities of a healthcare operations manager?
An operations manager oversees day-to-day hospital functions, including patient admissions, discharge processes, staff coordination, equipment availability, and quality control. Their goal is to reduce inefficiencies and improve patient experiences.
What educational qualifications are needed for these careers?
- Hospital Administrators: Usually require a bachelor’s degree in healthcare administration, business administration, or public health, with many pursuing a Master of Healthcare Administration (MHA) or MBA.
-
Operations Managers: Typically hold degrees in healthcare management, business management, or operations management, often supported by certifications like Lean Six Sigma or Project Management Professional (PMP).
Which role offers better career growth opportunities?
Both roles offer strong growth potential due to the rising demand for healthcare professionals. Hospital administrators often grow into executive positions like CEO or Director, while operations managers advance into roles like Operations Director, Quality Manager, or Healthcare Consultant.
Which career is better for someone interested in problem-solving and efficiency?
If you enjoy analyzing systems, fixing inefficiencies, and working hands-on with processes, operations management is the better choice. Hospital administration is more suitable for those who prefer strategy, policy-making, and leadership at a higher level.
Can hospital administration and operations management work together?
Yes—these roles are highly interdependent. Administrators set the hospital’s vision and policies, while operations managers ensure those policies are implemented effectively in daily practice. Together, they create a balance between strategy and execution, which is essential for quality healthcare delivery.