Table of Contents
A culture is made or destroyed, by its articulate voices. Civilization is a level of development at which people live together to form communities. Ancient civilization is the basis for later states, empires and nations which is also known as first to settle communities. The study of ancient civilization is documented in a subject termed as ancient history. The ancient history began when writing was invented. A civilization is also referred as a complex culture in which large numbers of human beings share a number of common elements. The most important six characteristics of civilizations are the cities, government, religion, social structure, writing and art. The civilization was identified when humans first decided to give up their nomadic life or a hunter-gatherer lifestyle and decided to settle at a place. The six distinct cradles of civilization can be identified as Egypt and Mesopotamia in the middle east, the Indus Valley the now Pakistan and India, The Huang He valley of China, Mexico and Peru. In this article let us check the ancient civilizations of the world.
Attempt free mock test for competitive examinations
Ancient Civilizations of the World
Below mentioned are the few of the oldest civilization of the world.
| Sl. No | Civilization | Period | Original location | Current location | Significance |
| 1 | Australian Aboriginals
|
50,000 B.C. – Present Day | Australia | Australia | The first known human civilization |
| 2 | The Çatalhöyük Settlement
|
7500 B.C. – 5700 B.C. | Southern Anatolia | Turkey | Agriculture |
| 3 | Ain Ghazal
|
7,200 B.C. – 5,000 B.C. | Ayn Ghazal | Modern-day Amman, Jordan | Monumental statues |
| 4 | The Jiahu Culture
|
7,000 B.C. – 5,700 B.C. | Henan, China | Henan Province, China | Bone flutes, earliest example of Chinese writing |
| 5 | The Indus Valley Civilization
|
2600 B.C. – 1900 B.C. | Around the basin of the Indus river | Northeast Afghanistan to Pakistan, and Northwest India | One of the most widespread civilizations in history |
| 6 | The Mesopotamian Civilization
|
6,500 B.C. – 539 B.C. | Northeast by the Zagros Mountains, southeast by the Arabian Plateau | Iraq, Syria, and Turkey | First civilization in the world |
| 7 | The Danubian Culture, or Linearbandkeramik Culture
|
5500 B.C. – 3500 B.C. | Europe | Lower Danube Valley and the Balkan foothills | Goddess figurines and gold artifacts |
| 8 | The Norte Chico Civilization
|
3,000 B.C. – 1,800 B.C. | Peru | Andean Plateau along Peru’s west coast | Monumental architecture |
| 9 | The Ancient Egyptian Civilization
|
3150 B.C. – 30 B.C. | Banks of the Nile | Egypt | Construction of pyramids, mummification |
| 10 | The Mayan Civilization
|
2600 B.C. – 900 A.D. | Around present-day Yucatan | Yucatan, Quintana Roo, Campeche, Tabasco, and Chiapas in Mexico; south through Guatemala, Belize, El Salvador, and Honduras | Complex understanding of astronomy |
| 11 | The Chinese Civilization
|
1600 B.C. – 1046 B.C. | Yellow River and Yangtze region | Country of China | Invention of paper and silk |
| 12 | The Ancient Greek Civilization
|
2700 B.C. – 479 B.C. | Italy, Sicily, North Africa, as far west as France | Greece | Concepts of democracy, the Senate, the Olympics |
| 13 | The Persian Civilization
|
550 B.C. – 331 B.C. | Egypt in the west to Turkey in the north, through Mesopotamia to the Indus river in the east | Modern-day Iran | Royal road |
| 14 | The Roman Civilization
|
753 B.C. – 476 A.D. | The Tiber River in Italy | Rome | Monumental architecture |
| 15 | The Aztec Civilization
|
1325 A.D. – 1521 A.D. | South-central Mexico | Mexico | Highly advanced and complex society |
| 16 | The Incan Civilization
|
1438 A.D. – 1532 A.D. | Ancient Peru | Peru, Ecuador, Chile | Machu Picchu, engineering excellence |
Check here for study materials on Indian history
Oldest Civilization of India
1: Who was the first woman President of India?
The settled life that is which involved transition from foraging to farming and pastoralism began in South Asia around 7000 BCE. By around 4,500 BCE settled life had spread widely and it had evolved into the Indus Valley Civilization on of the early civilization of the world. Indus valley civilization flourished well between 2500 BCE and 1900 BCE. Due to continuous drought caused due to the population of the Indus valley civilization people scattered to villages and migrated. It was at this time of 1500 – 500 BCE the vedic period evolved.
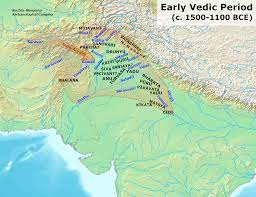
Vedic Civilization
- The Vedic period flourished between 1500 BCE to 500 BCE
- The Vedic culture was seen in the north-west part of India
- The Vedic Civilization flourished along the river Saraswati
- The Vedas comprises of four major texts that is the Rigveda, the Samaveda, the Yajurveda, and the Atharvaveda.
- Iron tools were adopted during this Vedic period.
- Vedic period witnessed the emergence of a hierarchy of social classes.
- Economy in the Vedic period was sustained by a combination of pastoralism and agriculture.
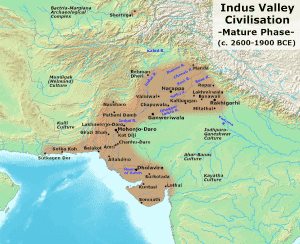
Indus Valley Civilization
- Indus valley civilization was a bronze age civilization from 3300 BCE to 1300 BCE.
- Along with ancient Egypt and Mesopotamia civilizations , Indus valley civilization was among three ancient civilizations of the world.
- The Indus valley civilization stretched from the northeast Afghanistan , through Pakistan to the western and northwestern India
- The cities of the Indus civilization was involved i urban planning
- They constructed baked brick houses , elaborate drainage system and water supply systems
- They involved in new techniques of handicraft including carnelian products and seal carving
- The large cities of Indus valley civilization were Mohenjo- daro and Harappa
- The Indus valley civilization was also known as Harappan Civilization
- The five major urban sites of the Indus valley civilization are Harappa, Mohenjo daro, Dholavira, Ganeriwala, and Rakhigarhi.
- It was during the Indus valley civilization where the people achieved great accuracy in measuring length, mass and time
- The people of Indus valley civilization involved in sculptor making . They also made anatomically detailed figurines in terracotta .
- Over population and the persistent droughts were the reason to the decline of Indus Valley civilization with people migrating to different villages in the east and south.
Subscribe Entri and attempt free mock test on General awareness
Ancient civilization was the base for what we witness and live now. Literature and invention of writing helped us know about the history. Civilization was the beginning of what is now. Learn more about the History of the world and appreciate it for it is what you are experiencing now.