Table of Contents
Plastics have become more popular and began to be produced on a massive scale after the Second World War. Its adverse effects have been seen from that time itself. And as time went by, it became one of the most threatening of the issues humanity as well as the planet and its ecosystem is facing. By the year 2016, it was calculated that 60% of the plastic produced became plastic waste. Now plastic pollutants are omnipresent; in land, air, water and even inside living organisms. Let’s learn more about the plastic pollution, its causes, harmful effects and prevention.
Click here to read more about the GK topics necessary for competitive exams!
What is Plastic?
Plastic is a polymeric substance that is easily moldable or formed. It comes from the polymers found in plants, minerals, coal, oil, and natural gas, among other natural materials. Polymerization is the chemical process that joins a sizable collection of monomers to form polymers. Plastics are made from two different types of polymers: synthetic and natural. The natural polymers come from cellulose, which is found in plants and trees, wool, and silk. Synthetic polymers generated from petroleum, coal, oil, and natural gas are also used to make plastics. Hydrocarbons as well as other elements including oxygen, nitrogen, carbon, hydrogen, Sulphur, and chlorine are found in plastics.
What are the different Types of Plastic?
1: Who was the first woman President of India?
Plastics are classified into two categories: thermosetting polymers and thermoplastics, depending on how the polymers are processed. While thermosetting polymers, also known as thermosets, can only be consolidated to a permanent shape, thermoplastics can be heated and remolded repeatedly. Examples of thermoplastics and thermosets include:
| No. | Thermosetting plastic | Thermoplastic |
| 1 | Bakelite | Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC) |
| 2 | Urea-Formaldehyde/ Amino plastic / carbamide-methanol | Polystyrene – PS |
| 3 | Epoxy Resins | High-density polyethylene – HDPE |
| 4 | Polyimides | Polypropylene-PP |
| 5 | Melamine-Formaldehyde Resins | Low-density polyethylene – LDPE |
| 6 | Duroplast | Polyethylene terephthalate –PET |
Join us to attend the best GK coaching classes for Government exams!
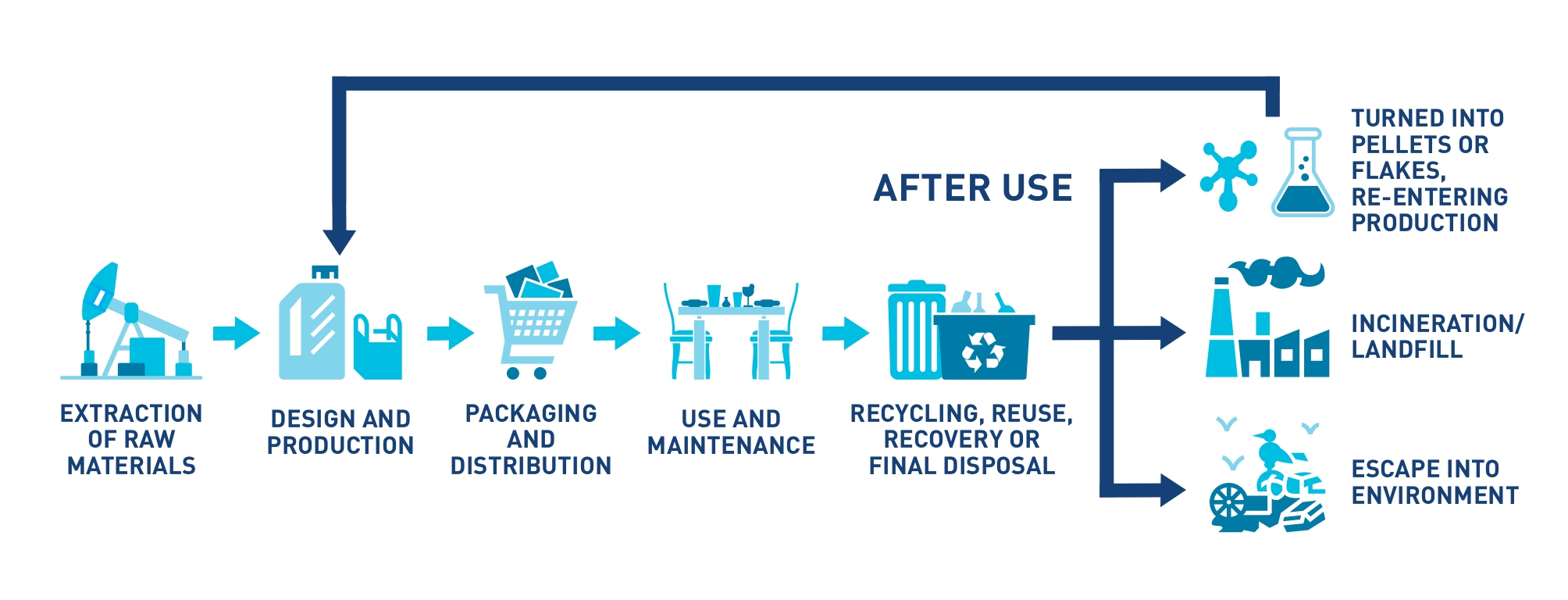
The Lifecycle of Plastics?
The entire life cycle of plastics presents a challenge in terms of design, manufacture, consumption, and disposal: plastic pollution. Inefficient waste management systems, non-existent or ineffective regulation, unsustainable consumption patterns, and a lack of coordination across several sectors are only a few of the many variables that contribute to the problem. The life cycle of plastic is providing blow.
What is Plastic Pollution?
We can define plastic pollution as the accumulation of plastic residues and wastes getting accumulated in the environment causing adverse effects on the climate, environment, ecosystem and organisms living in it.
What are the Causes of Plastic Pollution?
90% of the plastic waste is post-consumer waste while the rest were pre-consumer wastes that were rejected during the manufacturing process due to unsuitable colour, hardness or other properties. A significant portion of post-consumer waste where plastic packaging. This includes
- plastic bottles
- pots
- tubs
- trays
- plastic film shopping bags
- rubbish bags
- bubble wrap
- plastic or stretch wrap
- plastic foams
In the agricultural sector plastic wastes are generated in the forms given below.
- irrigation pipes
- greenhouse covers
- fencing
- pellets
In the construction sector, they are in the following forms.
- Pipes
- Paints
- flooring
- roofing
- insulants
- sealants
Plastic wastes are generated by the transportation industry in the following forms.
- abraded tyres
- road surfaces
- road markings
Besides the industries listed above, there are also wastes from the electrical and electronic sectors (e-waste) and the ones from the medical and pharmaceutical industries. It is the mismanagement of waste that leads to plastic leakage into the environment.
Get in the government services with the help of the Entri app coaching classes! Click to join!
Types of Plastic Wastes?
The three main types of plastic debris are microplastics, megaplastics and macroplastics. This division is according to particle size. They can also be divided into primary and secondary plastics. Primary plastics are the wastes that are found in their original form while secondary plastic wastes are the smaller forms that are formed as a result of degradation of the primary plastics.
Micro debris is tiny bits of plastic that range in size from 2 to 5 mm. When plastic debris degrades and collides, breaking it down into tiny pieces, it can become micro debris from starting as meso- or macro debris. Nurdles are a more popular term for micro debris. Nurdles are easily discharged into the environment during manufacture because of their small size, even if they are recycled to make new plastic objects. They frequently make their way to the ocean via rivers and streams. Scrubbers are another term for micro debris from cosmetic and cleaning goods. Because scrubbers and micro debris are so tiny, filter-feeding organisms frequently eat them.
These nurdles reach the ocean from spills from transportation as well as from its land sources. These microplastics have the potential to build up in the oceans and facilitate the accumulation of persistent bioaccumulating toxins, particularly PCBs, DDT, polystyrene, and bisphenol A. These toxins are hydrophobic and can have detrimental effects on human health.
When plastic debris is greater than 20 mm, it is classified as macro debris. Among them are products like plastic grocery bags. Macro debris is frequently found in ocean environments and can seriously harm native species. One of the main sources of pollution has been fishing nets. They keep capturing plastic waste and other aquatic life even after they are abandoned. These abandoned nets eventually increase weight and become too heavy to pull out of the ocean.
Why did Plastic Gain Popularity?
Plastic use gained popularity in the modern world for several reasons. Some of them are listed below.
- Plastics are inexpensive
- Plastics are durable
- They are easily adaptable for a variety of uses
Decomposition of Plastic Matter?
But the very thing that made them popular is what makes them dangerous. Their longevity or to be more precise, the long period required for the decomposition process. Their chemical structure is in such a way that they resist the natural process of decomposition. This large amount of plastic material enters the ecosystem as a result of bad or inefficient waste management strategies and methods. This will then continue existing in the environment and creating problems in the natural habitat and life cycle of the living beings and even entering the food web.
Many types of plastics exist depending upon their precursors and the kind of polymerisation they undergo. The chemical composition of a plastic or resin has a great influence on its contaminant adsorption and absorption. Plastic debris tends to persist in certain environments. For example, in the ocean, the decomposition of plastic wastes is very slow due to the coldness and saline environment. But the latest studies show that this is not as slow as we anticipated earlier. This is due to exposure to rough conditions like sun, rain etc. This type of decomposition results in the release of many toxic chemicals. However, the increase in the volume of plastic waste reaching the ocean again decreases this decomposition speed.
Join the best coaching classes for the year 2024! Watch demo classes here!
Harmful Effects of Plastic Pollution
Plastic pollution can affect the land and water equally. The studies say that tonnes of plastic waste enter the oceans from the coastal communities alone. The animals may suffer from the mechanical effects of the plastic debris such as entanglement inside plastic objects and losing mobility, getting their head stuck and suffocating, and cutting through their limbs or bodies. They also could ingest plastic waste leading to health complications and even leading to fatal conditions. Degraded plastic wastes can be ingested directly by humans or indirectly consumed through plants and animals. This can lead to several problems and can even disrupt hormone mechanisms. They also create huge issues for the overall planetary health.
Effects of Plastic Pollution on the Environment
The distribution of plastic waste varies greatly depending on factors such as wind and ocean currents, shoreline topography, urban regions, and trade routes. A significant part of this is also influenced by the human population in some locations. Furthermore, heavy metals and persistent organic pollutants can be transported through plastics as vectors of chemical contamination. Plastic waste breaks down into pieces as it weathers, which even tiny marine creatures may consume and contaminate the food chain. Because of their microscopic size, they are impossible to track down to their source and very challenging to eradicate from open ocean areas.
Effects of Plastic Pollution on Climate
Plastic pollution is a huge contributing factor to the climate change scenario our planet is currently facing. The incineration of plastics is one of the main reasons for the release of huge amounts of greenhouse gases into the atmosphere. The emission of gases released during the decomposition of plastics has a major effect on phytoplankton and as a result on the climate.
Effects of Plastic Pollution on Land and Its Ecosystem
Plastic pollution on the land causes harm to plants, animals and humans. The amount of plastic dumped on the land is many times more than the one in the case of oceans and other water resources. Plastic is rampantly used in every industry including agriculture and they are mismanaged at dangerous levels after its use is over. The chemicals released by the plastics left on land eventually enter the groundwater and pollute and endanger the lives of living beings depending on the neighbouring water bodies for sustenance. Industrial effluents contain large amounts of plastic.
The plastic waste dumped into drains in the urban areas clogs the city drains and this leads to flash floods. Even the tap water used for consumption by the people is severely polluted by microplastics. The main reason is that the wastewater treatment plants cannot remove the microplastics from water before the release.
Mismanagement led plastic waste to enter the terrestrial ecosystems. These first settle on the soil and then later enter the subsoil. This leads to soil pollution. This will affect the balance of microorganisms in the soil and hence the fertility of the soil. And this will in turn affect plant growth. Given below are the after-effects that happen to the plant physiology after such exposure.
- Decreased levels of seedling germination
- less number of leaves
- less stem diameter
- less chlorophyll content in plants
Microplastics in the soil pose a threat to human health and food safety in addition to the biodiversity of the soil. In agricultural businesses, plant growth depends on the biodiversity of the soil. The use of municipal garbage and plastic mulching are two agricultural practices that lead to soil contamination with microplastics. Although it is a widespread practice to employ soils modified by humans to increase agricultural output, the results are more detrimental than beneficial.
Effects of Plastic Pollution on Water Bodies and their Ecosystem
In the marine ecosystem, plastic pollution will cause the following issues.
- Entanglement of marine organisms in physical objects like abandoned fishing nets.
- toxicological effects due to ingestion of plastics.
- suffocation of animals due to large plastic objects.
- Starvation
- Dispersal of organisms from natural habitat
- rafting of organisms
- provision of new habitats
- introduction of invasive species
- loss of biodiversity.
- Lacerations and infections due to injuries caused by debris.
- reduced ability to swim
- internal injuries
- intestinal blockages finally resulting in loss of appetite and starvation
And all of these above-mentioned things will cause the negative influence of socioeconomic factors of the particular region. Things such as tourism, shipping, fishing, and human health all will be severely affected.
The latest studies show that 90% of seabirds have plastic debris inside their body. Many animals such as seabirds, whales, fish and turtles are under the threat of extinction due to this.
Effects of Plastic Pollution on Humans
Plastic pollution affects human health as well. They mainly enter the human body from the plastics used for food packaging, the water they drink and consuming the animals that already ingested plastics or microplastics. Biological magnification caused by this is seriously threatening to several sensitive species. Look at the following side effects plastic pollution might cause to humans.
- There is a change in the intestinal microbiomes of several organisms due to the ingestion of plastics or microplastics. Humans are no different.
- Messing up the functioning of the endocrine system. Some of them imitate oestrogen, some of them destroy the thyroid hormones
- Affects steroid biosynthesis and hence spermatogenesis.
- It causes DNA damage to the spermatozoa and this reduces the sperm viability.
- Some plastic pollutants cause dermatitis.
- Damage to the immune as well as reproductive systems of women.
Plastic Pollution in Recent Times
There has been a rise in the demand for protective equipment as well as packaging materials in recent times due to the pandemic. All these masks and medical wastes mostly end up being dumped into water bodies and accumulate in the ocean. There have been reports suggesting that plastic manufacturing companies are taking advantage of the health crisis and the need for disposable masks and packaging material to promote the usage of previously banned or controlled production of single use plastic products.
Plasticosis
A novel disease called Plasticosis, which is exclusively caused by plastics, was found in seabirds in 2023. The disease-afflicted birds have damaged their digestive systems as a result of consuming plastic garbage. It has been discovered that little fragments of plastic that birds eat cause intestinal inflammation. The ongoing inflammation impairs growth, digestion, and survival over time by leaving tissues damaged and deformed.
Join Entri GK coaching classes for the best results in the upcoming government exams!
Steps for Prevention of Plastic Pollution
Prevention is better than cure. Let us apply the same principle to the case of water pollution as well. Here some methods to prevent plastic pollution are provided.
- Reduce the use of virgin plastic.
- Avoid disposable plastic items as much as possible.
- Take your cloth shopping bag while shopping.
- Don’t buy bottled water unless necessary. Take a durable bottle and fill it with a water filter.
- Avoid cosmetics with microbeads. Use natural exfoliants.
- Cook more at home to avoid take-out containers.
- Buy the things in bulk so that there will be less packaging material wastage.
- Make strategies that are internationally coordinated to manage the waste products globally.
- Use degradable bags instead of plastic bags in markets.
- Discourage the use of plastic bags by charging the plastic bags in markets or by taxing them.
- Promote a ban on single-use plastics.
- Increase recycling of plastic wastes.
- Encourage research and production of biodegradable plastics.
- Discourage the practice of incineration and landfilling of plastic wastes.
- Encourage reusable packaging, zero-waste stores and refill shops.
Conventions for Plastic Waste Management
The Basel Convention was amended in May 2019 to control the import and export of plastic trash. The main goal of this regulation is to stop the transfer of plastic garbage from developed to developing nations. This agreement has been ratified by almost all nations. To eradicate plastic pollution, 175 nations committed on March 2, 2022, in Nairobi, to draft a legally binding agreement by the end of 2024.
There have been serious efforts to reduce plastic pollution in certain parts of the world by reducing its consumption, active and efficient litter cleaning methods and promoting recycling.
Join the Entri app to learn GK at your own pace! Click here to register today!
Plastic Pollution FAQs
- What makes plastic pollution such a problem?
- In addition to causing climate change and endangering the health of people and animals, plastic pollution also affects the safety and quality of food and water.
- How is global warming caused by plastic?
- Since single-use plastic is comprised of fossil fuels, the production of single-use plastic produces a significant amount of greenhouse emissions. This, in turn, causes global warming.