Table of Contents
The Human Body has five basic sense organs. They are often called sensory organs and consists of the eyes, ears, nose, tongue and skin. Moreover, each one is associated with sight, hearing, smell, taste and touch respectively. The sense organ analogous to each sense help to send information to the brain. This, consequently aid us to perceive and understand the world around us in a better way. This article deals exclusively with the Human Eye- Structure, Parts, Function.
All the sense organs are valuable and important. Out of this, the Human Eye is regarded as the most sensitive sense organ. It is solely responsible for our vision. Most importantly, it enables us to see the beautiful and colorful world around us. In this article, you will read about the structure and parts of the human eye. Then, you will also read about the different functions of the human eye.
Be Ahead of All in the Exam Race! Join Entri Today!
Structure of the Human Eye
The Human Eye has a distinctive structure. Moreover, it is not a perfectly spherical in shape. It is placed in the eye pockets in the skull. In addition, it is harbored to the sockets by help of muscles. We shall learn the structure of human eye under two distinguished heads. They are:
- External Elements: The parts of the human eye which are visible externally.
- Internal Elements : the parts of the human eye which cannot be seen externally.
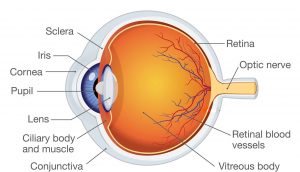
Parts of the Human Eye
1: Who was the first woman President of India?
The table given below shows the External and Internal parts of the human eye:
| External Elements | Internal Elements |
|
Sclera Conjunctiva Cornea Iris Pupil |
Lens Retina Optic Nerve Aqueous Humour Vitreous Humour |
All the elements of the eye are equally important for its proper functioning. Also, damage to any one element may cause serious impairments. Let us now learn about each part in detail.
External Elements
Sclera
Sclera is the external white part of the eye. Moreover, it surrounds the cornea. Furthermore, it is the opaque, tough, fibrous and protective layer of the human eye. Interestingly, it constitutes more than 80 percent of the surface area of the eye ball.
Conjunctiva
Conjunctiva is a clear, thin membrane which covers the surface of the eyeball. It is made up of loose connective tissue. Additionally, it has many small blood vessels which provide nutrients to the eyes and lids.
Cornea
The clear, protective layer of the eye is called the cornea. It acts as a protective shield against micro -organism, dirt, etc. Therefore, it serves similar function to sclera. Furthermore, it plays a vital role in vision. It does so, by refracting or bending the light ray, with its curved edge.
Iris
Iris is the colored, ring shaped membrane of the eye. It is located behind the cornea. In addition, it is made up of connective tissue and muscles that surround the pupil. Iris determines the color of our eyes. It does so, by determining the amount of pigment present in iris. Apart from all these, it controls the diameter of pupil depending on the amount of light.
Pupil
The pupil is a small opening present in the centre of iris. The major function of pupil is to control the amount of light entering the eye. Furthermore, it focuses the light onto retina. In short, it is called as the Aperture of the human Eye.
Get Unlimited Mock Tests On Entri ! Subscribe Today!
Internal Elements
Lens
The Human Eye has a biconvex, crystalline lens. Along with the cornea, it helps to refract light and to focus it on retina. Furthermore, the Human Eye is usually compared to a camera. In the working of a camera, the camera lens focuses the light onto the film. Similarly, cornea and lens of the eye functions as a camera lens whereas the retina acts like a film.
Retina
Retina is the inner most layer of tissue which lines the human eye. It is light sensitive. Also, it is located near the optic nerve. Moreover, it is composed of many layers such as photoreceptor cells. The human eye contains two types of photoreceptor cells. These are the rod cells and the cone cells.
Optic Nerve
The optic nerve connects the human eye to the brain. They carry the impulses formed by the retina to the brain. Moreover, it is often called as second cranial nerve. It is usually paired and cylindrical in nature.
Aqueous Humour
Aqueous Humour is the transparent, watery fluid present in the front part of the eyes. To be precise, it is present between the cornea and the lens of the human eye. It is very similar to plasma. However, it has low protein concentration. It nourishes the eye. Furthermore, it keeps the eye inflated. The eye constantly produces a small amount of this fluid.
Vitreous Humour
Vitreous Humour is a gelatinous fluid present between the lens and the retina of the humans. It has a major role in protecting the eye. Furthermore, it helps to hold the nearly spherical shape of the eye.
Ace you Exam Preparation with Entri!
Free UPSKILLING Courses!
Take your first step toward mastering in-demand skills, acing interviews, and securing top-tier jobs with Entri's free upskilling courses.
Start Learning!Functions of the Human Eye
As we have studied the structure of the Human Eye, it is important to learn the function that each part performs.
The functions of the different parts of the human are given below:
| Part | Function |
| Cornea | Provides path for the light to enter the eyes |
| Iris | Controls the amount of light entering the eyes |
| Pupil | Acts like an aperture by dilating and contracting |
| Lens | Focuses the light entering the eyes |
| Ciliary Muscles | Helps to change the focal length by holding the lens |
| Retina | Image formation takes place here |
| Optic Nerve | Carries signals from retina to the brain |
| Aqueous Humour | Provides nutrition to the eye |
| Vitrous Humour | Helps to hold the shape of the eye |
To sum up, the functions of the human eye may be listed as follows:
- Adjusts the amount of light into the eye
- Focuses on objects-both near and far.
- Produces continuous images
- Transmit the signals instantly to the brain.
Click Here to Get Science Notes on various topics!
Why Learn from Entri:
- Top notch & experienced tutors to learn from.
- Mock tests in various regional languages available.
- Download for Free! Get access to video classes, exams and study cards with a single subscription fee.
- Full length Mock Tests and previous year question papers available.
And lots more! Subscribe Today!