Table of Contents
UI/UX Design Trends are changing how users interact online. Design now focuses more on user comfort. People expect fast and easy experiences. Simple layouts help users navigate better. Design must work smoothly across devices. User needs guide every design decision. Clean interfaces improve engagement and clarity. Good design feels natural and effortless. Designers must evolve with technology.
Digital platforms are becoming more interactive. Users prefer smooth and responsive interfaces. Voice and touch interactions are increasing. Accessibility is now very important. Small animations improve user understanding. Consistent design builds user trust. New technologies influence interface behavior. Designers must adapt to modern expectations.
Get Certified in UI/UX Design — Build User-Friendly Experiences with Confidence!
Introduction: User-centric Design Evolution
UI/UX design has changed greatly in recent years. Design is no longer only about good visuals. It now focuses strongly on user comfort. Every product must feel easy to use. Users expect smooth and simple digital journeys.
Earlier designs focused mainly on appearance. Modern design focuses on experience and usability. Users want clarity at every step. They avoid confusing layouts and heavy interfaces. Design must guide users naturally.
User-centric design puts people first. Design decisions begin with user needs. Understanding users helps create better products. Designers study behavior, habits, and challenges. This knowledge shapes every interface element.
Navigation must be clear and predictable. Users should know what to do next. Buttons, icons, and menus need clarity. Content must be easy to scan. Simple layouts reduce mental effort.
Technology growth changed user expectations. People use phones, tablets, and smart devices. Design must work smoothly everywhere. Consistency across platforms is very important. Users expect similar experiences on every screen.
Personalization is becoming more common. Interfaces adapt to user preferences. Content changes based on behavior. Smart design improves engagement levels. Users feel valued through personalized experiences.
Accessibility plays a major role today. Design must support all users equally. Readable text helps visual clarity. Proper contrast improves usability. Accessible design benefits everyone.
Emotional connection matters in design. Users prefer friendly and human experiences. Colors influence mood and attention. Spacing improves visual comfort. Clean design increases trust.
Modern design favors simplicity. Minimal layouts remove distractions. Users focus better with fewer elements. Clear structure improves understanding. Less clutter creates better experiences.
User expectations continue to rise. Design must adapt to constant change. Trends evolve with technology and habits. Designers must learn continuously. Improvement never truly stops.
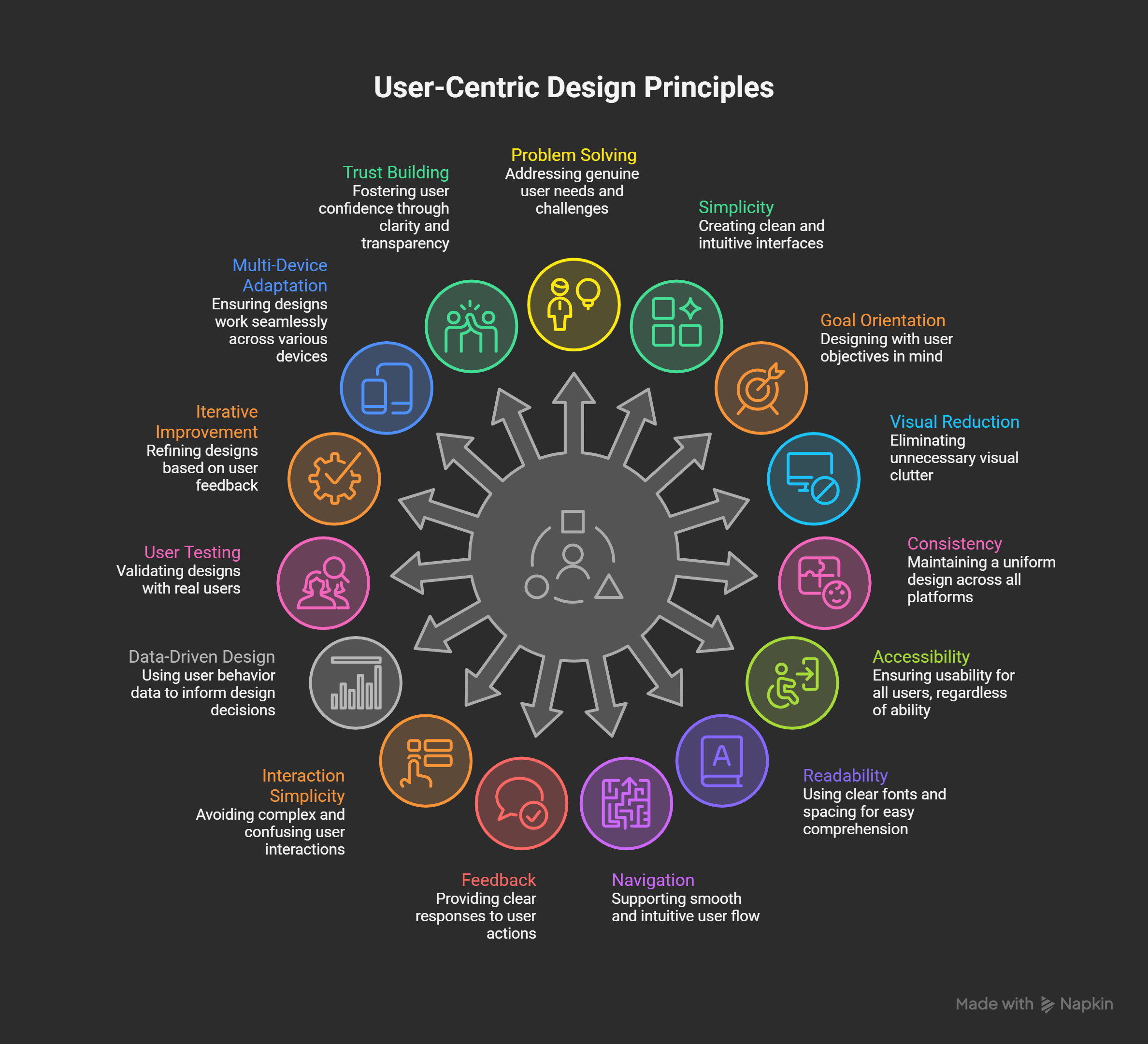
Key elements of user-centric design evolution
- Focus on solving real user problems.
- Keep interfaces clean and simple.
- Design with user goals in mind.
- Reduce unnecessary visual elements.
- Maintain consistency across all screens.
- Ensure accessibility for all users.
- Use readable fonts and spacing.
- Support smooth navigation flow.
- Provide clear feedback for actions.
- Avoid complex interactions.
- Use data to understand behavior.
- Test designs with real users.
- Improve based on feedback.
- Adapt designs for multiple devices.
- Build trust through clarity.
User-centric design shapes modern digital experiences. It improves satisfaction and engagement. Designers now think beyond visuals. They design meaningful user journeys. This evolution defines the future of UI/UX.
Top UI/UX Design Trends in 2026
The UI/UX industry continues evolving rapidly. Designers now face higher user expectations. Technology strongly influences modern design decisions. Users want faster, smarter, and simpler experiences. Design must balance creativity and usability.
The following trends define UI/UX in 2026. Each trend improves how users interact digitally. Designers must understand these changes deeply. These trends shape future digital experiences.
AI-Powered Design Tools
AI-powered design tools are transforming modern UI/UX workflows. Designers no longer rely only on manual processes. Artificial intelligence supports faster and smarter decisions. It improves efficiency without reducing creativity. Design teams now work more productively.
AI helps designers focus on experience quality. Repetitive tasks are handled automatically. This allows deeper problem solving. Design becomes more strategic and user-focused.
What Are AI-Powered Design Tools
AI design tools use machine learning algorithms. They analyze data and user behavior. These tools generate intelligent design suggestions. They learn from patterns and feedback.
AI tools support designers, not replace them. Human judgment remains essential. AI simply enhances creative workflows.
Key Capabilities of AI Design Tools
1. Automated layout generation
- Creates layouts instantly
- Suggests spacing and alignment
- Maintains design consistency
2. Smart color and typography suggestions
- Recommends readable font combinations
- Maintains visual hierarchy
- Ensures contrast compliance
3. Design system automation
- Generates reusable components
- Updates elements automatically
- Reduces inconsistencies
4. Predictive usability analysis
- Identifies possible user issues
- Suggests layout improvements
- Improves conversion potential
Benefits for Designers
| Benefit | Explanation |
|---|---|
| Faster workflows | Reduces production time |
| Higher accuracy | Fewer manual errors |
| Better consistency | Unified design system |
| Data insights | Informed decisions |
| Scalability | Supports large products |
How AI Improves User Experience
AI analyzes user interaction data. It identifies behavior patterns quickly. Interfaces adapt based on preferences. Content becomes more personalized. Users receive relevant experiences.
Adaptive layouts improve usability. Navigation adjusts based on habits. Design feels intuitive and intelligent.
Popular AI Use Cases in UI/UX
- Rapid wireframe creation
- Smart prototyping assistance
- Accessibility issue detection
- Content hierarchy optimization
- Real-time design validation
These features reduce rework. They improve overall product quality.
Skills Designers Must Develop
- Understanding AI-driven workflows
- Interpreting design analytics
- Using AI-based plugins
- Managing automated design systems
- Balancing creativity with automation
AI literacy is becoming mandatory. Designers must adapt continuously.
Why This Trend Matters in 2026
Products are becoming more complex. Design timelines are shrinking rapidly. Companies expect faster results. AI enables high-quality output. This makes it essential in 2026.
Voice & Gesture-Based UI
Voice and gesture-based interfaces are reshaping user interaction. Users no longer depend only on touch screens. Natural interaction methods are gaining importance. People prefer faster and hands-free experiences. This shift influences modern UI/UX design strongly.
Voice and gesture interfaces improve convenience. They reduce physical effort during interactions. They support multitasking situations effectively. These interfaces feel more human and intuitive.
What Is Voice-Based User Interface
Voice-based UI allows spoken commands. Users interact using natural language. Systems respond through audio or visuals. Communication becomes conversational and simple.
Common voice UI examples include:
- Virtual assistants
- Smart home controls
- Automotive dashboards
- Voice search systems
Voice interfaces are expanding rapidly. Smart devices accelerate their adoption.
What Is Gesture-Based User Interface
Gesture-based UI responds to physical movements. Users control systems without touching screens. Sensors detect hand or body motion. Cameras interpret user actions.
Common gesture inputs include:
- Hand swipes
- Air taps
- Finger movements
- Head gestures
Gesture UI is useful in touchless environments. It supports hygiene and accessibility needs.
Why Voice and Gesture UI Matter
These interfaces improve digital accessibility. They support users with physical limitations. These interfaces enable interaction without keyboards. They reduce dependency on screens.
Key advantages include:
- Hands-free operation
- Faster task completion
- Improved accessibility
- Natural interaction flow
- Better user comfort
These benefits improve overall user satisfaction.
Design Challenges in Voice and Gesture UI
Designing non-visual interfaces is complex. Feedback becomes difficult without screens. Users may feel confused easily.
Common challenges include:
- Background noise interference
- Speech recognition errors
- Limited gesture accuracy
- Learning command structures
- Privacy and security concerns
Designers must reduce cognitive effort. Clear feedback is essential.
Best Practices for Designers
- Keep commands short and simple
- Provide voice confirmations
- Offer visual fallback options
- Maintain consistent command structure
- Allow error recovery
Design must remain flexible. Users should never feel stuck.
Industries Using Voice and Gesture UI
| Industry | Application |
|---|---|
| Smart homes | Voice automation |
| Healthcare | Touchless systems |
| Automotive | Gesture navigation |
| Retail | Voice shopping |
| Education | Interactive learning |
Why This Trend Matters in 2026
Smart devices continue growing worldwide. Users expect natural interactions. Voice search usage increases yearly. Touchless technology gains popularity.
Designers must adapt interaction thinking. Future interfaces will be multimodal.
Inclusive & Accessible Design
Inclusive and accessible design is now essential. Digital products must support every user equally. Accessibility is no longer optional. It is a core UX responsibility. Design must consider human diversity.
Users have different abilities and limitations. Some challenges are permanent. Some challenges are temporary. Design must adapt to all situations. Inclusive thinking improves usability for everyone.
What Is Inclusive Design
Inclusive design focuses on user diversity. It considers different abilities and contexts. Design supports varied physical and cognitive needs. Products become usable by wider audiences.
Inclusive design does not create separate solutions. It creates flexible experiences for all users.
Types of Accessibility Needs
Users may face many limitations.
Common accessibility categories:
- Visual impairments
- Hearing difficulties
- Motor limitations
- Cognitive challenges
- Age-related conditions
Design must respect these differences.
Core Accessibility Principles
Accessible design follows global standards.
Perceivable
- Content must be visible and readable
Operable
- Users must navigate easily
Understandable
- Interfaces should remain predictable
Robust
- Works with assistive technologies
These principles guide accessible UX.
Common Accessibility Features
- High color contrast
- Adjustable font sizes
- Keyboard navigation support
- Screen reader compatibility
- Clear error messages
These features improve comfort. They reduce user frustration.
Benefits of Inclusive Design
| Benefit | Description |
|---|---|
| Wider reach | Serves more users |
| Better usability | Improves clarity |
| Legal compliance | Meets regulations |
| Brand trust | Builds credibility |
| SEO improvement | Enhances structure |
Why Accessibility Improves UX
Accessible design benefits all users. Clear text improves readability. Simple layouts reduce confusion. Logical navigation saves time. Consistent patterns build confidence.
Good accessibility equals good usability.
Designer Skills Required
Designers must learn accessibility standards. Understanding WCAG guidelines is important. Contrast testing skills are required. Keyboard navigation must be tested. Screen readers must be considered.
Empathy plays a major role. Designers must think inclusively.
Accessibility Tools Designers Use
- Contrast checkers
- Screen reader testing tools
- Accessibility audit plugins
- Keyboard testing methods
- Automated accessibility scanners
These tools improve design quality.
Why This Trend Matters in 2026
Digital inclusion expectations continue growing. Accessibility laws become stricter globally. Users demand ethical digital products. Companies prioritize inclusive design strategies.
Designers must embed accessibility early. It defines modern UI/UX success.
Get Certified in UI/UX Design — Build User-Friendly Experiences with Confidence!
Micro-Interactions & Motion UI
Micro-interactions and motion UI enhance user experiences. They add life to digital interfaces. Small movements communicate important feedback. They help users understand system responses. Design feels more interactive and human.
Modern interfaces are no longer static. Users expect responsive behavior. Motion helps guide attention naturally. It improves clarity without extra text. Well-designed motion supports usability.
What Are Micro-Interactions
Micro-interactions are small visual responses. They react to specific user actions. They occur during simple interactions. These moments improve user awareness.
Common examples include:
- Button hover effects
- Toggle switches
- Loading animations
- Notification indicators
- Swipe confirmations
Each interaction has a clear purpose.
Components of Micro-Interactions
Every micro-interaction contains four elements.
1. Trigger
- User clicks or taps
2. Rules
- System defines what happens
3. Feedback
- Visual or motion response
4. Loops
- Determines repetition behaviour
These components ensure smooth interaction.
Purpose of Micro-Interactions
Micro-interactions serve multiple goals.
- Confirm user actions
- Reduce uncertainty
- Provide system feedback
- Guide user attention
- Increase engagement
They make interfaces easier to understand.
What Is Motion UI
Motion UI uses animation to explain behavior. It shows relationships between elements. It connects screens smoothly. Motion creates continuity during navigation.
Motion should feel natural. It must never overwhelm users.
Effective Motion UI Examples
- Page transitions
- Menu expansions
- Card movements
- Loading progress indicators
- Form validation feedback
Each animation communicates meaning.
Best Practices for Motion Design
- Keep animations subtle
- Maintain consistent timing
- Use natural easing curves
- Avoid excessive movement
- Respect reduced-motion settings
Motion must support usability.
Benefits of Micro-Interactions and Motion UI
| Benefit | Result |
|---|---|
| Better feedback | Clear system response |
| Higher engagement | Improved interaction |
| Smooth flow | Seamless navigation |
| Emotional connection | Friendly experience |
| Improved retention | Better memory recall |
Accessibility Considerations
Motion can cause discomfort for some users. Designers must provide control options. Reduced-motion settings should be supported. Animations should never block actions.
Accessibility and motion must coexist.
Why This Trend Matters in 2026
Users expect polished experiences. Subtle animations signal product quality. Motion improves perceived performance. Design systems rely on consistent motion.
Micro-interactions define premium UX. They separate good design from great design.
AR/VR User Experiences
AR and VR are transforming digital interaction. They introduce immersive user experiences. Interfaces move beyond flat screens. Users interact within three-dimensional spaces. Design becomes spatial and experiential.
These technologies blend physical and digital worlds. User engagement increases significantly. Experiences feel realistic and memorable. Designers must rethink traditional UI patterns. Spatial thinking becomes essential.
What Is Augmented Reality
Augmented Reality overlays digital content onto reality. Users view enhancements through cameras or glasses. AR adds information to the real world.
Common AR examples include:
- Virtual product previews
- Navigation overlays
- Interactive manuals
- Educational visual aids
- Try-before-buy experiences
AR improves decision confidence.
What Is Virtual Reality
Virtual Reality creates fully immersive environments. Users enter simulated digital spaces. Headsets block physical surroundings completely.
VR applications include:
- Training simulations
- Virtual tours
- Remote collaboration spaces
- Skill development programs
- Therapy and education systems
VR delivers deep immersion.
Why AR/VR Matters in UI/UX
AR and VR enhance experience depth. They support experiential learning. Users understand concepts visually. Interaction becomes memorable.
Key advantages include:
- High engagement levels
- Better knowledge retention
- Realistic simulations
- Reduced physical risk
- Strong emotional impact
UX Challenges in AR/VR Design
Designing immersive systems is complex.
Common challenges include:
- Motion sickness risks
- Hardware limitations
- Performance optimization
- Navigation confusion
- Physical safety concerns
Design must prioritize comfort.
Core Principles of Spatial UX Design
- Maintain realistic scale
- Use natural interactions
- Provide orientation guidance
- Avoid interface clutter
- Respect physical movement limits
Spatial UX requires empathy.
Interaction Methods in AR/VR
- Hand gestures
- Eye tracking
- Voice commands
- Controller input
- Head movement
Designers must combine methods wisely.
Industries Using AR/VR UX
| Industry | Application |
|---|---|
| Retail | Virtual try-ons |
| Real estate | Property walkthroughs |
| Education | Immersive learning |
| Healthcare | Medical simulations |
| Manufacturing | Safety training |
Benefits of AR/VR Experiences
| Benefit | Impact |
|---|---|
| Engagement | Deep involvement |
| Understanding | Visual clarity |
| Training | Risk-free practice |
| Exploration | Realistic previews |
| Innovation | Future readiness |
Why This Trend Matters in 2026
AR and VR hardware is improving rapidly. Devices are becoming lighter and affordable. Enterprise adoption is increasing. Consumer usage continues expanding.
Designers must prepare early. Spatial UX defines future interaction.
Skills Designers Must Learn
UI/UX design continues evolving rapidly. Designers must upgrade skills continuously. Tools, users, and technologies keep changing. Learning never stops in design careers. Future designers must stay adaptable.
Modern designers need both creative and technical abilities. They must understand users deeply. They must collaborate across teams. Skills now extend beyond visual design. Strategic thinking is equally important.
1. User Research and Design Thinking
Understanding users is the foundation of UX. Designers must study real user problems. Research guides better design decisions.
Key research skills include:
- User interviews
- Survey creation
- Usability testing
- Persona development
- Journey mapping
These methods reveal user behavior. Design decisions become evidence-based.
2. AI and Automation Awareness
AI is now part of design workflows. Designers must understand AI capabilities. Automation improves speed and accuracy.
Important AI-related skills:
- Using AI design tools
- Interpreting behavioural data
- Applying predictive insights
- Managing automated design systems
Designers must guide AI outputs carefully. Human creativity remains essential.
3. Interaction and Motion Design
Modern interfaces rely on interaction design. Motion explains how systems behave. Designers must master movement principles.
Motion design skills include:
- Micro-interaction creation
- Animation timing
- Easing and transitions
- Motion accessibility understanding
Motion must enhance usability. It should never distract users.
4. Accessibility and Inclusive Design
Accessibility is a mandatory design requirement. Designers must design for all users. Inclusive design improves usability universally.
Accessibility skills required:
- WCAG guideline understanding
- Color contrast testing
- Keyboard navigation design
- Screen reader awareness
Accessibility must begin early. Fixing later increases complexity.
5. Multimodal Interface Design
Interfaces are no longer screen-only. Users interact using voice and gestures. Designers must support multiple interaction modes.
Multimodal design skills include:
- Voice flow design
- Conversational UX writing
- Gesture interaction mapping
- Error handling design
These interfaces require new thinking.
6. Prototyping and Design Tools Mastery
Design tools evolve constantly. Designers must stay updated.
Essential tool skills include:
- High-fidelity prototyping
- Design system management
- Component-based design
- Collaboration workflows
Speed and accuracy matter greatly.
7. Collaboration and Communication Skills
Designers rarely work alone. They collaborate with developers and managers. Clear communication avoids misunderstandings.
Key soft skills include:
- Presenting design decisions
- Explaining user logic
- Accepting feedback positively
- Cross-team collaboration
Good communication increases design impact.
8. Data and UX Metrics Understanding
Design decisions require validation. Metrics help measure success.
Important UX metrics include:
- Task completion rate
- Error frequency
- Conversion rate
- Engagement duration
Designers must understand numbers. Data strengthens design credibility.
Key Skills Summary Table
| Skill Area | Purpose |
|---|---|
| User research | Understand real users |
| AI awareness | Improve efficiency |
| Motion design | Enhance interaction |
| Accessibility | Universal usability |
| Multimodal UX | Support new inputs |
| Prototyping | Faster validation |
| Communication | Team alignment |
| UX metrics | Measure impact |
Why Skill Development Matters
UI/UX roles are becoming competitive. Employers expect versatile designers. Specialization alone is insufficient. Hybrid skills increase career stability. Continuous learning ensures long-term success.
Get Certified in UI/UX Design — Build User-Friendly Experiences with Confidence!
Career Opportunities
UI/UX design offers strong career growth. Digital transformation increases design demand. Every industry requires user experience professionals. Companies compete through better digital experiences. Design careers continue expanding globally.
UI/UX roles are no longer limited. Designers now work across domains. Technology growth creates specialized positions. Career paths have become more diverse. Design skills apply to many industries.
Why UI/UX Careers Are Growing
Businesses focus on user satisfaction. Good experience improves customer retention. Design influences revenue and engagement. Companies invest heavily in UX teams.
Key growth drivers include:
- Mobile application expansion
- SaaS product development
- E-commerce growth
- AI-based digital products
- AR and VR adoption
These trends increase long-term opportunities.
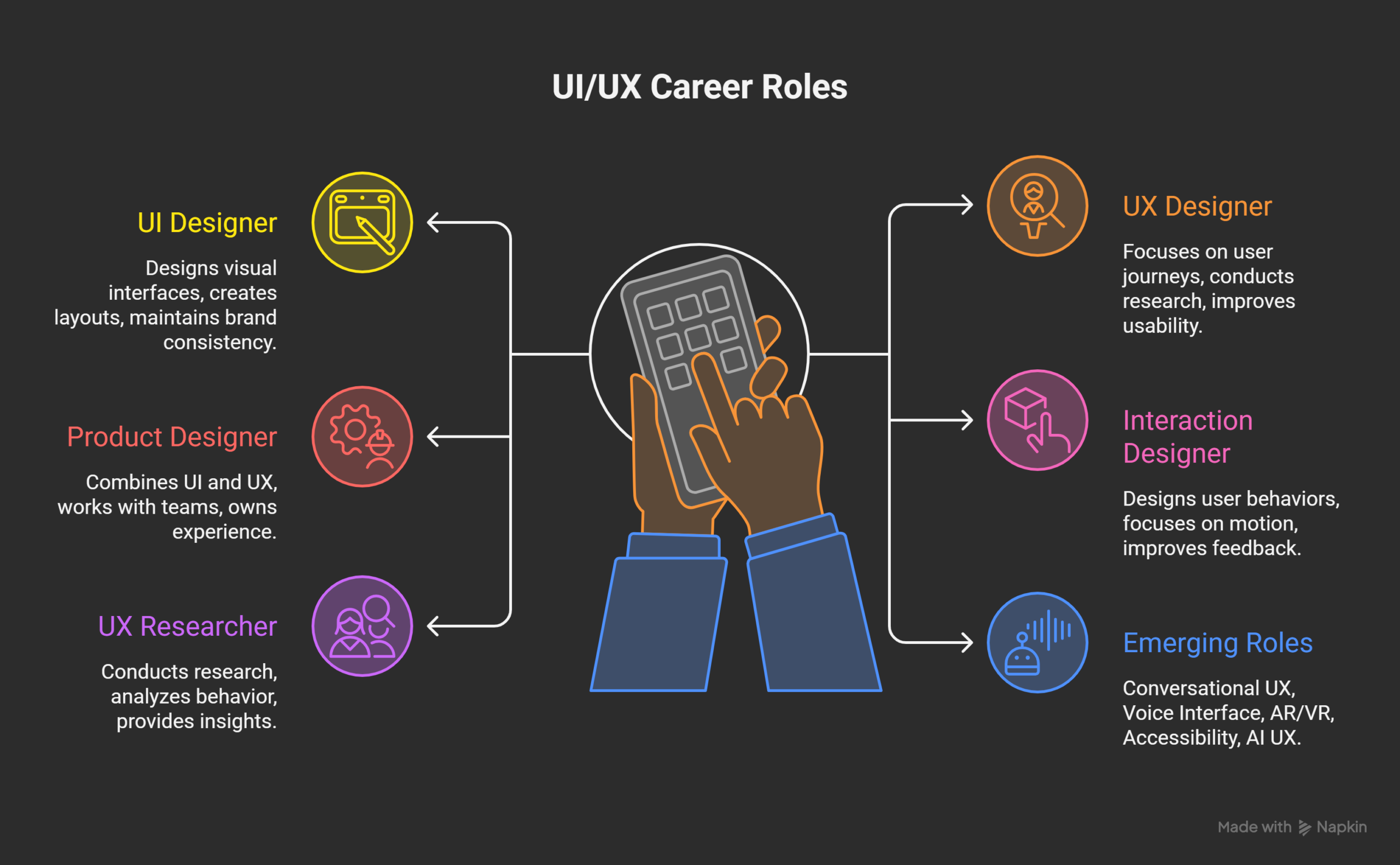
Popular UI/UX Career Roles
1. UI Designer
- Designs visual interfaces
- Creates layouts and components
- Maintains brand consistency
2. UX Designer
- Focuses on user journeys
- Conducts research and testing
- Improves product usability
3. Product Designer
- Combines UI and UX skills
- Works closely with product teams
- Owns end-to-end experience
4. Interaction Designer
- Designs user behaviours
- Focuses on motion and transitions
- Improves interface feedback
5. UX Researcher
- Conducts qualitative research
- Analyzes user behaviour
- Provides data-backed insights
Emerging Career Roles
Technology creates new design positions.
- Conversational UX Designer
- Voice Interface Designer
- AR/VR Experience Designer
- Accessibility Specialist
- AI UX Strategist
These roles grow rapidly in 2026.
Industries Hiring UI/UX Designers
| Industry | Opportunity |
|---|---|
| IT & Software | Web and SaaS products |
| E-commerce | Shopping experiences |
| Fintech | Secure interfaces |
| Healthcare | Patient platforms |
| Education | Learning systems |
| Gaming | Interactive experiences |
| Real estate | Virtual tours |
Designers can work across multiple sectors.
Career Levels in UI/UX
Entry-level roles
- UI/UX Designer
- Junior Product Designer
- UX Analyst
Mid-level roles
- Product Designer
- Interaction Designer
- UX Specialist
Senior-level roles
- Lead Designer
- UX Manager
- Design Strategist
Career progression is flexible.
Salary and Growth Potential
UI/UX offers competitive salaries. Pay increases with experience and specialization. Global remote roles boost earning potential.
Salary growth depends on:
- Skill depth
- Portfolio strength
- Industry domain
- Location
- Tool expertise
Specialized designers earn higher compensation.
Freelance and Remote Opportunities
UI/UX supports remote work models. Designers can work globally. Freelancing offers flexible income streams.
Common freelance projects include:
- Website redesigns
- Mobile app interfaces
- Design systems
- UX audits
- Prototype development
Strong portfolios attract international clients.
Skills That Improve Career Growth
- Problem-solving mindset
- Strong portfolio presentation
- Case-study storytelling
- Communication clarity
- Continuous learning attitude
Employers value thinking over visuals.
Career Opportunities Summary Table
| Role Type | Career Scope |
|---|---|
| UI Designer | Visual expertise |
| UX Designer | Experience optimization |
| Product Designer | End-to-end ownership |
| Researcher | User insights |
| AR/VR Designer | Immersive experiences |
| Accessibility Expert | Inclusive design |
| Freelancer | Global projects |
Future Career Outlook
UI/UX design remains future-proof. User experience drives digital success. Technology will continue evolving. Design roles will adapt continuously. Skilled designers will stay in demand.
Conclusion
UI/UX design continues evolving with technology and user needs. Designers must focus on creating meaningful experiences. User-centred thinking defines successful digital products. Emerging tools expand creative possibilities. Design now blends empathy with innovation. Adaptability remains the most valuable skill. Learning new trends ensures long-term relevance.
The future of UI/UX looks promising and dynamic. Design careers offer flexibility and global opportunities. Skills will matter more than job titles. Strong portfolios demonstrate real problem solving. Continuous learning supports career growth. Designers who evolve will lead change. The journey of design never truly ends.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the most important UI/UX design trends in 2026?
The most important UI/UX design trends in 2026 include AI-powered design tools, voice and gesture-based interfaces, inclusive and accessible design, advanced micro-interactions with motion UI, and immersive AR/VR user experiences. These trends focus on improving usability, personalization, accessibility, and emotional engagement across digital platforms.
Why are AI-powered tools becoming essential for designers?
AI-powered tools help designers automate repetitive tasks, analyze user behavior, generate layouts, maintain design consistency, and predict usability issues. This allows designers to spend more time on creative thinking, problem solving, and user research while delivering faster and more accurate design outputs.
How does voice and gesture-based UI improve user experience?
Voice and gesture-based interfaces enable users to interact naturally without touch, making digital products more accessible, convenient, and efficient. These interfaces are especially useful in smart homes, automobiles, healthcare systems, and wearable devices where hands-free interaction significantly enhances usability.
What is inclusive and accessible design, and why is it important?
Inclusive and accessible design ensures that digital products can be used by people of all abilities, including those with visual, hearing, motor, or cognitive challenges. It is important because it improves overall usability, expands audience reach, ensures legal compliance, and creates ethical digital experiences that prioritize equality.
How do micro-interactions improve UI/UX design?
Micro-interactions provide subtle visual feedback for user actions such as clicking buttons, submitting forms, or loading content. They help users understand system responses, reduce confusion, guide attention, and create smoother interactions that make digital experiences feel intuitive and responsive.
What role does motion UI play in modern interfaces?
Motion UI helps explain transitions, create visual continuity, and communicate hierarchy between interface elements. When used thoughtfully, motion improves navigation clarity, enhances emotional connection, and makes digital products feel modern without overwhelming users.
How are AR and VR changing user experience design?
AR and VR introduce immersive experiences that allow users to interact with digital environments in three-dimensional space. They are widely used for virtual product previews, training simulations, education, healthcare, and real estate, helping users understand concepts better through experiential learning.
What skills should a UI/UX designer learn in 2026?
Designers should focus on user research, accessibility standards, AI-driven design workflows, motion design, voice and conversational UX, prototyping tools, data interpretation, and strong communication skills. These combined skills help designers remain competitive in a rapidly evolving industry.
Is UI/UX design a good career choice in 2026?
Yes, UI/UX design remains a strong career option in 2026 due to continuous digital transformation across industries. Demand exists in software, fintech, healthcare, education, e-commerce, and emerging technologies like AR, VR, and AI-driven platforms.
What industries hire UI/UX designers the most?
UI/UX designers are widely hired in IT services, SaaS companies, e-commerce platforms, fintech firms, healthcare technology providers, edtech companies, gaming studios, and startups developing AI and immersive digital solutions.