Table of Contents
Software testing is changing faster than ever before. Software Testing Trends now shape modern development practices. Businesses demand faster, smarter, reliable testing methods. Manual testing alone cannot support complex applications. Automation improves speed, accuracy, and test coverage. AI tools enhance testing efficiency and decision making. Quality assurance now supports continuous software delivery. Testing teams adapt to agile and DevOps workflows. Future testing focuses on innovation and intelligence.
Technology growth pushes testing beyond traditional boundaries. AI and automation redefine quality assurance roles. Testing integrates deeply into development pipelines. Early testing reduces risks and development costs. Performance and security gain stronger testing focus. Testers now act as quality strategists. Learning new tools becomes career essential. Software testing evolves with business needs.
Join Entri’s Software Testing Course Today!!
Introduction: Evolution of Software Testing
Software testing has evolved alongside software development itself. In the early days, testing was a manual and reactive process. Teams tested applications only after development was completed. The main goal was finding visible bugs before release. This approach often caused delays, higher costs, and missed defects. As software systems became complex, traditional testing proved insufficient.
Over time, structured testing methods were introduced. Test cases, documentation, and testing phases became standard. Quality assurance emerged as a separate and important function. Testing started aligning with development life cycles. However, long release cycles still limited speed and flexibility. Businesses needed faster delivery without compromising quality.
The rise of agile development changed testing significantly. Testing shifted from a final phase to a continuous activity. Testers collaborated closely with developers and product teams. Automation tools reduced repetitive manual efforts. Frequent testing helped detect issues earlier in development. This marked the beginning of modern testing practices.
Today, software testing is driven by automation and AI. Testing supports rapid releases, cloud applications, and microservices. Quality is now built into every stage of development. Testing teams focus on user experience, performance, and security. The role of testers has become more strategic and technical. In 2026, testing continues to evolve with intelligent technologies.
Key Highlights of Software Testing Evolution
- Manual testing dominated early software projects
- Testing occurred after development completion
- Bugs were costly and time consuming to fix
- Quality assurance became a dedicated discipline
- Structured testing models improved reliability
Transition to Agile and Automation
- Agile introduced continuous testing practices
- Automation reduced repetitive testing tasks
- Faster feedback improved development quality
- Collaboration increased between testers and developers
- Release cycles became shorter and more frequent
Modern Software Testing Approach
- AI enhances test creation and maintenance
- Testing integrates with DevOps pipelines
- Performance and security testing gain importance
- User experience becomes a testing priority
- Testers evolve into quality engineers
This evolution shows how software testing transformed from simple bug detection into a critical business function. In 2026, embracing modern testing trends is essential for delivering reliable, secure, and high-quality software.
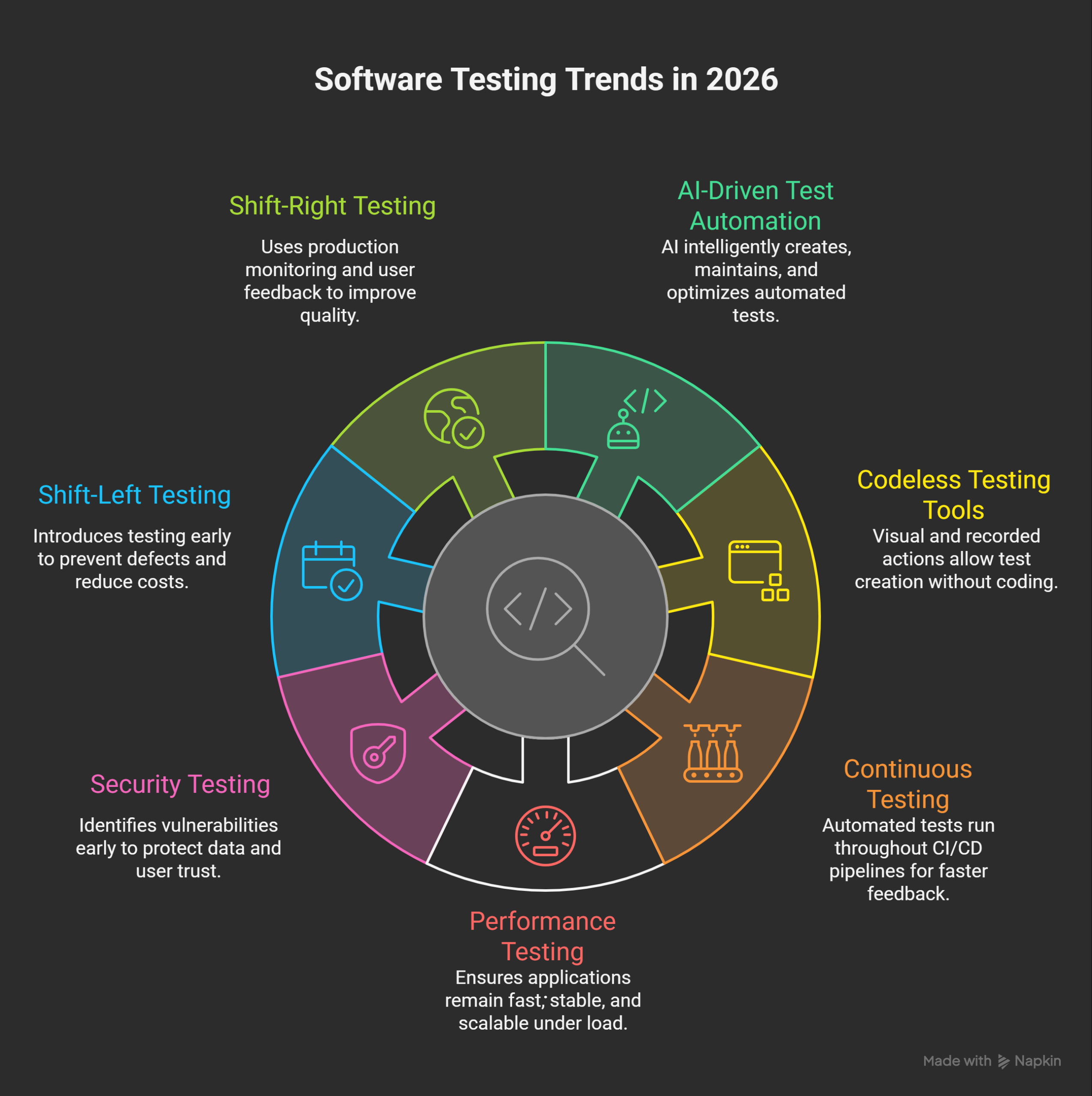
Key Trends in Software Testing for 2026
1: What is software testing?
Software testing is evolving faster than ever. Technology growth reshapes how applications are tested. Quality assurance now supports business success. Modern software demands speed and reliability. Testing ensures systems meet user expectations. New testing trends define quality standards in 2026.
Organizations release software more frequently today. Traditional testing approaches no longer scale. Automation and intelligence now guide testing strategies. Testing teams adapt to changing development models. Quality becomes everyone’s responsibility. These trends shape future testing careers.
AI-Driven Test Automation
AI-driven automation leads modern testing transformation. It replaces repetitive and time-consuming manual work. AI enhances accuracy and testing speed. Smart systems learn from application behavior. Automation becomes adaptive and predictive.
Understanding AI-Driven Test Automation
AI-driven testing uses machine learning algorithms. These algorithms analyze application data continuously. They learn from past test executions. AI predicts defect-prone areas early. Testing becomes proactive instead of reactive.
Traditional automation relies on static scripts. AI automation adapts scripts automatically. Self-healing tests reduce script failures. This improves automation stability. Maintenance effort reduces significantly.
How AI Enhances Test Creation
AI automatically generates test cases. It analyzes user flows and usage data. Critical paths receive higher testing priority. Edge cases are detected intelligently. Coverage improves without manual planning.
AI creates tests for different platforms. Mobile, web, and desktop testing improve. Cross-browser testing becomes easier. Visual testing accuracy increases. UI inconsistencies are detected faster.
AI-Based Test Maintenance
Script maintenance consumes significant testing time. AI solves this major automation challenge. It updates locators automatically. Broken scripts repair themselves intelligently. Maintenance cost reduces dramatically.
Testers focus on strategy instead of fixing scripts. Automation reliability increases long term. Execution failures decrease significantly. Test stability improves release confidence. Teams trust automation results more.
Benefits of AI-Driven Test Automation
- Faster test execution cycles
- Reduced manual intervention
- Improved defect prediction accuracy
- Lower automation maintenance effort
- Higher test coverage
AI Use Cases in Testing
- Regression testing optimization
- Test case prioritization
- Failure pattern recognition
- Visual UI testing
- Performance anomaly detection
AI Testing Tools Overview
| Tool Name | AI Capability | Primary Usage |
|---|---|---|
| Testim | Self-healing scripts | UI testing |
| Mabl | Intelligent automation | End-to-end testing |
| Applitools | Visual AI testing | UI validation |
| Functionize | Autonomous testing | Functional testing |
Codeless Testing Tools
Codeless testing removes coding complexity. Automation becomes accessible to non-programmers. Testing participation expands across teams.
Delivery speed improves significantly. Automation adoption increases organization-wide.
What Are Codeless Testing Tools
Codeless tools use visual interfaces. Users create tests through recordings. Actions convert into automated workflows. Logic builds using drag-and-drop options. No scripting knowledge is required.
Business users contribute to testing. Testers focus on validation logic. Developers reduce testing workload. Collaboration improves across teams. Quality responsibility spreads evenly.
Why Codeless Testing Is Growing
Software releases are more frequent now. Teams need faster testing solutions. Coding automation takes longer initially. Codeless tools reduce learning curves. Time-to-market improves significantly.
Organizations face skill shortages. Codeless tools fill testing gaps. Training costs reduce substantially. Automation scales faster across projects. Testing becomes more inclusive.
Advantages of Codeless Testing Tools
- No programming skills required
- Faster automation development
- Easy test maintenance
- Improved team collaboration
- Quick onboarding
Challenges of Codeless Testing
Codeless tools have limitations. Complex logic may require scripting. Tool dependency risks exist. Customization options can be limited. Scalability challenges may arise.
Large enterprise systems need flexibility. Hybrid automation approaches work better. Codeless tools support most scenarios. Advanced cases need technical expertise. Balanced usage delivers best results.
Popular Codeless Testing Tools
| Tool Name | Best Suited For | Strength |
|---|---|---|
| Katalon | Beginners | Easy setup |
| Leapwork | Enterprises | Visual workflows |
| TestProject | Teams | Free automation |
| Ranorex | Desktop apps | Stability |
Continuous Testing in DevOps
DevOps changes software delivery practices. Testing integrates throughout development pipelines. Quality checks occur continuously. Defects are detected early. Releases become faster and safer.
What Is Continuous Testing
Continuous testing runs automated tests constantly. Testing starts with code commits. Every build undergoes validation. Feedback reaches teams instantly. Issues resolve before deployment.
Testing continues after deployment. Monitoring validates system stability. User experience issues are identified. Quality assurance becomes continuous. DevOps success depends on testing.
Role of Testing in DevOps Pipelines
Testing integrates with CI/CD tools. Automated tests trigger during builds. Quality gates prevent faulty deployments. Failures stop pipelines automatically. Risk reduces significantly.
Developers and testers collaborate closely. Shared responsibility improves quality. Testing feedback guides development decisions. Automation ensures consistency. DevOps maturity improves steadily.
Benefits of Continuous Testing
- Faster delivery cycles
- Reduced production defects
- Early risk identification
- Improved collaboration
- Higher customer satisfaction
Testing Types Used in DevOps
- Unit testing
- Integration testing
- API testing
- Regression testing
- Smoke testing
DevOps Testing Tools
| Tool | Purpose | Usage |
|---|---|---|
| Jenkins | CI automation | High |
| Selenium | UI automation | Medium |
| JUnit | Unit testing | High |
| Postman | API testing | High |
Performance and Security Testing
Users expect fast and secure applications. Performance issues impact user retention. Security breaches damage brand trust. Testing protects systems and data. These tests are business-critical.
Performance Testing Trends
Performance testing evaluates application responsiveness. It measures speed under various conditions. Scalability testing ensures growth readiness. Cloud systems need dynamic performance validation. AI improves performance prediction accuracy.
Modern applications face unpredictable traffic. Load testing simulates real users. Stress testing identifies breaking points. Monitoring tracks live performance metrics. Optimization improves user satisfaction.
Types of Performance Testing
- Load testing
- Stress testing
- Spike testing
- Endurance testing
- Scalability testing
Security Testing Trends
Cyber threats increase every year. Security testing prevents data breaches. Automation strengthens security validation. Testing integrates into development pipelines. Compliance drives security investments.
Shift-left security testing gains popularity. Vulnerabilities are detected earlier. Continuous scans protect live systems. Security becomes proactive. Testing ensures regulatory compliance.
Types of Security Testing
- Vulnerability scanning
- Penetration testing
- Security auditing
- Risk assessment
- Compliance testing
Performance and Security Tools
| Tool | Testing Type | Usage |
|---|---|---|
| JMeter | Performance | Load testing |
| LoadRunner | Performance | Enterprise testing |
| OWASP ZAP | Security | Vulnerability scanning |
| Burp Suite | Security | Penetration testing |
Shift-Left and Shift-Right Testing
Testing spans the entire lifecycle. Shift strategies improve quality outcomes. Issues are detected early and late. Costs reduce across development stages. User satisfaction improves continuously.
Shift-Left Testing Explained
Shift-left testing starts early. Testing begins during requirement discussions. Developers write tests alongside code. Early detection reduces fixing costs. Feedback loops shorten significantly.
Unit testing gains importance. API testing starts earlier. Automation supports early validation. Defects reduce before integration. Quality improves from the start.
Benefits of Shift-Left Testing
- Early defect detection
- Reduced development costs
- Faster feedback cycles
- Better code quality
- Improved requirement clarity
Shift-Right Testing Explained
Shift-right testing happens post-deployment. Testing continues in production environments. Monitoring tools track user behavior. Live feedback improves releases. Real usage data guides improvements.
Observability becomes essential. A/B testing validates new features. Error tracking identifies hidden issues. Performance monitoring ensures stability. Testing never truly ends.
Benefits of Shift-Right Testing
- Real user insights
- Faster issue resolution
- Improved user experience
- Better reliability monitoring
- Continuous improvement
Shift-Left vs Shift-Right Comparison
| Aspect | Shift-Left | Shift-Right |
|---|---|---|
| Testing stage | Early development | Post-deployment |
| Focus | Prevention | Observation |
| Cost impact | Lower | Medium |
| Tools used | Unit tests | Monitoring tools |
Why These Trends Matter in 2026
Software complexity continues increasing. Users expect flawless digital experiences. Testing ensures business continuity. Automation enables faster innovation. AI enhances testing intelligence.
Codeless tools expand testing accessibility. DevOps requires continuous quality validation. Performance ensures application reliability. Security protects sensitive data. Shift strategies cover complete lifecycles.
Final Thoughts on Testing Trends
Software testing is no longer optional. It is a strategic business function. Trends shape modern quality assurance. Skills must evolve with technology. Learning these trends ensures relevance.
Organizations adopting these trends succeed faster. Quality becomes a competitive advantage. Testing careers grow with innovation. 2026 demands intelligent testing approaches. Future-ready testers embrace continuous learning.
Master Testing Skills with Industry Experts
Become a Test Engineer: Learn Core Skills from Industry-Leading Mentors and Land High-Paying Testing Jobs!
Explore ProgramSkills Testers Need in 2026
Software testing roles are rapidly changing. Testers must adapt to new technologies. Automation and AI redefine testing responsibilities. Manual testing alone is no longer enough. Modern testers act as quality engineers. Skill development ensures long-term career growth.
Testing now supports business goals directly. Testers collaborate with developers and stakeholders. They ensure faster and safer software delivery. Continuous learning becomes essential for success. The right skills create competitive advantage. 2026 demands versatile and future-ready testers.
Automation and Scripting Skills
Automation remains a core testing skill. Testers must understand automation frameworks. They design, execute, and maintain automated tests. Automation improves speed and accuracy. It supports frequent software releases.
Key Automation Skills Required
- Understanding automation concepts
- Writing reusable test scripts
- Handling test data efficiently
- Managing automation frameworks
- Debugging automation failures
Popular Automation Technologies
- Selenium for web automation
- Cypress for modern applications
- Playwright for cross-browser testing
- Appium for mobile testing
- TestNG or JUnit frameworks
Automation knowledge improves tester productivity. It reduces repetitive manual efforts. Testers focus on critical scenarios. Automation skills increase job opportunities. Most companies expect automation expertise.
AI and Machine Learning Awareness
AI influences modern testing approaches. Testers need basic AI understanding. They work with AI-driven testing tools. AI improves test accuracy and coverage. Awareness is more important than deep coding.
AI-Related Skills for Testers
- Understanding AI testing concepts
- Using AI-powered automation tools
- Interpreting AI-generated insights
- Managing self-healing test scripts
- Validating AI system outputs
Why AI Skills Matter
AI reduces script maintenance efforts. It improves defect prediction accuracy. Testing becomes predictive and intelligent. Testers make better decisions. AI skills future-proof testing careers.
DevOps and CI/CD Knowledge
DevOps reshapes software development workflows. Testing integrates into DevOps pipelines. Testers must understand CI/CD concepts. Automation runs during every build. Testing becomes continuous and collaborative.
Essential DevOps Skills
- Understanding CI/CD pipelines
- Integrating tests into pipelines
- Working with build tools
- Monitoring pipeline failures
- Collaborating with DevOps teams
Common DevOps Tools
| Tool | Purpose | Skill Level |
|---|---|---|
| Jenkins | CI automation | Basic |
| Git | Version control | Mandatory |
| Docker | Container testing | Intermediate |
| GitHub Actions | Pipeline automation | Basic |
DevOps knowledge improves testing efficiency. It reduces deployment risks. Testers contribute earlier to development. Collaboration improves across teams. DevOps skills are highly valued.
API and Backend Testing Skills
Modern applications rely on APIs. Frontend testing alone is insufficient. Testers must validate backend systems. API testing ensures data accuracy. It improves system reliability.
API Testing Skills Required
- Understanding REST and HTTP methods
- Validating request and response data
- Testing authentication mechanisms
- Handling status codes
- Automating API test cases
Popular API Testing Tools
- Postman for manual testing
- Rest Assured for automation
- SoapUI for web services
- Swagger for API understanding
API skills enhance testing depth. They catch defects earlier. Backend issues are costly. API testing prevents system failures. Most companies expect API knowledge.
Performance and Security Testing Basics
Quality includes performance and security. Testers must understand basic concepts. They ensure applications handle real users. They protect systems from vulnerabilities. These skills support business trust.
Performance Testing Skills
- Understanding load concepts
- Identifying bottlenecks
- Interpreting performance metrics
- Running basic load tests
Security Testing Awareness
- Understanding common vulnerabilities
- Using security scanning tools
- Supporting compliance testing
- Reporting security risks
Performance and Security Tools
| Tool | Testing Area | Usage |
|---|---|---|
| JMeter | Performance | Load testing |
| LoadRunner | Performance | Enterprise |
| OWASP ZAP | Security | Vulnerability scanning |
These skills improve tester value. They expand testing responsibilities. Organizations prefer multi-skilled testers. Performance and security knowledge boosts credibility. Basic skills are often sufficient.
Soft Skills and Analytical Thinking
Technical skills alone are insufficient. Soft skills define testing effectiveness. Testers must communicate clearly. They analyze problems critically. Decision-making skills matter.
Important Soft Skills
- Clear communication
- Attention to detail
- Logical thinking
- Collaboration skills
- Adaptability
Testers explain defects clearly. They work closely with developers. They support product improvements. Analytical thinking improves test coverage. Soft skills enhance leadership potential.
Summary of Essential Skills
| Skill Category | Importance Level |
|---|---|
| Automation | Critical |
| AI Awareness | High |
| DevOps | High |
| API Testing | Mandatory |
| Performance Basics | Medium |
| Security Awareness | Medium |
| Soft Skills | Essential |
In Short
Software testing roles evolve continuously. Testers must upgrade skills regularly. Automation and AI dominate future testing. DevOps knowledge ensures collaboration. API testing strengthens system reliability.
Performance and security skills add value. Soft skills improve career growth. Learning never stops for testers. Skilled testers remain industry relevant. 2026 rewards adaptable quality professionals.
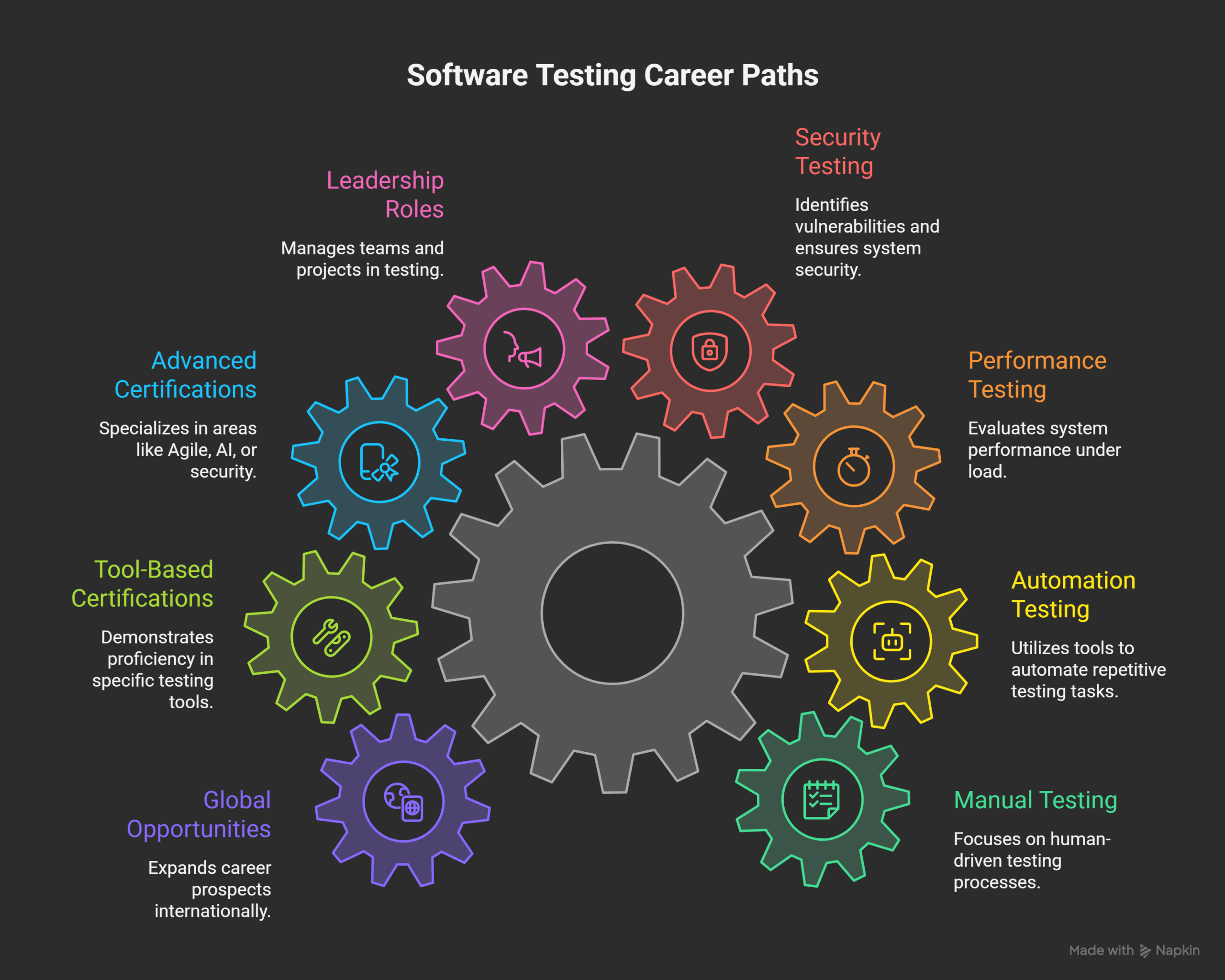
Career Growth and Certifications in Software Testing
Software testing offers strong career growth opportunities. Demand for skilled testers continues increasing. Modern testing roles are diverse and specialized. Automation and AI create new career paths. Continuous learning drives long-term success.
Testing careers no longer remain entry-level only. Professionals move into leadership and specialist roles. Career progression depends on skills and certifications. Certified testers gain industry recognition. Certifications improve credibility and confidence.
Career Paths in Software Testing
Software testing provides multiple career directions. Testers can choose technical or managerial paths. Specialization improves career stability. Growth depends on interests and strengths. Each role requires specific skill sets.
Common Testing Career Roles
- Manual Test Engineer
- Automation Test Engineer
- Performance Test Engineer
- Security Test Engineer
- Quality Analyst
Advanced Career Roles
- Senior Test Engineer
- Test Lead
- QA Manager
- Automation Architect
- Quality Consultant
Career growth is not linear. Professionals can switch paths. Upskilling enables role transitions. Experience increases responsibility levels. Leadership roles require strong communication skills.
Automation and AI Career Opportunities
Automation skills unlock higher-paying roles. AI testing creates new job titles. Organizations need intelligent testing specialists. Automation engineers are in high demand. AI expertise boosts career differentiation.
Automation-Focused Roles
- Automation Engineer
- Test Automation Lead
- SDET professional
- Framework Architect
AI-Related Testing Roles
- AI Test Specialist
- Test Data Analyst
- Intelligent Automation Engineer
These roles require continuous learning. Hands-on experience matters most. Tool knowledge improves employability. AI roles grow rapidly. Future testing careers depend on automation.
Importance of Certifications
Certifications validate testing knowledge. They demonstrate professional commitment. Employers trust certified professionals. Certifications improve job prospects. They support career transitions.
Certified testers stand out in interviews. They understand industry best practices. Learning becomes structured and focused. Certifications boost confidence levels. Global recognition increases opportunities.
Popular Software Testing Certifications
Foundational Certifications
- ISTQB Foundation Level
- CSTE certification
- Software Testing Fundamentals
Advanced and Specialized Certifications
- ISTQB Advanced Level
- ISTQB Agile Tester
- ISTQB AI Testing
- Performance Testing certifications
- Security Testing certifications
Automation Tool Certifications
- Selenium certification
- Cypress certification
- Playwright certification
- Appium certification
Certification Benefits by Career Stage
| Career Stage | Recommended Certifications |
|---|---|
| Beginner | ISTQB Foundation |
| Intermediate | Automation tools |
| Advanced | ISTQB Advanced |
| Specialist | Performance or Security |
| Leadership | Agile and Management |
Certifications align with career goals. Choosing the right certification matters. Practical experience should complement certifications. Learning never replaces hands-on practice. Balance theory and real projects.
Salary Growth and Career Advancement
Certified testers often earn higher salaries. Automation roles offer better compensation. Specialized skills increase earning potential. Leadership roles provide stable growth. Global opportunities expand career scope.
Experience plays a major role. Certifications accelerate promotions. Skill diversity improves job security. Continuous upskilling prevents stagnation. Career growth depends on adaptability.
Future Outlook for Testing Careers
Software testing remains a stable career. Technology evolution creates new opportunities. AI and DevOps increase testing importance. Quality assurance becomes business-critical. Testing professionals gain strategic roles.
Future testers act as quality leaders. Certifications support lifelong learning. Career growth favors adaptable professionals. Learning trends ensures long-term relevance. Testing careers thrive beyond 2026.
Take the Next Step with the Right Learning Path
Software testing careers grow with the right guidance. Learning from structured platforms saves time. Industry-aligned courses build practical confidence. The right course connects skills with real jobs. Smart learners choose trusted learning partners.
Why a Guided Learning Platform Matters
Self-learning often lacks clear direction. Expert-designed courses simplify complex topics. Hands-on practice improves real-world readiness. Mentor support helps overcome learning blocks. Career support adds long-term value.
How Entri Supports Future Testers
Entri offers industry-focused software testing training. The course covers manual and automation testing. Modern tools and real projects are included. Learning stays aligned with industry needs. The approach suits beginners and upskillers.
Learning Benefits You Can Expect
- Clear fundamentals and strong foundations
- Exposure to popular testing tools
- Practical assignments for skill confidence
- Guidance from experienced trainers
- Career-oriented learning structure
Move Forward with Confidence
Choosing the right course matters. Small decisions shape long-term careers. Explore Entri’s software testing course thoughtfully. Build skills steadily and confidently. Start preparing for testing roles in 2026.
Conclusion
Software testing continues evolving with technology and business needs. Automation and AI now drive modern quality practices. Codeless tools expand testing access across teams. DevOps enables continuous and reliable testing workflows. Performance and security ensure user trust and stability. Shift testing strategies improve quality throughout lifecycles.
Future testers must learn adaptable and in-demand skills. Career growth depends on continuous learning and certifications. The right training builds confidence and practical expertise. Structured learning supports long-term success. Modern testing creates strong career opportunities. Prepared testers lead quality in 2026.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the most important software testing trends in 2026?
The most important software testing trends in 2026 include AI-driven test automation, codeless testing tools, continuous testing in DevOps, performance and security testing, and shift-left and shift-right testing. These trends focus on faster releases, better quality, and smarter testing processes. They help organizations manage complex applications and frequent deployments efficiently.
How does AI-driven test automation improve software testing?
AI-driven test automation improves testing by automatically creating, updating, and maintaining test cases. It uses machine learning to detect patterns, predict defect-prone areas, and reduce script failures through self-healing mechanisms. This significantly lowers maintenance effort and improves test accuracy and speed.
Are codeless testing tools suitable for beginners?
Yes, codeless testing tools are highly suitable for beginners and non-technical users. They allow users to create automated tests using visual interfaces, recordings, and drag-and-drop actions instead of coding. This reduces the learning curve and helps teams adopt automation faster.
Why is continuous testing important in DevOps environments?
Continuous testing is essential in DevOps because it ensures quality checks at every stage of development and deployment. Automated tests run with each code change, providing instant feedback to developers. This helps detect defects early, reduce production risks, and support faster, more reliable releases.
What role do performance and security testing play in modern applications?
Performance testing ensures applications remain fast, stable, and scalable under real user loads. Security testing protects applications from vulnerabilities, data breaches, and compliance risks. Together, they help maintain user trust and safeguard business reputation in competitive digital markets.
What is the difference between shift-left and shift-right testing?
Shift-left testing focuses on testing early in the development lifecycle to prevent defects. Shift-right testing focuses on testing after deployment using monitoring, analytics, and real user feedback. Together, they ensure quality across the entire application lifecycle.
What skills should software testers focus on for career growth in 2026?
Testers should focus on automation, AI awareness, API testing, DevOps and CI/CD knowledge, performance and security basics, and strong analytical skills. Soft skills like communication and collaboration are also important. These skills help testers stay relevant and competitive.
Are certifications necessary for a software testing career?
Certifications are not mandatory, but they greatly improve career prospects. They validate knowledge, demonstrate commitment, and help candidates stand out in interviews. Certifications like ISTQB, automation tool certifications, and AI or Agile testing certifications are especially valuable.
Can freshers start a career in software testing in 2026?
Yes, software testing remains an excellent entry point for freshers. With proper training in manual testing, automation basics, and modern tools, beginners can build strong careers. Structured courses and practical projects help freshers gain job-ready skills.
How can a software testing course help professionals adapt to future trends?
A well-designed software testing course provides structured learning, hands-on experience, and exposure to modern tools and practices. It helps learners understand industry expectations, build confidence, and transition into advanced roles. Courses like Entri’s software testing program offer guided learning aligned with current industry needs.