Table of Contents
Knowing how to ask questions is an important part of language proficiency. Whether you are trying to navigate through your daily life situations or start a conversation, asking questions is essential. Mastering W Fragen questions in German will boost your confidence and aid you in engaging with native speakers. In this blog, we will discuss everything you need to know about forming and using W-question words in German.
Join the Entri Elevate German proficiency course! Ace your Goethe certificate A1 level exam!
W Fragen Questions in German: Introduction
W-Fragewörter are “w” question words or w words. The questions made using such words are known as W-Fragen, i.e., W questions. You cannot have effective communication if you don’t know how to ask questions. And how can you ask questions without having vocabulary suitable for the said action?
This is why W-Fragen questions are crucial for mastering the German language. Daily conversations are not possible without knowing W-Fragen.
Preparing for the Goethe C2 level certification exam? Join the Entri German Language course now!
German Sentence Structure for Questions
1: How do you say "Good Morning" in German?
In a W-Fragen or W-question, the interrogative element in the sentence is followed by the verb. But in a question lacking an interrogative element, the verb takes the initial position in the sentence. The elementary structure of a sentence in German is subject + verb + object. But one of the qualities of German language syntax is that it is flexible. In dative and genitive cases, you can start the sentence with an objective. Native German speakers do this so that they can emphasize different parts of the sentence. But in the nominative case, the verb will stay in the second position irrespective of whether you start the sentence with a subject or not. The application of all these rules is pretty consistent, even when you are forming a question with a W question word.
Learn W Fragen from a local language-speaking mentor! Join Entri Elevate now!
Free German A1 Mock Tests – Powered by AI!
Test your skills on our interactive platform. Get instant feedback from our AI to help you communicate better and track your progress. Start your free German mock test now.
Test Your German A1 for FreeW Questions Vs Yes or No Questions
There are two types of questions in the German language. The first type of question has an interrogative element. They are called W-Fragen. This is because all German interrogative pronouns and adverbs start with the letter w. The second type of question in German doesn’t start with an interrogative pronoun or adverb. They are known as Ja-Nein Fragen or yes or no questions. This is because the answers to these questions can be given by a simple yes or no.
What Are W-Fragen?
W-Fragen are the questions in the German language that start with W-Fragewörter, i.e., W-question words. W-Fragen are used to ask open-ended questions. These questions ask for more information rather than just a yes or a no. Just like in English, the question words go to position one, and the second position is occupied by the conjugated verb.
|
Goethe 2025 Exam Dates: Multiple Centers |
|
| Trivandrum Goethe Exam Dates | Kochi Goethe Exam Dates |
| Chennai Goethe Exam Dates | Coimbatore Goethe Exam Dates |
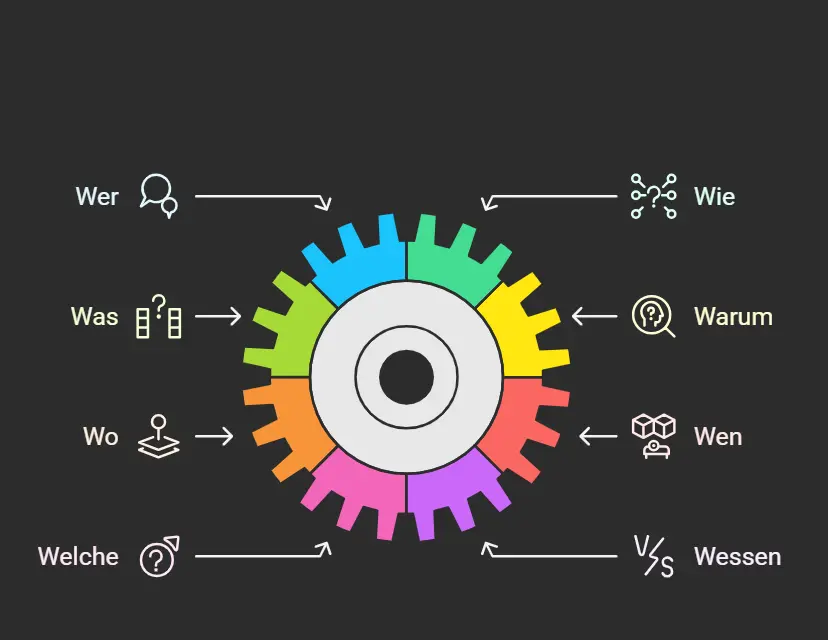
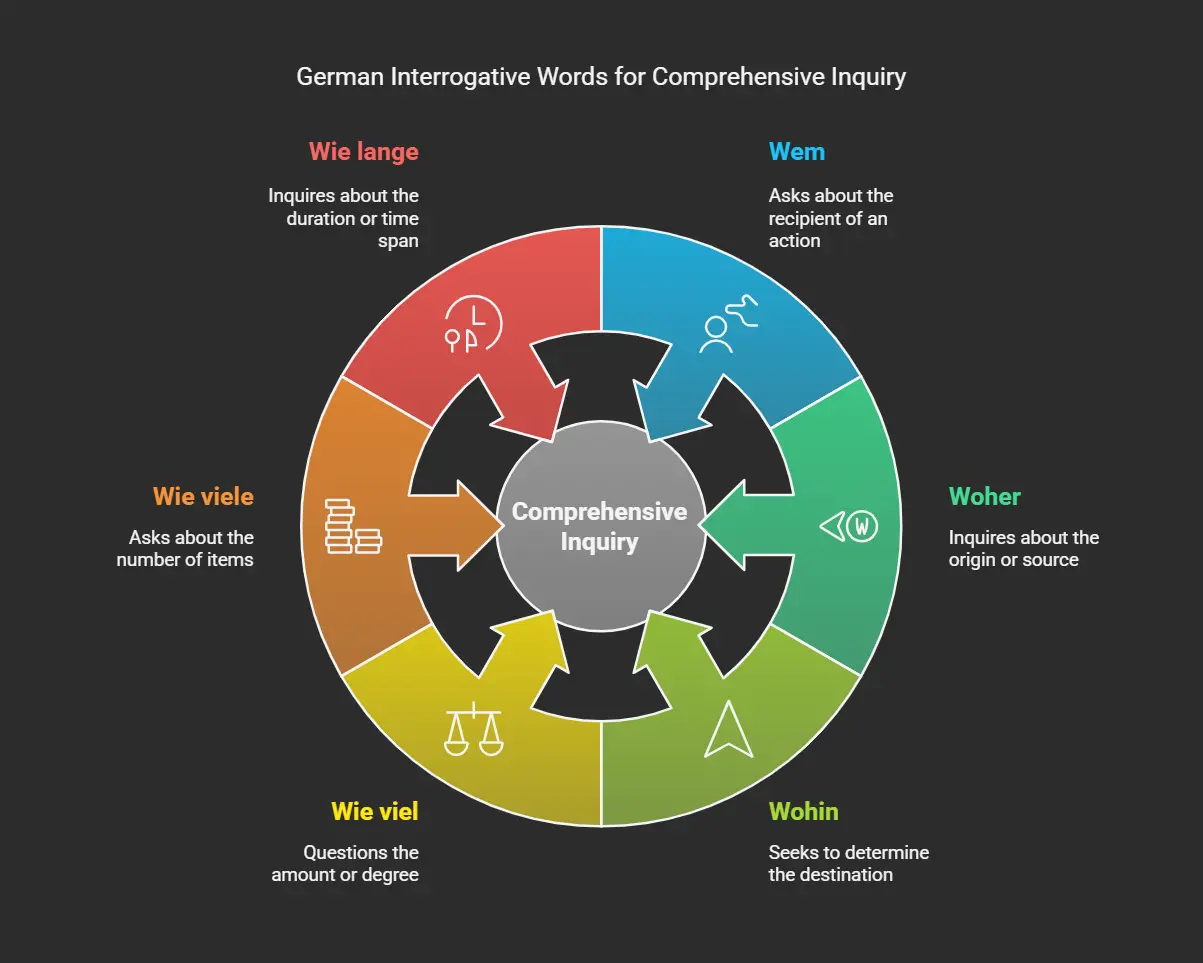
Wh Question Words in German
Have you already learned all the W-Fragewörter or question words in German? If not, a list of W-Fragewörter is given below for reference.
| English | German |
| how | wie |
| who | wer |
| what | was |
| where | wo |
| why | warum / weshalb / wieso |
| from where | woher |
| how long | wie lange |
| to where | wohin |
| whom | wen |
| which | welche |
| to whom | wem |
| how much / how many | wie viel / wie viele |
| whose | wessen |
Free German A1 Mock Tests – Powered by AI!
Test your skills on our interactive platform. Get instant feedback from our AI to help you communicate better and track your progress. Start your free German mock test now.
Test Your German A1 for FreeGrammar Rules for W-Fragen
General rules that one needs to follow while using W-Fragen questions in German are given below. Some of them are already discussed above. Nevertheless, the list here is more organized and helps you to understand the concept more easily. So, here we go.
- W Fragen follows the structure W-Word + conjugated form of Verb + Subject + (Other Elements).
- The W-word comes at the beginning of the question.
- The conjugated verb directly follows the W-word. This is in accordance with the verb-second word order rule for questions.
- In case prepositions are required, they will come first, i.e., before the W-word.
- “Welch-” should be followed by a noun as it functions like an adjective. The verb should only come after that.
Now you are familiar with the whole set of rules you have to follow while dealing with W Fragen questions in German. Learn these rules so that you will not make mistakes in the upcoming W Fragen questions exercise.
Tips for Using W-Fragen
Some tips that will help you use W Fragen are discussed below.
- Start simple. First, learn to use simple W-Fragewörter or w-words before moving to complex words and cases.
- Make sure the W-Fragewörter you are using is the correct one needed in the context. For example, if you are asking about time, then you must use “wann.” But if you are asking for a reason or explanation for something, then you have to use “warum.”
- You have to practice the verb placement. The verbs always come just after the w word.
- Don’t hesitate to combine these questions with prepositions if you find it necessary.
Some tips for practicing W Fragen questions too are discussed here.
- Try roleplaying. You have to practice forming questions that can be used in everyday real-life situations. This could be asking for directions or asking for a particular document that you need at work.
- Expand the vocabulary needed for asking questions.
- Watch German media and imitate how the native speakers are using these words.
- Find creative ways to ask a question by experimenting with newly learned words.
Get the best mentors to teach you for your C2 level German proficiency exam! Join now!
Basic Wh Questions in German
Some basic W Fragen questions in German are discussed here. We will provide numerous examples of such questions for several words we have discussed before.
Wo (Where)
Some sentences using “wo” and their English meaning are discussed here.
| English | German |
| Where do you live? | Wo wohnen Sie? |
| Where is Lukas? | Wo ist Lukas? |
| Where is my laptop? | Wo ist mein Laptop? |
| Where is Berlin? | Wo ist Berlin? |
| Where do they live? | Wo wohnen sie? |
| Where do you work? | Wo arbeiten Sie? |
| Where is your school? | Wo ist deine Schule? |
| Where is the university? | Wo ist die Universität? |
| Where is the train station? | Wo ist der Bahnhof? |
| Where should I look for you? | Wo soll ich dich suchen? |
| Where should I place the pen? | Wo muss ich den Kuli liegen? |
| Where can I wait? | Wo kann ich warten? |
Woher (From Where)
Some sentences using “woher” and their English meaning are discussed here.
| English | German |
| From where do you come? | Wohere kommen Sie? (polite) |
| From where do you come? | Woher kommst du? (familiar) |
| Where are these students from? | Woher kommen diese Studenten? |
| From where do you learn German? | Woher lernen Sie Deutsch? |
| Where is your wife from? | Woher kommt deine Frau? (familiar) |
| Where is your wife from? | Woher kommt Ihre Frau? (polite) |
Wer (Who)
Some sentences using “wer” and their English meaning are discussed here.
| English | German |
| Who are you? | Wer sind Sie? |
| Who is your brother? | Wer ist dein Bruder? |
| Who is your sister? | Wer ist deine Schwester? |
| Who are you? | Wer bist du? |
| Who is looking for me? | Wer sucht mich? |
| Who always eats my bread? | Wer isst mein Brot immer? |
| Who is standing there? | Wer steht da? |
| Who should come tomorrow? | Wer soll morgen kommen? |
| Who else has to eat? | Wer muss noch essen? |
Wann (When)
Some sentences using “wann” and their English meaning are discussed here.
| English | German |
| When do you go? | Wann gehen Sie? |
| When do you come? | Wann kommen Sie? |
| When is the October fest? | Wann ist das Oktoberfest? |
| When are you going to Berlin? | Wann fahren Sie nach Berlin? |
| When are you travelling back? | Wann fahren Sie zurück? |
Wohin (Where to)
Some sentences using “wohin” and their English meaning are discussed here.
| English | German |
| Where does this train go? | Wohin fährt dieser Bahn? |
| Where are you going? | Wohin läufst du? |
| Where are you running? | Wohin rennst du? |
| Where are you going today? | Wohin gehst du heute? |
| Where do you have to go today? | Wohin musst du heute gehen? |
| Where should I go today? | Wohin soll ich heute fahren? |
Wen (Whom)
Some sentences using “wen” and their English meaning are discussed here.
| English | German |
| Whom are you asking? | Wen fragen Sie? |
| Whom are you searching for? | Wen suchst du? |
| Whom should I ask? | Wen soll ich fragen? |
| Whom do you want to see? | Wen willst du sehen? |
| Whom he wants to look for? | Wen will er suchen? |
| Whom does he see? | Wen sieht er? |
| Whom are you chasing? | Wen jagen Sie? |
| Whom do you love? | Wen liebst du? |
Wie (How)
Some sentences using “wie” and their meaning are discussed here.
| English | German |
| How are you called? | Wie heißen Sie? |
| How is the weather? | Wie ist das Wetter? |
| How are you? | Wie geht es? |
| How do you travel to Berlin? | Wie fährst du nach Berlin? |
| How much money do you need? | Wie viel Geld brauchen Sie? |
| How many cars do you have? | Wie viele Autos haben Sie? |
| How long do you stay in Berlin? | Wie lange bleiben Sie in Berlin? |
| How old are you? | Wie alt sind Sie? |
| How should I write your name? | Wie soll ich Ihr Name schreiben? |
| How do you want to travel to Berlin? | Wie willst du nach Berlin fahren? |
| How do you want to do that? | Wie willst du das machen? |
The word “wie” is also used to ask a person’s name. Some examples are given below.
| English | German |
| What is your name? | Wie heißen Sie? |
| What is your name? | Wie ist Ihr Name? |
Warum or Wieso (Why)
Some sentences using “warum or Wieso ” and their English meaning are discussed here.
| English | German |
| Why do you learn German? | Warum lernen Sie Deutsch? |
| Why do you cook? | Warum kochen Sie? |
| Why is he not working today? | Wieso arbeitet er nicht heute? |
| Why are you coming so late? | Warum kommst du zu spät? |
| Why are you asking? | Warum fragst du? |
| Why do you ask so many questions? | Warum stellst du so viele Fragen? |
| Why should I come tomorrow? | Warum soll ich morgen kommen? |
| Why do I have to answer all the questions? | Warum muss ich alle Fragen antworten? |
| Why should only he come tonight? | Warum soll nur er heute Nacht kommen? |
Was (What)
Some sentences using “was” and their English meaning are discussed here.
| English | German |
| What do you see? | Was sehen Sie? |
| What is this? | Was ist das? |
| What are you doing here? | Was machen Sie hier? |
| What do you eat? | Was essen Sie? |
| What is there? | Was steht dort? |
| What are you looking for? | Was suchen Sie? |
| What is she drinking? | Was trinkt sie? |
| What is there? | Was liegt dort? |
| What do I have to place there? | Was muss ich dort liegen? |
| What does this mean? | Was soll das heißen? |
| What is your brother eating? | Was isst dein Bruder? |
| What does he want to drink? | Was will er trinken? |
| What do you want to eat? | Was sollen wir jetzt machen? |
Welcher (Which)
Some sentences using “welcher” and their English meaning are discussed here.
| English | German |
| Which car do you have? | Welches Auto haben Sie? |
| Which cars do you have? | Welche Autos haben Sie? |
| Which house is yours? | Welches Haus ist dein? |
Join the Entri German course to attend the best German language mock tests and assessments!
Practice W Fragen German Exercises
Some practice exercises to learn W Fragen questions in German are given below. Answer them and look at the solutions to find the scores and hence find out the level of understanding you have on the subject.
W Fragen Questions and Answers Set 1
Let us solve the first set of w fragen questions in German.
- ____ kosten die Karten?
- Was
- Wie viel
- Wan
- Wer
- ____ bedeutet dieser Satz?
- Was
- Wie viel
- Wan
- Wer
- ____ haben wir Urlaub?
- Was
- Wie viel
- Wan
- Wer
- ____ ist Angelina Jolie?
- Was
- Wie viel
- Wan
- Wer
- ____ lebt Marta?
- Wo
- Wei oft
- Wie lange
- Woher
- ____ rennen Sie?
- Wo
- Wei oft
- Wie lange
- Woher
- ____ ist das Spiel?
- Wo
- Wei oft
- Wie lange
- Woher
- _____ kommen ihr?
- Wo
- Wei oft
- Wie lange
- Woher
- _____ist sein Lieblingsfilm?
- Wie lange
- Woher
- Was
- Wo
- ______studierst du Englisch?
- Wie lange
- Woher
- Was
- Wo
Answers
- Wie viel
- Was
- Wan
- Wer
- Wo
- Wei oft
- Wie lange
- Woher
- Was
- wo
W Fragen Questions and Answers Set 2
Now let us see the second set of W fragen questions in German. Try finding answers without options or solutions.
- ____ weinen Sie?
- ____ arbeitet er?
- _________ hast du dieses Buch gekauft?
- ____ kostet das rote Kleid?
- _________ hast du gestern getroffen?
- ____ spielt dein Team?
- ____ lange schläft ein Baby pro Tag?
- _________ fährt der nächste Zug nach Berlin?
- _________ möchtest du heute essen?
- ____ fährt Marin im nächsten Monat?
How many answers were you able to find? Was your level of German proficiency more or less than what you expected? Do you think you need a mentor to help you with the learning process? Are you thinking about joining an online course to supplement your German learning? Entri Elevate is now offering a German language proficiency course that will make your language learning journey smooth sailing.
The features provided by the Entri Elevate German language proficiency course are listed below. Read through it and decide if it fits all the language learning needs you have.
- Demo classes
- Online mode
- 8 months duration
- A1 to C2 level training
- Live interactive sessions
- Recorded classes
- Course blueprint
- Assessment
- Course Blueprint
- To-Do Assignments
- PDF Notes
- Mock test
- Mentor with local language knowledge
Does this check all the boxes for you? Then register for the Entri Elevate German course today!
Click here to register for the Entri German language proficiency course! Join now!
W Fragen German A1 Exercises
Here are 20 W Fragen German exercises for you to practice ahead of your A1 exam:
Match the following
Match the following questions in Column A with the correct answers in Column B.
| Column A (Questions) | Column B (Answers) |
|---|---|
| 1. Wie heißt du? | A. Am Montag. |
| 2. Wo wohnst du? | B. Weil ich müde bin. |
| 3. Was machst du gern? | C. Ich komme aus Spanien. |
| 4. Wann ist der Termin? | D. Ich trinke Wasser. |
| 5. Warum bist du zu spät? | E. Ich bin Anna. |
| 6. Was trinkst du? | F. Ich wohne in München. |
| 7. Woher kommst du? | G. Am Bahnhof. |
| 8. Wie alt bist du? | H. Ich lese gern. |
| 9. Wo ist der Bus? | I. Ich bin 25 Jahre alt. |
| 10. Wie geht es dir? | J. Mir geht es gut, danke. |
Answer Key:
1-E, 2-F, 3-H, 4-A, 5-B, 6-D, 7-C, 8-I, 9-G, 10-J
Fill in the Blanks
Fill in the blank with the appropriate W-frage
-
______ heißt du? → (Name)
-
______ wohnst du? → (Place)
-
______ machst du gern? → (Hobby)
-
______ ist das? → (Object)
-
______ ist dein Lehrer? → (Person)
-
______ alt bist du? → (Age)
-
______ kommt der Bus? → (Time)
-
______ ist der Bahnhof? → (Location)
-
______ gehst du ins Kino? → (Reason)
-
______ geht es dir? → (Well-being)
Answer Key:
-
Wie
-
Wo
-
Was
-
Was
-
Wer
-
Wie
-
Wann
-
Wo
-
Warum
-
Wie
W Fragen Questions in German: Conclusion
Sometimes a yes or no is not a good enough answer for an inquiry. You need more information. This is why W Fragen questions in German are important. They are essential everywhere. From asking for the location of a grocery section in a supermarket to asking about caring methods for your sick child to a doctor, these words are essential. How is someone to go about their life without being able to ask questions? So, it is essential to learn and practise W-Fragen regularly.
There are so many rules and tips that will help you understand and use W fragen questions in German more easily. Almost all of that is covered in this blog. Some exceptions are also discussed in the FAQ section. However, learning from an experienced mentor beats all other forms of learning. Enrol in the Entri Elevate German course to start practising W-Fragen today! Improve your German language proficiency faster! Prepare for your upcoming language proficiency exams and migration dreams.
|
Related Blogs |
|
5 Common Mistakes with German Possessive Pronouns and How to Avoid Them |
Free German A1 Mock Tests – Powered by AI!
Test your skills on our interactive platform. Get instant feedback from our AI to help you communicate better and track your progress. Start your free German mock test now.
Test Your German A1 for FreeFrequently Asked Questions
Explain the case in which “wer” is used as “whoever”?
In some cases “wer” is used as “whoever”. An example sentence and its meaning are given below.
| English | German |
| Whoever doesn’t ask stays dumb. | Wer nicht fragt bleibt dumm. |
Explain the case of using the word “was” in the meaning of “something”
Sometimes the word “was” is sued to convey the meaning “something”. In such cases, the initial position is taken by the verb. It is then followed by a pronoun or noun as a second element. If there is some place or time reference in case of such a question, they are placed at the end of the sentence. Some examples of questions framed in such cases are given in the table below.
| English | German |
| Are you doing something? | Machen Sie was? |
| Are you doing something here? | Machen Sie was hier? |
| Are you doing something important? | Machen Sie was wichtig |
The word “was” in the lines above is a contraction of the German word “etwas,” which also means “something.”
What is the difference between liegen and stehen?
The question will be asked using the verb “liegen” if something is lying on a horizontal surface. The question will be asked using the verb “stehen” if something is in an upstanding (vertical) position.
How do question words in sentences with verb-preposition combinations work?
Many German verbs need a preposition. When they occur in a question the preposition stays with the question word. But there are some rules when it comes to these sentences. They are:
- If the said preposition is referring to a thing, then use wo- + preposition. For example, Worüber, Woran, Wofür etc.
- If the said preposition is referring to a person, then use präposition + wen/wem. For example, Über wen, An wen, Für wen etc.
Some examples of the sentences of the above type are given below.
| English | German |
| What are you laughing about? | Worüber lachst du? |
| Who are you laughing about? | Über wen lachst du? |
Do we use question words as Nebensätze?
Yes. Question words are often used as Nebensätze i.e. Subordinate Conjunctions. Question words are used as Subordinate Conjunctions in indirect questions. In such cases, the verb moves to the end of the clause.
Eg: Kannst du mir sagen, was du machst?
What happens to question words as the case of the sentence changes?
Only the words Wer and welcher vary according to the case. Other question words, such as was and warum, stay the same.
Why do we put an object before a verb while using "Welch”?
Since “welch-” (which) is a determiner, it always requires a noun (object). It cannot stand alone and works similarly to an adjective. The formula for a sentence in this case is Welch- + Noun + Verb (2nd position) + Subject + Other Elements.
Eg: Welches Buch liest du?
What is the structure of forming questions in German?
The word order formula for w fragen in German is Question Word + Conjugated Verb + Subject + Other Elements.
How to use w fragen in German?
W-Fragen in German start with a question word like Wer (who), Was (what), or Wo (where), followed by the verb and then the subject. This structure forms open-ended questions such as Was machst du (What are you doing). Learning W-Fragen is essential for everyday conversations and clear communication in German.
What is the format of the W Frage question?
W-Fragen (W-questions) in German follow this structure: W-word + verb + subject + other elements. The question word (e.g., wer, was, wann) always comes first, followed by the conjugated verb, then the subject, and finally any additional information.