Table of Contents
Childhood development can be magical, with leaps in physical movement, coordination, independence, and discovery. Among the most important blocks for this growth are fine motor and gross motor skills. These skills lay the foundation for lifelong competence, confidence, and creativity.
In this guide, find out the science behind fine and gross motor development, learn the milestones, activities for skill building, and see how Entri’s Montessori course provides a hands-on environment for these basic skills.
Key Takeaways:
- Fine motor skills are small muscle movements, typically in the hands and fingers.
- Gross motor skills include larger muscle groups and are important for activities requiring balance, coordination, and movement.
- The Montessori method promotes fine and gross motor development with hands-on work, practical life exercises, and movement-integrated learning.
- Taking an Entri Montessori course enables teachers to foster and cultivate these motor skills in a Montessori environment.
What Are Fine Motor Skills?
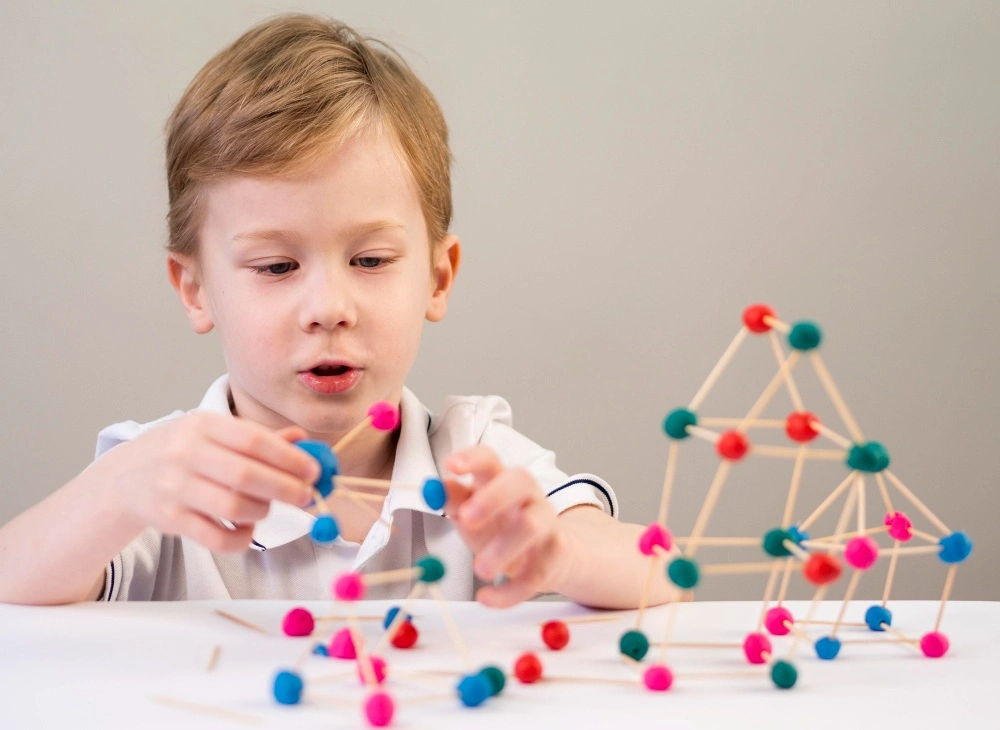
Fine motor skills involve the use of small muscle groups, such as those in the hands and fingers. These are the type of skills that we rely on for a lot of our daily activities – writing, scissors cutting, buttoning, and using utensils to eat. In other words, fine motor skills are all about hand-eye coordination.
Prime Examples of Fine Motor Skills
- Writing and drawing
- Picking up small objects (i.e., beads or blocks)
- Buttoning, zipping, and tying shoelaces
- Using scissors to cut paper
- Feeding ourselves with a spoon or fork
As for fine motor skills, Montessori trains them via engaging, tactile activities that prompt kids to handle different objects and tools. They’re all cleverly crafted to improve a child’s coordination, focus, and accuracy, all while encouraging autonomy.
How Montessori Supports Fine Motor Growth
Practical Life Activities:
Montessori classrooms abound with fine motor practical life activities. Kids can pretend to be a barista and practice pouring, scooping, buttoning and tying. These types of activities improve hand-eye coordination and support children in feeling competent and autonomous.
Sensorial Materials:
Montessori materials such as the pink tower, the color tablets, and the sandpaper letters all develop fine motor skills through manipulation of these small objects, whilst engaging children in lessons on size, color, and texture.
Art and Craft:
Creative use of hands through drawing, painting, and playing with clay promotes fine motor control in children. They also serve as a support for writing and for using tools, helping both with precision and with gripping.
Unlock your passion for education and shape young minds as a Montessori teacher!
What Are Gross Motor Skills?
1: What is the primary focus of the first plane of development in the Montessori method?
Conversely, gross motor skills engage larger muscle groups, especially in the arms, legs, and torso. They are needed for activities involving balance, coordination, and full-body movements. Gross motor skills are the bedrock of physical development and enable a child to engage confidently with their world.
Key gross motor skill examples:
- Running, jumping, and skipping
- Climbing stairs or playground equipment
- Walking and balancing
- Throwing and catching a ball
- Pedaling a bicycle or tricycle
In the Montessori classroom, gross motor skills are just as important as fine motor, and traditions provide all-day opportunities to practice. Montessori teachers incorporate movement-based learning and physical activities into their classrooms to nurture a child’s physical development and health.
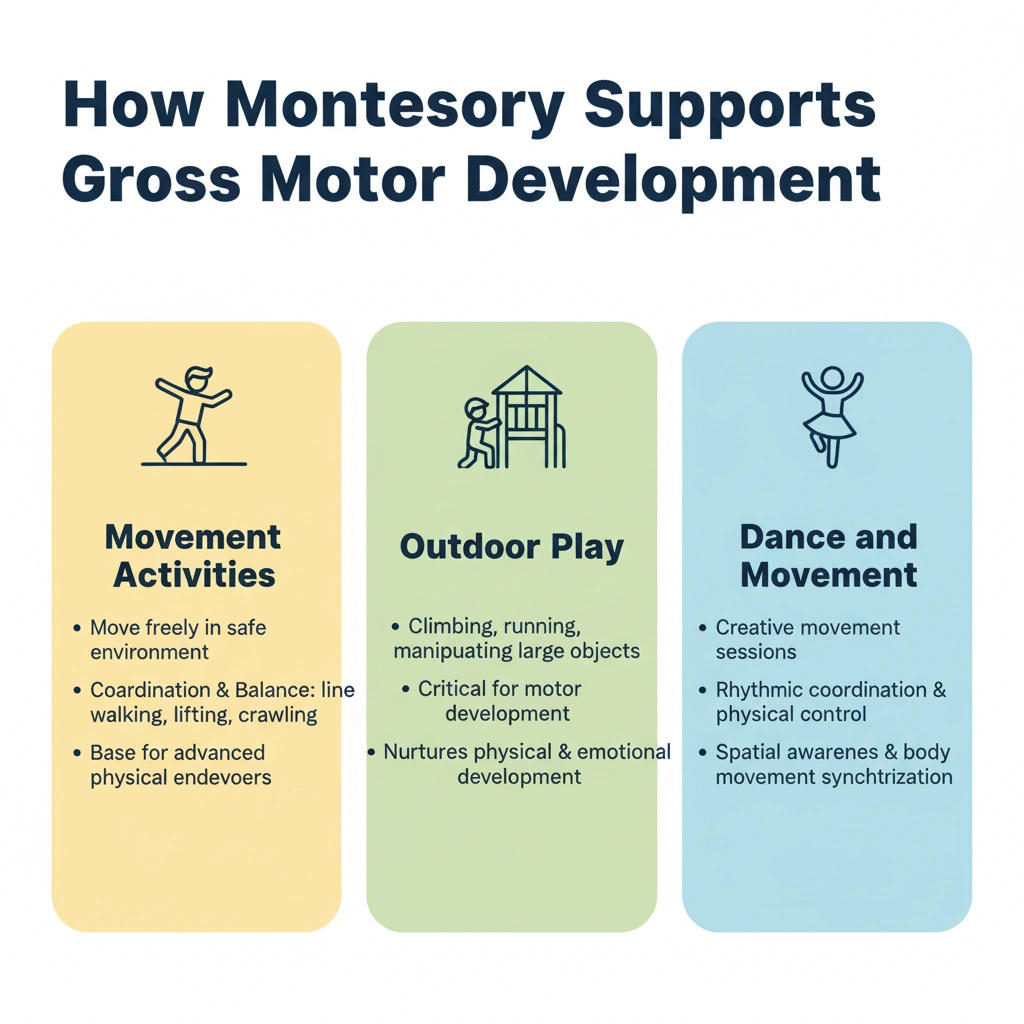
How Montessori Supports Gross Motor Development
Movement Activities:
Montessori classrooms are designed to encourage children to move freely within a safe environment. Basic tasks such as one foot in front of the other on a line, lifting heavy things, or crawling under tables develops coordination and balance. These activities provide a base for more advanced physical endeavors as the child matures.
Outdoor Play:
Montessori education promotes activities such as climbing, running, and manipulation of large physical objects. This is a critical component of the child’s motor development. By encouraging children to encounter the natural world, Montessori nurtures not only children’s physical but also emotional development.
Dance and Movement:
Creative movement sessions, including dancing to music, help children develop rhythmic coordination and physical control. They also help develop spatial awareness and body movement synchronization, which are critical for gross motor activities.
Get Certified & Start Your Montessori Career
Montessori Teacher Training Course by Entri App: Gain expert skills, earn certification, and kickstart your teaching career.
Join Now!Distinctions: Fine Motor vs. Gross Motor Skills
The difference boils down to muscle groups and degree of movement:
| Aspect | Fine Motor Skills | Gross Motor Skills |
|---|---|---|
| Muscles Used | Small muscles: hands, wrists, fingers, toes | Large muscles: legs, arms, torso, core |
| Movement Type | Precise, controlled, small-scale | Broad, powerful, whole-body |
| Typical Activities | Writing, cutting, eating, dressing | Walking, running, jumping, climbing |
| Development Timeline | Refined later in infancy/childhood | Fundamental skills develop earlier |
| Coordination Required | Hand-eye, finger-eye, object manipulation | Multisensory, spatial, whole-body |
Both skill types are interconnected as strong gross motor control aids balance for fine activities, while precise fine skills may be supported by postural stability from gross motor abilities.
The Impact of Montessori Education on Motor Skill Development
Prepared Environment
One of Montessori’s core principles is the prepared environment, an environment that supports the child’s development in all areas, including physical. This classroom arrangement has kids getting up and wandering and interacting with things in a manner that instinctively exercises fine and gross motor skills.
Montessori classrooms are generally open and spacious, with child-sized furniture, accessible materials, and lots of room to move. This fosters independence and lets children practice skills at their own pace, learning independently.
Freedom of Movement
In Montessori classrooms, children can freely roam the room, which directly promotes gross motor skills. They’re not stuck at desks or seats forever – they can get up and really investigate and learn with their bodies. Montessori teachers witness and nurture the child’s wandering, leading them to activities that engage fine and gross motor skills.
Holistic Development
The Montessori method doesn’t simply hone academic skills, but a child’s physical, emotional, social, and cognitive development too. By weaving motor skills into everyday activities, Montessori education crafts a holistic learning experience that prepares children with the skills they need to thrive in all corners of their lives.
The Significance of Fine and Gross Motor Skills in Early Childhood Education
The development of fine and gross motor skills is of utmost importance at an early age. Such skills are important not only for physical activity but also correlate with academic as well as social-emotional outcomes.
Cognitive Development
Hand-eye coordination and other fine motor skills play a role in early writing and drawing activities . These skills develop focus, concentration, and analysis. Likewise, improving gross motor skills allows the child to coordinate his movements and develop spatial awareness, which in turn would support math and science learning.
Social skills and emotional development
The outdoor play and group games also ensure the development of important social skills, of sharing, cooperation, and respect for personal space. Because they are team-oriented, activities based on gross motor skills, such as team sports or cooperative games, emphasize collaboration, thus promoting children’s emotional intelligence as well as collaboration skills.
Self-Confidence
Children experience a sense of accomplishment as they master physical tasks such as cutting paper with scissors or running across the playground. It allows for self-confidence, self-esteem, and all the necessary things that come along with mental and emotional development. The Montessori method promotes encouraging and honoring of children for working at their own pace, feeling independence and self-esteem.
Get Certified & Start Your Montessori Career
Montessori Teacher Training Course by Entri App: Gain expert skills, earn certification, and kickstart your teaching career.
Join Now!How An Entri Montessori Course Develops These Skills
If you’re a teacher or parent seeking to assist kids in honing their motor skills, an Entri Montessori course is a great place to start. Entri’s Montessori Teacher Training Program equips you with the expertise to apply the Montessori method, emphasizing the significance of fine and gross motor skills in young learners.
Practical Life Exercises
The Entri Montessori lesson provides you with the means to lead kids through practical life tasks, exercises that hit at both fine and gross motor skills. You’ll discover how to create a captivating space filled with developmentally-appropriate resources and activities to promote movement.
Classroom Design and Organization
This course will guide you in creating a Montessori prepared environment where kids can feel free to explore and move about, building physical skills! You’ll discover the art of designing a secure, stimulating environment that encourages autonomy and movement.
Age-Appropriate Activities
Entri’s Montessori course also addresses how to customize the activities based on the child’s developmental stage, emphasizing sensorial activities, practical life tasks, and movement-based learning that encourage the development of motor skills.
Conclusion
Both fine and gross motor skills contribute to the child’s physical, cognitive, social, and emotional development. Montessori is uniquely suited to foster all of these capabilities through its movement and practical life, and experiential learning.
In a Montessori class, you’ll learn how to instill these skills in children. You will be armed with the tools and strategies to develop a supportive and fun learning environment to help kids develop into confident adults.
Both fine and gross motor skills contribute to the overall physical, cognitive, social, and emotional development of the child. Montessori does this in a unique way through movement, life skills, and experiential learning.
In the Entri Montessori training course, you will learn how to promote these skills in children. You will be equipped to set the stage for a positive learning experience and to help children become confident adults.
Get Certified & Start Your Montessori Career
Montessori Teacher Training Course by Entri App: Gain expert skills, earn certification, and kickstart your teaching career.
Join Now!Frequently Asked Questions
What are fine motor skills?
Fine motor skills are the ability to use small muscles in the hands, fingers, and wrists to perform precise tasks like writing, buttoning, and cutting.
What are gross motor skills?
Gross motor skills involve large muscles of the arms, legs, and torso that help with big movements such as walking, running, jumping, and climbing.
What is the difference between fine motor and gross motor skills?
Fine motor skills involve small, precise movements (e.g., holding a pencil), while gross motor skills involve larger, whole-body movements (e.g., running or balancing).
Why are fine motor skills important for children?
They are essential for daily activities like writing, dressing, eating, and school readiness, while also improving hand-eye coordination.
Why are gross motor skills important?
They help children build balance, strength, endurance, and independence, and support healthy physical and social development.
At what age do children develop fine motor skills?
Fine motor development begins in infancy (picking up objects) and continues through early childhood, with milestones like writing appearing around age 4–5.
How can parents improve fine motor skills at home?
By encouraging activities like colouring, threading beads, using playdough, cutting with scissors, and practicing zipping or buttoning clothes.
How can gross motor skills be developed?
Through activities like running, ball games, outdoor play, cycling, yoga, dancing, and climbing, which strengthen larger muscle groups.
How does Montessori education support motor skills?
Montessori classrooms use hands-on activities such as pouring, buttoning frames, puzzles, and free movement to naturally develop both fine and gross motor skills.
How can Entri Montessori course help teachers and parents?
The Entri Montessori course trains educators and parents to understand motor skill milestones, apply Montessori methods, and create activities that nurture children’s development.