Want to become a data analyst but don’t know where to start? The Data Analyst Career Path offers a structured journey from entry-level roles to advanced positions in data science and analytics. Whether you’re a student, a career switcher, or someone already working with data, understanding this path can help you set clear goals. In this blog, we’ll break down each stage of the journey, outline the skills you’ll need, and explore the growth opportunities available in the field of data analysis.
Enhance your data science skills with us! Join our free demo today!
Data Analyst Career Path: Introduction
Data is everywhere. Businesses use it to make smart decisions. But raw data alone isn’t useful. That’s where data analysts come in.
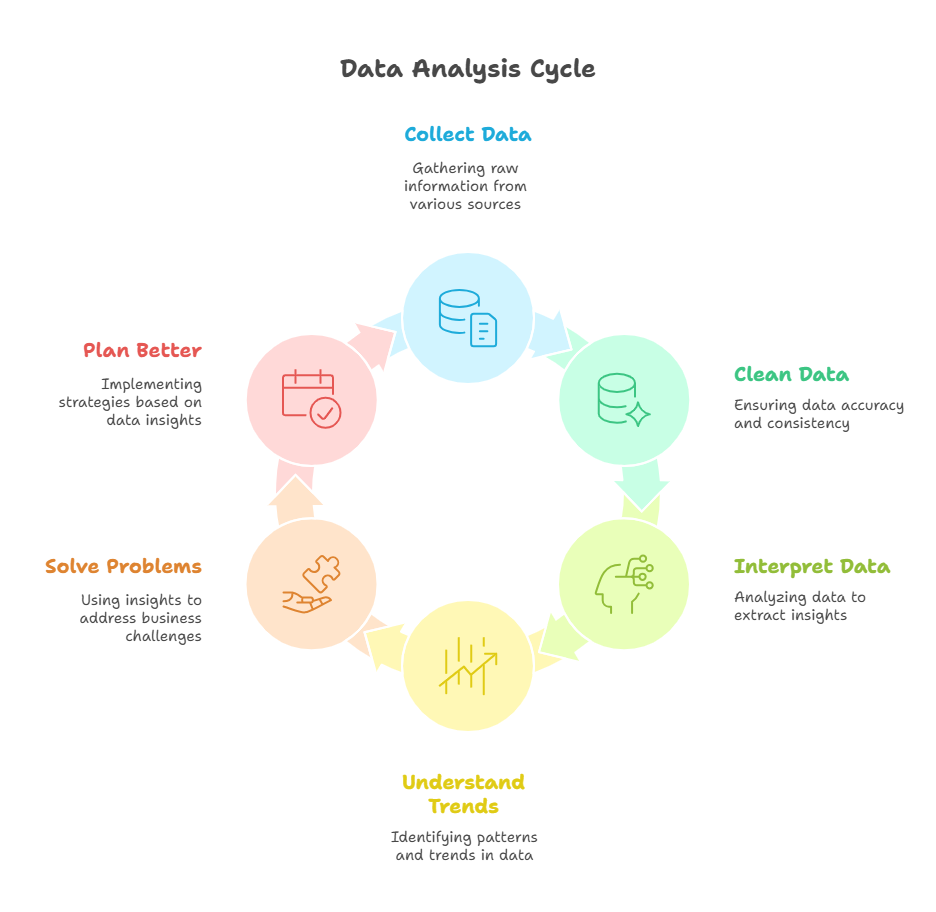
What Is Data Analysis?
-
It’s the process of collecting, cleaning, and interpreting data.
-
Helps businesses understand trends, solve problems, and plan better.
-
Used in marketing, finance, operations, healthcare, and more.
Why Are Data Analysts Important?
-
They turn raw data into useful insights.
-
Help teams make data-driven decisions.
-
Spot patterns, risks, and new opportunities.
What This Blog Covers
This guide outlines the full Data Analyst Career Path. You’ll learn about:
-
Roles from entry-level to senior and specialized positions.
-
Skills needed at each stage.
-
Tools to master and certifications that help.
-
How to keep learning and growing in this field.
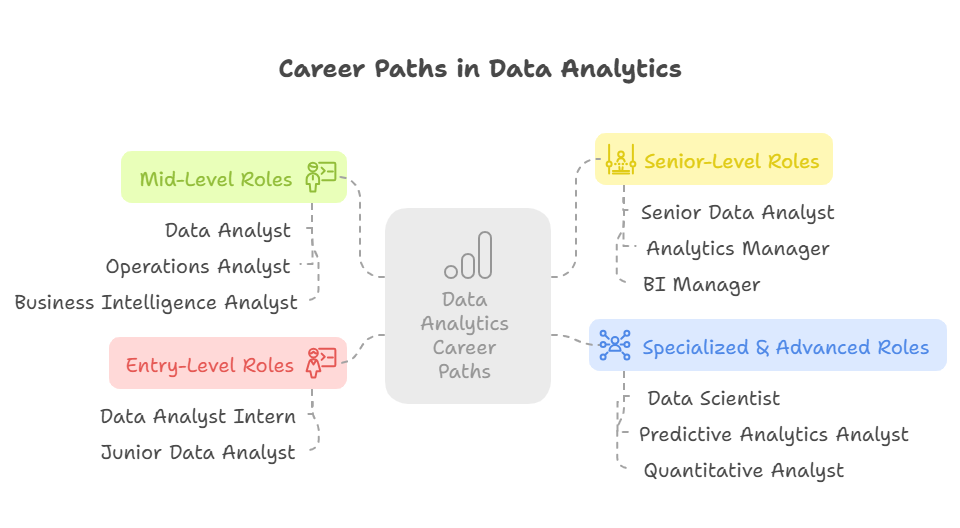
Data Analyst Career Path: Entry-Level Roles in Data Analysis
Starting a career in data analysis is both exciting and achievable. Entry-level roles help you build key skills and gain hands-on experience. These roles are perfect for students, recent graduates, or career changers.
1. Junior Data Analyst
-
Often the first full-time role in data analytics.
-
Focuses on cleaning data, formatting reports, and simple visualizations.
-
Helps senior analysts by preparing datasets and spotting errors.
-
Uses tools like Excel and SQL for daily tasks.
Key Tasks:
-
Importing and cleaning raw data.
-
Creating tables, charts, and basic dashboards.
-
Running queries to extract useful information.
2. Data Analyst Intern
-
Ideal for students or beginners exploring analytics.
-
Supports the analytics team with ongoing tasks and research.
-
Learns by working on real-world datasets.
-
Internships often lead to full-time roles.
Key Tasks:
-
Assisting in data collection and cleaning.
-
Helping create basic reports and summaries.
-
Learning tools like Tableau, PowerBI, and spreadsheets.
3. Business Intelligence (BI) Analyst
-
A role that overlaps with data analysis.
-
Focuses on using data to guide business decisions.
-
Works with dashboards, KPIs, and reporting tools.
-
Often collaborates with sales, marketing, or finance teams.
Key Tasks:
-
Building BI dashboards.
-
Analyzing business trends.
-
Recommending data-backed strategies.
Skills Needed at Entry-Level
| Skill | Why It Matters |
|---|---|
| Excel & Google Sheets | For organizing and analyzing raw data |
| SQL | To query and extract data from databases |
| Tableau / PowerBI | For creating simple, visual dashboards |
| Basic Statistics | To understand averages, distributions, and correlations |
| Attention to Detail | To clean data and catch inconsistencies |
These entry-level roles provide a strong foundation. They teach you how to work with data and support decision-makers. From here, you can move to more advanced roles with confidence.
Data Analyst Career Path: Mid-Level Roles in Data Analysis
Once you have some experience, you can move into mid-level roles. These jobs require more independence and analytical thinking. You’ll handle larger datasets, create insights, and influence decisions.
1. Data Analyst
-
The most common mid-level position.
-
Works independently on data projects.
-
Builds dashboards and reports for different teams.
-
Helps identify business trends and measure performance.
Key Tasks:
-
Writing SQL queries and pulling data.
-
Creating dashboards with Tableau or PowerBI.
-
Presenting insights to non-technical teams.
2. Advanced Data Analyst
-
A step above the general analyst.
-
Works with complex data problems and predictive models.
-
Often supports product, marketing, or finance teams.
-
Uses tools like Python, R, or advanced Excel features.
Key Tasks:
-
Running regression models or cluster analysis.
-
Building predictive tools using Python or R.
-
Cleaning and transforming big datasets.
3. Operations Analyst
-
Focuses on improving internal processes.
-
Works with logistics, HR, supply chain, or finance data.
-
Uses data to reduce costs and increase efficiency.
-
Often builds models to simulate business outcomes.
Key Tasks:
-
Analyzing workflow data and KPIs.
-
Building reports to track performance.
-
Suggesting process improvements using trends.
Skills Needed at Mid-Level
| Skill | Use Case |
|---|---|
| Intermediate SQL | For complex joins, subqueries, and optimization |
| Excel (Advanced) | For pivot tables, formulas, and data modeling |
| Tableau / PowerBI | To create interactive dashboards |
| Python / R | For data wrangling, analysis, and automation |
| Problem-Solving Skills | To interpret messy data and make smart conclusions |
At this stage, you’re no longer just handling data—you’re shaping how the business sees it. Mid-level roles help you grow fast and set you up for leadership positions.
Data Analyst Career Path: Senior Roles in Data Analysis
With years of experience, you can move into senior roles. These positions involve leadership, complex data work, and strategy. You also guide junior analysts and drive big decisions.
1. Senior Data Analyst
-
Leads end-to-end data projects.
-
Works with large and messy datasets.
-
Mentors interns and junior analysts.
-
Partners with management to solve business problems.
Key Tasks:
-
Designing dashboards and KPIs for leadership.
-
Coordinating across teams for data consistency.
-
Presenting findings to C-level executives.
2. Data Analytics Manager
-
Heads the analytics department or team.
-
Sets goals and strategy for data analysis.
-
Manages hiring, training, and project timelines.
-
Ensures analysis supports overall business goals.
Key Tasks:
-
Assigning roles and managing team performance.
-
Communicating data needs across departments.
-
Overseeing the delivery of analytics reports.
3. Business Intelligence (BI) Manager
-
Oversees BI strategy and reporting systems.
-
Focuses on advanced data modeling.
-
Works closely with IT, data engineers, and analysts.
-
Uses BI tools to provide company-wide insights.
Key Tasks:
-
Building long-term BI roadmaps.
-
Managing enterprise-level data dashboards.
-
Aligning data tools with business strategy.
Skills Needed at Senior Level
| Skill | Use Case |
|---|---|
| Leadership & Team Management | To lead analytics teams and mentor members |
| Strategic Thinking | To align analytics with business outcomes |
| Advanced Tools (SQL, Python) | To manage large-scale data pipelines and models |
| Business Process Knowledge | To understand how data impacts each department |
| Communication Skills | To present insights clearly to executives |
Senior roles are about big-picture thinking. You’re not just analyzing data—you’re shaping business direction. These roles often lead to executive or specialized data leadership positions.
Enhance your data science skills with us! Join our free demo today!
Data Analyst Career Path: Specialized Career Paths in Data Analysis
Some analysts choose to specialize. These paths focus on niche areas and require deeper technical skills. Specialized roles often offer higher pay and industry-specific challenges.
1. Data Scientist
-
Moves beyond analysis to predictive modeling.
-
Uses algorithms, machine learning, and automation.
-
Finds patterns in large and unstructured data.
-
Works closely with engineering and product teams.
Key Tools:
-
Python, R, TensorFlow, scikit-learn
-
Jupyter Notebooks, cloud platforms (AWS, GCP)
Key Tasks:
-
Creating machine learning models.
-
Running experiments on customer behavior.
-
Automating reports and prediction engines.
2. Predictive Analytics Analyst
-
Focuses on forecasting future trends.
-
Uses historical data to predict sales, demand, or churn.
-
Common in marketing, sales, and finance departments.
-
Builds scoring models to guide business actions.
Key Tools:
-
Python, R, Excel, PowerBI
-
Time series models, regression, forecasting tools
Key Tasks:
-
Analyzing customer trends.
-
Predicting sales or inventory needs.
-
Improving marketing ROI with forecast models.
3. Quantitative Analyst (Quant)
-
Works mostly in finance or investment firms.
-
Uses math, stats, and data to inform financial decisions.
-
Builds trading algorithms or risk models.
-
Needs a strong background in finance and programming.
Key Tools:
-
MATLAB, Python, R, Excel VBA
-
Bloomberg Terminal, financial modeling tools
Key Tasks:
-
Modeling stock trends or interest rate movements.
-
Analyzing portfolio risks.
-
Developing data-driven investment strategies.
Skills Needed in Specialized Roles
| Skill | Application Area |
|---|---|
| Machine Learning | Data science and predictive analytics |
| Industry Knowledge | Finance, healthcare, marketing, etc. |
| Programming (Python, R) | Data modeling, automation, forecasting |
| Statistical Modeling | Predictive analysis, quant models |
| Domain-Specific Tools | Tools like Bloomberg, TensorFlow, etc. |
These specialized paths are ideal for those who enjoy deep analysis and technical challenges. They often lead to roles like Chief Data Scientist or Director of Analytics.
Data Analyst Career Path: Continuous Learning and Career Development
The data field evolves fast. To stay relevant, learning must never stop. Upskilling opens doors to better jobs and higher pay.
1. Certifications
-
Help you learn new tools and frameworks.
-
Prove your skills to employers.
-
Many options are self-paced and affordable.
Popular Certifications:
| Platform | Course/Certificate | Focus Area |
|---|---|---|
| Coursera | Google Data Analytics Professional Certificate | Beginner data analysis skills |
| edX | Microsoft Professional Program in Data Science | Full data science lifecycle |
| Udacity | Data Analyst Nanodegree | SQL, Python, statistics, visualization |
| Excel & Tableau Training Paths | Data handling and dashboards | |
| Entri | Data Analytics Certification | Python, SQL, Power BI, Excel, job assistance |
2. Higher Education
-
Best for those seeking leadership or research roles.
-
Offers deep knowledge and networking opportunities.
-
Can specialize in business analytics, data science, or AI.
Top Degrees:
-
Master’s in Data Science
-
MBA with Data Analytics concentration
-
M.S. in Business Intelligence or Applied Statistics
3. Networking & Industry Events
-
Keeps you updated on trends and tools.
-
Helps build your professional brand.
-
Connects you with recruiters and mentors.
Where to Network:
| Platform/Event | Purpose |
|---|---|
| Build visibility, join data groups | |
| Kaggle | Practice skills through competitions |
| Meetup / Eventbrite | Attend local analytics meetups |
| Conferences (e.g., ODSC) | Learn from industry leaders and workshops |
Learning is your biggest long-term investment. Stay curious, stay current, and your data career will keep growing.
Enhance your data science skills with us! Join our free demo today!
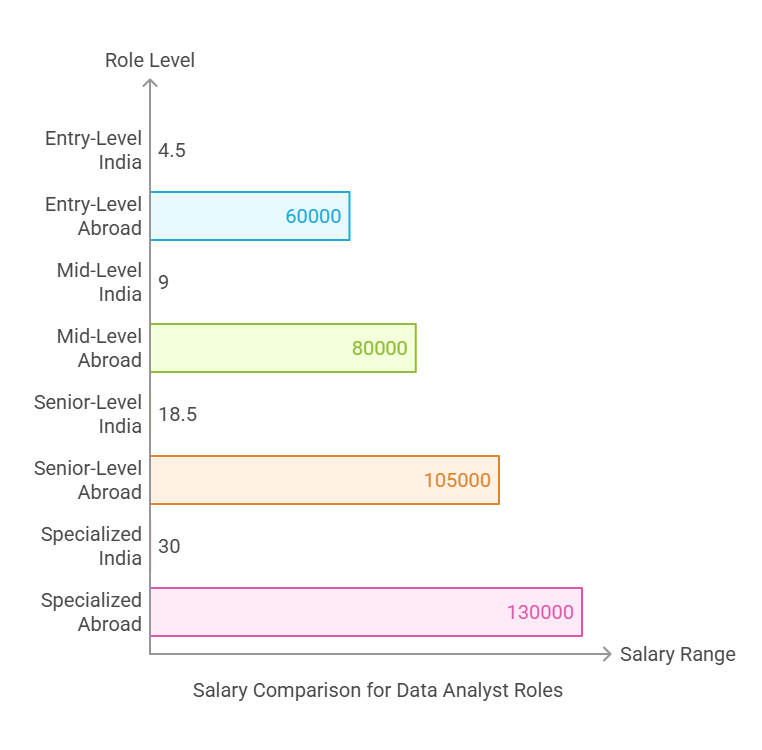
Career Path Salaries in Data Analysis
Salaries in data analysis vary based on experience, role, and location. Below is an overview of what you can expect in both Indian and foreign markets.
1. Entry-Level Salaries
For junior roles like data analysts or interns, salaries typically start lower but can grow quickly with experience.
Entry-Level Salary Range:
| Role | Salary Range (India) | Salary Range (Foreign) |
|---|---|---|
| Junior Data Analyst | ₹4,00,000 – ₹6,00,000 | $50,000 – $65,000 per year |
| Data Analyst Intern | ₹2,50,000 – ₹4,00,000 | $35,000 – $50,000 per year |
| Business Intelligence Analyst | ₹5,00,000 – ₹7,00,000 | $60,000 – $70,000 per year |
2. Mid-Level Salaries
As you gain experience, salaries rise significantly. Mid-level data analysts or advanced analysts can expect a higher pay range.
Mid-Level Salary Range:
| Role | Salary Range (India) | Salary Range (Foreign) |
|---|---|---|
| Data Analyst | ₹7,00,000 – ₹10,00,000 | $70,000 – $90,000 per year |
| Advanced Data Analyst | ₹10,00,000 – ₹14,00,000 | $90,000 – $110,000 per year |
| Operations Analyst | ₹8,00,000 – ₹11,00,000 | $75,000 – $95,000 per year |
3. Senior-Level Salaries
At the senior level, roles like data analytics managers or business intelligence managers command top salaries. These positions involve leadership and high-level strategic decision-making.
Senior-Level Salary Range:
| Role | Salary Range (India) | Salary Range (Foreign) |
|---|---|---|
| Senior Data Analyst | ₹12,00,000 – ₹18,00,000 | $100,000 – $130,000 per year |
| Data Analytics Manager | ₹18,00,000 – ₹25,00,000 | $120,000 – $150,000 per year |
| Business Intelligence Manager | ₹20,00,000 – ₹28,00,000 | $125,000 – $160,000 per year |
Salary Factors
-
Location: Salaries are typically higher in foreign markets like the US, UK, and other tech hubs.
-
Industry: High-paying industries include finance, tech, and healthcare.
-
Company Size: Larger companies often provide better salary packages.
These salary ranges provide an idea of what you can expect in both Indian and foreign markets as you progress through the data analysis career path.
Conclusion
A career in data analysis offers strong growth at every level. Starting from entry-level positions, the field grows quickly. Data analysts play a key role in shaping business decisions. With the right skills, you can advance and earn more. Continuous learning keeps you competitive in the evolving field.
Key Takeaways:
-
Data analysis is crucial for business decisions.
-
Career paths range from junior to senior roles.
-
Continuous learning is essential for growth.
-
Salaries increase with experience and expertise.
-
Opportunities are available across various industries.
🚀 Start Coding Today! Enroll Now with Easy EMI Options. 💳✨
Equip yourself with in-demand skills to land top-tier roles in the data-driven world.
Start Learning Now with EMI OptionsFrequently Asked Questions
What does a data analyst do?
A data analyst collects, cleans, and interprets data to help businesses make informed decisions. They often use tools like Excel, SQL, and visualization software.
What qualifications do I need to become a data analyst?
A degree in statistics, computer science, or business is helpful. However, certifications like the Entri Data Analytics Course also offer job-ready skills.
Is coding necessary for data analysis?
Basic coding is essential. SQL is a must, and Python or R is useful for advanced analysis.
How do I get started with no experience?
Start with online courses, build a portfolio with sample projects, and apply for internships or junior roles.
What tools should I learn first?
Start with Excel, SQL, and Tableau or PowerBI. These are common in most data roles.
What is the difference between a data analyst and a data scientist?
Data analysts interpret data for trends. Data scientists build predictive models and use machine learning.
How long does it take to grow into a mid-level role?
Usually 1–3 years. You’ll need project experience and strong technical skills to progress.
Can I become a data analyst without a tech background?
Yes, many switch from business, marketing, or finance by learning data skills through courses or bootcamps.
What are the highest-paying roles in data analysis?
Data Scientists, Quantitative Analysts, and Analytics Managers earn the most, especially in finance and tech.
Are certifications worth it for career growth?
Yes. Certifications from platforms like Entri, Coursera, or edX show employers you’re serious and skilled.