Table of Contents
Introduction
The Nvidia Embedded Software Engineer interview tests strong fundamentals. It focuses on real world embedded engineering challenges. Interviewers value applied knowledge over theoretical explanations. Problem solving ability receives higher importance than speed. Clear coding logic is closely observed during evaluations. Hardware software interaction understanding is extremely important. Project discussions reveal genuine hands on engineering experience. Focused preparation helps candidates approach interviews confidently.
The interview process follows a structured technical evaluation approach. Each round measures technical depth and communication clarity. Embedded concepts are tested through scenario based questioning. Candidates must explain decisions using logical engineering reasoning. Debugging methodology and thought process receive close attention. Calm explanations under pressure create strong interviewer impressions. Consistent preparation improves performance across all interview stages.
This blog provides a complete preparation roadmap. It helps candidates understand Nvidia interview expectations clearly. Each section focuses on practical embedded engineering readiness.
What This Blog Covers
This blog explains the Nvidia interview process in detail.
-
Complete Nvidia interview structure explanation
-
Embedded software skills Nvidia evaluates
-
Technical knowledge areas candidates must prepare
-
Coding, debugging, and design expectations
-
Project discussion patterns and evaluation criteria
Each section focuses on practical interview preparation. Examples reflect real embedded engineering scenarios.
Kickstart your embedded systems career and turn your tech passion into high-demand skills!
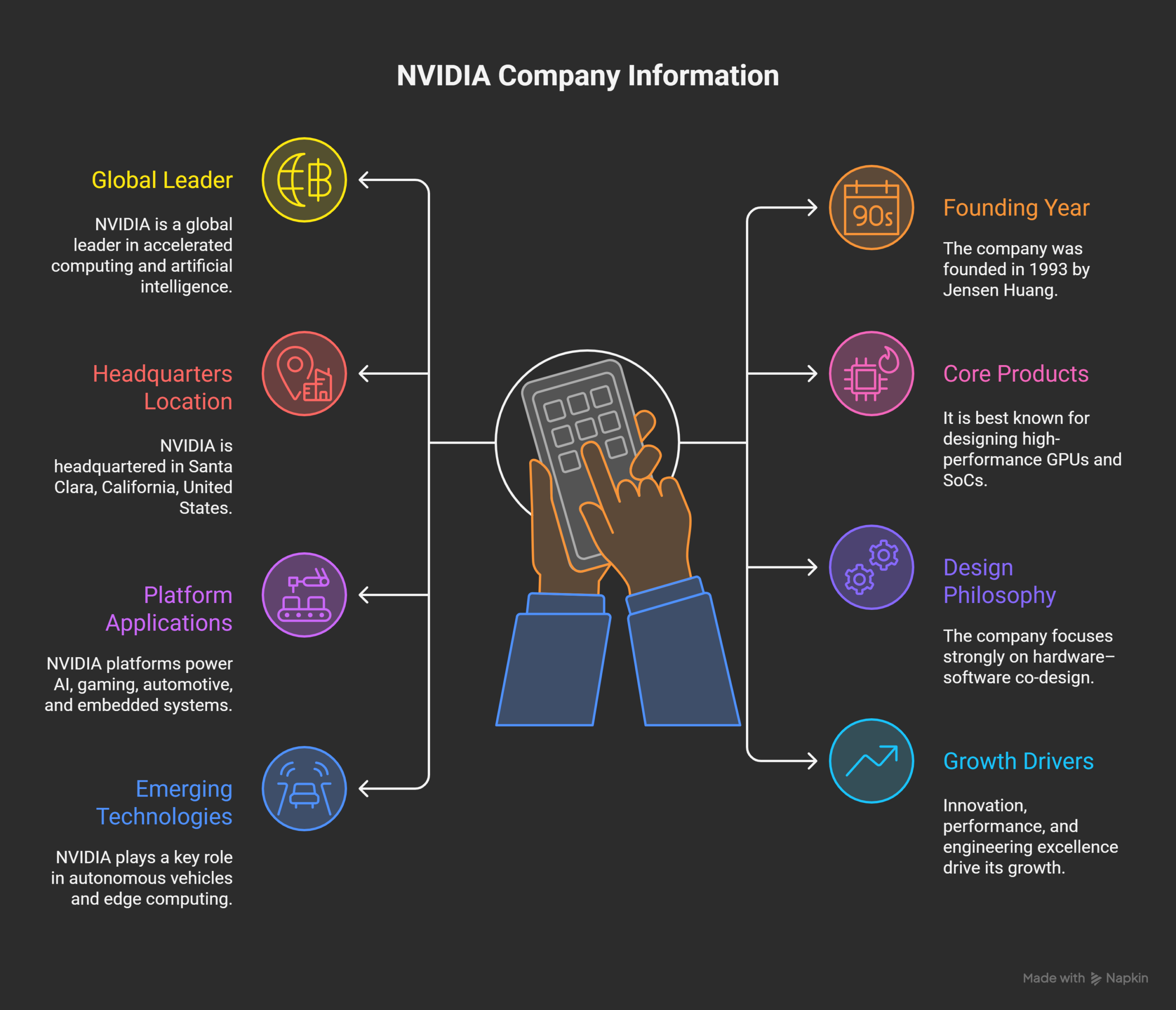
About NVIDIA – Company Overview
NVIDIA is a global leader in accelerated computing. The company is headquartered in Santa Clara, California. It was founded in 1993 by Jensen Huang. NVIDIA designs GPUs and advanced computing platforms. Its technologies power AI, automotive, and embedded systems.
The company focuses on high performance computing solutions. Artificial intelligence is a core business area. NVIDIA platforms support both training and inference workloads. Embedded systems play a critical role in product offerings.
Research and innovation drive NVIDIA’s long term growth. Engineering excellence defines the company’s global reputation. Employees work on cutting edge technologies worldwide.
NVIDIA Global Reach and Industry Expertise
NVIDIA operates across multiple technology driven industries. Its platforms serve both consumer and industrial applications. Embedded engineers support diverse product domains.
Artificial Intelligence and Data Centers
NVIDIA accelerates machine learning and deep learning workloads. GPUs enable large scale data processing efficiently. AI frameworks integrate tightly with hardware platforms. Embedded software ensures reliable edge inference performance.
Automotive and Autonomous Systems
NVIDIA builds platforms for autonomous vehicle development. ADAS systems rely on embedded software reliability. Safety and performance are critical automotive requirements. Real time processing supports perception and decision making.
Embedded and Edge Computing
Jetson platforms power robotics and IoT systems. Low power computing enables intelligent edge devices. Embedded software optimizes performance within power constraints. Real time responsiveness is extremely important.
Gaming and Visualization
NVIDIA leads real time graphics rendering technologies. GPUs deliver immersive gaming and visualization experiences. Embedded systems support display and control logic.
Healthcare and Robotics
Medical imaging systems use NVIDIA computing platforms. Robotics applications rely on embedded AI processing. Precision and reliability are mandatory requirements.
Embedded and Software Engineering at NVIDIA
NVIDIA has specialized embedded software engineering teams. Engineers work on SoCs and firmware layers. Hardware software co design is a core responsibility. Performance optimization is always a critical requirement.
Embedded engineers develop software close to hardware. Understanding SoC architecture is extremely important. Low level programming skills are frequently required.
Embedded Engineering Responsibilities
-
Firmware development for NVIDIA system on chips
-
Bootloader development and board bring up activities
-
RTOS and Embedded Linux integration tasks
-
Device driver and middleware development
-
Power, memory, and performance optimization
-
Hardware debugging and system validation
Engineers collaborate closely with hardware designers. System level thinking is strongly expected.
Engineering Culture and Core Values
NVIDIA emphasizes innovation and engineering excellence. Engineers are encouraged to solve complex problems. Ownership and accountability are strongly promoted internally. Continuous learning is actively supported by leadership. Quality and performance guide engineering decisions.
Teams value collaboration and technical discussions. Constructive feedback improves individual growth. Engineers are expected to adapt quickly.
Master Embedded Systems Programming!
Launch your tech career with our Embedded Systems Course in Kerala, designed for hands-on learning and industry readiness.
Know MoreInterview Overview
The NVIDIA interview follows a structured assessment framework. Each stage evaluates specific technical competencies. The process tests coding, debugging, and system design skills. Communication clarity is evaluated throughout interviews.
Candidates progress based on overall performance. Each round builds upon previous evaluations. Practical knowledge is valued at every stage.
NVIDIA Interview Stages Overview
The interview process usually includes multiple evaluation rounds. Each round focuses on different skill areas.
Typical Interview Flow
| Interview Stage | Primary Focus |
|---|---|
| Online Assessment | Programming fundamentals |
| Technical Interview | Embedded systems knowledge |
| Project Discussion | Practical engineering experience |
| System Design Interview | Architecture and optimization |
| HR Round | Communication and cultural fit |
Selection depends on combined round performance. Consistency across rounds improves selection chances.
Online Assessment Overview
The online assessment is the first filtering stage. It evaluates basic programming and logical reasoning. Candidates must demonstrate clean coding practices. Embedded C and C++ fundamentals are tested.
Logical clarity matters more than advanced algorithms. Simple mistakes can impact overall evaluation. Time management is important during this stage.
Technical Interview Overview
Technical interviews test core embedded knowledge deeply. Interviewers ask scenario based technical questions. Candidates must explain concepts using simple language. Practical understanding is valued more than definitions.
Topics progress from basics to advanced systems. Follow up questions test depth of understanding. Calm explanations create strong impressions.
Project Discussion Overview
Project discussion validates resume claims. Interviewers focus on real project involvement. Candidates must explain individual contributions clearly. Honesty and clarity are extremely important.
Design decisions are discussed in detail. Debugging challenges receive special attention. System understanding is evaluated thoroughly.
System Design Interview Overview
System design evaluates architectural thinking ability. Candidates design scalable embedded solutions. Trade offs must be explained logically. Performance and reliability are key discussion points.
Interviewers observe structured thinking approach. Clarity matters more than complex architectures.
HR and Behavioral Interview Overview
The HR round evaluates attitude and communication skills. Cultural fit plays an important role in selection.
Candidates must show professionalism and adaptability. Motivation and learning mindset are assessed.
Clear and honest responses create positive impressions. Confidence without arrogance is preferred.
Key Skills NVIDIA Evaluates
NVIDIA seeks engineers with strong technical foundations. Practical knowledge is valued over theoretical depth. Candidates must demonstrate structured problem solving ability. Adaptability and continuous learning mindset are important.
Core Skill Areas Evaluated
-
Embedded C and C++ programming skills
-
Hardware and SoC architecture understanding
-
RTOS and Embedded Linux fundamentals
-
Communication protocol knowledge
-
Debugging and troubleshooting capability
-
Project ownership and responsibility clarity
Each skill area is evaluated carefully. Balanced competency improves overall selection chances.
Kickstart your embedded systems career and turn your tech passion into high-demand skills!
Nvidia Embedded Software Engineer Interview Questions
Core Technical Interview Questions and Answers
The technical interview evaluates deep embedded systems understanding. Interviewers focus on practical knowledge and reasoning ability. Questions progress from basic concepts to advanced scenarios. Candidates must explain answers clearly and confidently. Real world examples strengthen interview responses significantly.
Interviewers observe thinking approach carefully. Logical flow matters more than memorized definitions. Calm explanations under pressure create strong impressions. Strong fundamentals improve success across technical rounds.
Embedded C Programming Interview Questions
Question 1: What is Embedded C?
Embedded C is C language used for hardware programming. It allows direct control of microcontroller resources. It is optimized for memory constrained systems.
Question 2: What is the volatile keyword?
The volatile keyword prevents compiler optimization.It ensures variable value is always read. It is used for hardware registers. It is also used inside interrupt routines.
Question 3: Difference between const and #define?
Const variables occupy memory locations. They provide type checking during compilation. Define performs text substitution only. Define does not allocate memory.
Question 4: Why are pointers important in embedded systems?
Pointers allow direct register access. They reduce memory usage significantly. They improve code efficiency and speed. They enable hardware software interaction.
Question 5: What is the use of static variables?
Static variables retain values between function calls. They maintain state across executions. Scope remains limited to defined region.
Question 6: What causes stack overflow?
Deep recursive function calls cause overflow. Large local variables consume stack memory. Stack size is limited in embedded systems.
Memory Management Interview Questions
Question 7: Difference between stack and heap memory?
Stack memory is fast and limited. It stores local variables and function calls. Heap memory is dynamic and flexible. Heap allocation requires careful management.
Question 8: What is memory mapped input output?
Peripheral registers map to memory addresses. CPU accesses them like normal variables. It enables direct hardware control.
Question 9: What is a memory leak?
Memory leak occurs due to missing deallocation. Heap memory remains unused permanently. It causes system instability over time.
Question 10: What is the role of linker?
The linker combines object files together. It assigns memory addresses. It generates final executable output.
Microcontroller and Hardware Questions
Question 11: What is a microcontroller?
A microcontroller is a complete computing system. It contains CPU, memory, and peripherals. It is used for embedded applications.
Question 12: What is an interrupt?
An interrupt signals an urgent hardware event. It pauses normal program execution. Interrupt Service Routine handles the event.
Question 13: What is an ISR?
ISR stands for Interrupt Service Routine. It executes when an interrupt occurs. ISR should be short and efficient.
Question 14: Polling versus interrupt handling?
Polling continuously checks device status. It wastes CPU processing time. Interrupts respond only when events occur. Interrupts improve system efficiency.
Question 15: What is a watchdog timer?
Watchdog timer monitors software execution. It resets system during software failure. It improves system reliability significantly.
Communication Protocol Interview Questions
Question 16: Difference between UART and SPI?
UART is asynchronous communication protocol. SPI is synchronous communication protocol. SPI supports higher data rates.
Question 17: How does UART communication work?
UART uses start and stop bits. Baud rate controls communication speed. No clock line is required.
Question 18: How does I2C communication work?
I2C uses two communication lines. Devices communicate using slave addresses. It supports multiple slave devices. Arbitration prevents data collision.
Question 19: What is SPI communication?
SPI uses master slave architecture. It uses separate clock and data lines. It supports full duplex communication.
Question 20: What is CAN protocol used for?
CAN is used in automotive systems. It supports real time communication. It provides strong error detection.
Question 21: Why are pull up resistors used?
Pull up resistors prevent floating inputs. They maintain stable logic levels. They are commonly used in I2C.
RTOS Interview Questions and Answers
Question 22: What is an RTOS?
RTOS stands for Real Time Operating System. It manages tasks with timing constraints. It ensures deterministic task execution.
Question 23: What is a task?
A task is an independent execution unit. It performs specific application functionality. Multiple tasks run concurrently.
Question 24: What is task scheduling?
RTOS decides task execution order. Scheduling is usually priority based. Higher priority tasks execute first.
Question 25: Difference between mutex and semaphore?
Mutex allows exclusive resource access. Semaphore controls resource count. Mutex supports ownership concept.
Question 26: What is priority inversion?
Lower priority task blocks higher task. It causes timing issues. RTOS uses priority inheritance to solve.
Question 27: What is context switching?
CPU switches execution between tasks. Task context is saved and restored. Context switching consumes CPU cycles.
Debugging Related Interview Questions
Question 28: How do you debug embedded systems?
I analyze logs and error messages. I use breakpoints and register inspection. I isolate root cause systematically.
Question 29: What debugging tools have you used?
I have used GDB for debugging. I have used JTAG for hardware debugging. I have used oscilloscopes for signal analysis.
Question 30: How do you handle system crashes?
I check watchdog reset logs. I analyze stack and memory usage. I identify faulty module responsible.
Technical Interview Evaluation Criteria
Interviewers evaluate more than correct answers. They observe explanation clarity and structure. Logical reasoning is highly valued. Practical examples strengthen candidate evaluation.
Summary
This section covered core technical interview questions. Embedded C, memory, hardware, protocols were discussed. RTOS and debugging questions were explained clearly. Structured answers improve interview performance significantly.
Coding Test, Project Discussion, System Design, HR
Final Interview Rounds
The final rounds evaluate applied engineering and professional behavior. These rounds validate technical depth and cultural alignment. Interviewers observe confidence, clarity, and structured thinking. Candidates must communicate solutions calmly and logically. Practical exposure receives higher importance than theoretical knowledge.
These rounds often decide final selection outcomes. Preparation should focus on clarity and honesty. Strong explanations create lasting interviewer impressions. Confidence improves with thorough preparation.
Online Coding Test
The online coding test filters candidates initially. It evaluates core programming fundamentals clearly. Logic clarity matters more than complex optimizations. Code readability and structure receive close attention.
The test usually includes time constraints. Candidates must manage time efficiently. Simple mistakes can reduce evaluation scores. Practice improves speed and accuracy significantly.
Coding Test Focus Areas
The coding test evaluates fundamental embedded programming topics.
Commonly Tested Topics
-
Embedded C programming basics
-
Pointer handling and memory concepts
-
Bit manipulation logic
-
Loop and conditional structures
-
Basic algorithmic problem solving
Candidates should avoid unnecessary library functions. Writing clean logic improves evaluation outcomes. Edge cases should be handled carefully.
Sample Coding Test Question Patterns
| Topic | Sample Question |
|---|---|
| Arrays | Find second largest element |
| Strings | Reverse string manually |
| Pointers | Swap values using pointers |
| Bitwise | Set specific bit |
| Logic | Generate numeric pattern |
Interviewers value approach explanation. Correct logic matters more than syntax tricks.
Project Discussion Round
Project discussion validates resume mentioned experience. Interviewers assess hands on embedded engineering exposure. Candidates must explain projects confidently and clearly. Honesty during explanations builds interviewer trust.
This round focuses on real implementation experience. Interviewers ask deep follow up questions. Preparation requires thorough project revision. Candidates should recall design decisions clearly.
Project Explanation Structure
Candidates should explain projects step by step.
Recommended Explanation Flow
-
Project objective and application context
-
Hardware platform selection reasoning
-
Software architecture overview
-
Communication interfaces used
-
Debugging challenges faced
-
Final outcome and improvements
Simple explanations create stronger impressions. Avoid unnecessary technical jargon during explanation.
Common Project Discussion Questions and Answers
Question: Why did you choose this microcontroller?
I selected it for required peripherals. It met performance and memory requirements. Power consumption matched system constraints.
Question: How did you debug hardware issues?
I used logs and signal analysis tools. I isolated issues module by module. Root cause analysis guided final fixes.
Question: What challenges did you face?
Timing issues occurred during communication. Memory constraints required optimization changes. Testing revealed edge case failures.
Question: How did you optimize performance?
I reduced unnecessary function calls. I optimized memory access patterns. I improved task scheduling logic.
Debugging Discussion Expectations
Debugging approach receives close evaluation. Interviewers focus on systematic troubleshooting methods. Random guessing reflects weak problem solving skills.
Debugging Evaluation Criteria
-
Clear issue identification process
-
Tool usage explanation
-
Root cause analysis clarity
-
Final solution effectiveness
Candidates should explain debugging steps sequentially.
Logical flow strengthens technical credibility.
System Design Interview
System design evaluates architectural thinking ability. Candidates design scalable embedded solutions logically.
Interviewers assess trade off understanding carefully. Clear communication matters during design discussions.
Design questions may be open ended. Candidates should clarify requirements first. Assumptions must be stated clearly. Design decisions should be justified logically.
Common System Design Topics
-
Embedded system architecture design
-
Performance optimization strategies
-
Power management techniques
-
Reliability and fault handling mechanisms
Candidates should avoid overcomplicated designs. Simple scalable designs receive preference.
Sample System Design Questions
Question: Design an embedded monitoring system
Define sensors and data acquisition flow. Select microcontroller based on requirements. Design communication interface for data transfer. Include fault handling and logging mechanisms.
Question: How to handle power optimization?
Use sleep modes effectively. Optimize peripheral usage schedules. Reduce unnecessary processing cycles.
Question: How to ensure system reliability?
Implement watchdog timers. Add error detection mechanisms. Handle failures gracefully.
HR and Behavioral Interview
The HR round evaluates attitude and communication skills. Cultural fit plays an important role. Interviewers assess motivation and professionalism. Honest answers create positive impressions.
Candidates should remain calm and confident. Clear communication improves evaluation outcomes. Positive attitude matters significantly.
Common HR Interview Questions and Answers
Question: Tell me about yourself
I am an embedded software engineer. I enjoy firmware and system development. I focus on clean and reliable code.
Question: Why do you want NVIDIA?
NVIDIA works on cutting edge technologies. The culture encourages technical excellence. Learning opportunities align with my goals.
Question: How do you handle deadlines?
I prioritize tasks based on importance. I break work into manageable steps. I communicate risks early.
Question: How do you handle failures?
I analyze mistakes carefully. I learn and improve processes. Failures help refine engineering judgment.
Professional Behavior Expectations
Interviewers evaluate professionalism continuously. Respectful communication reflects strong work ethics. Openness to feedback is highly valued.
Candidates should avoid defensive responses. Acknowledging limitations shows maturity. Willingness to learn improves selection chances.
Kickstart your embedded systems career and turn your tech passion into high-demand skills!
Final Preparation Tips for Nvidia Embedded Software Engineer Interviews
Strong preparation directly impacts interview performance. Unstructured preparation often leads to weak explanations. Focused preparation improves confidence and clarity significantly. Candidates should follow a systematic preparation strategy.
Preparation must balance theory and practical understanding. Both coding and explanation skills require equal attention. Consistent revision helps retain important concepts. Confidence grows with repeated practice and clarity.
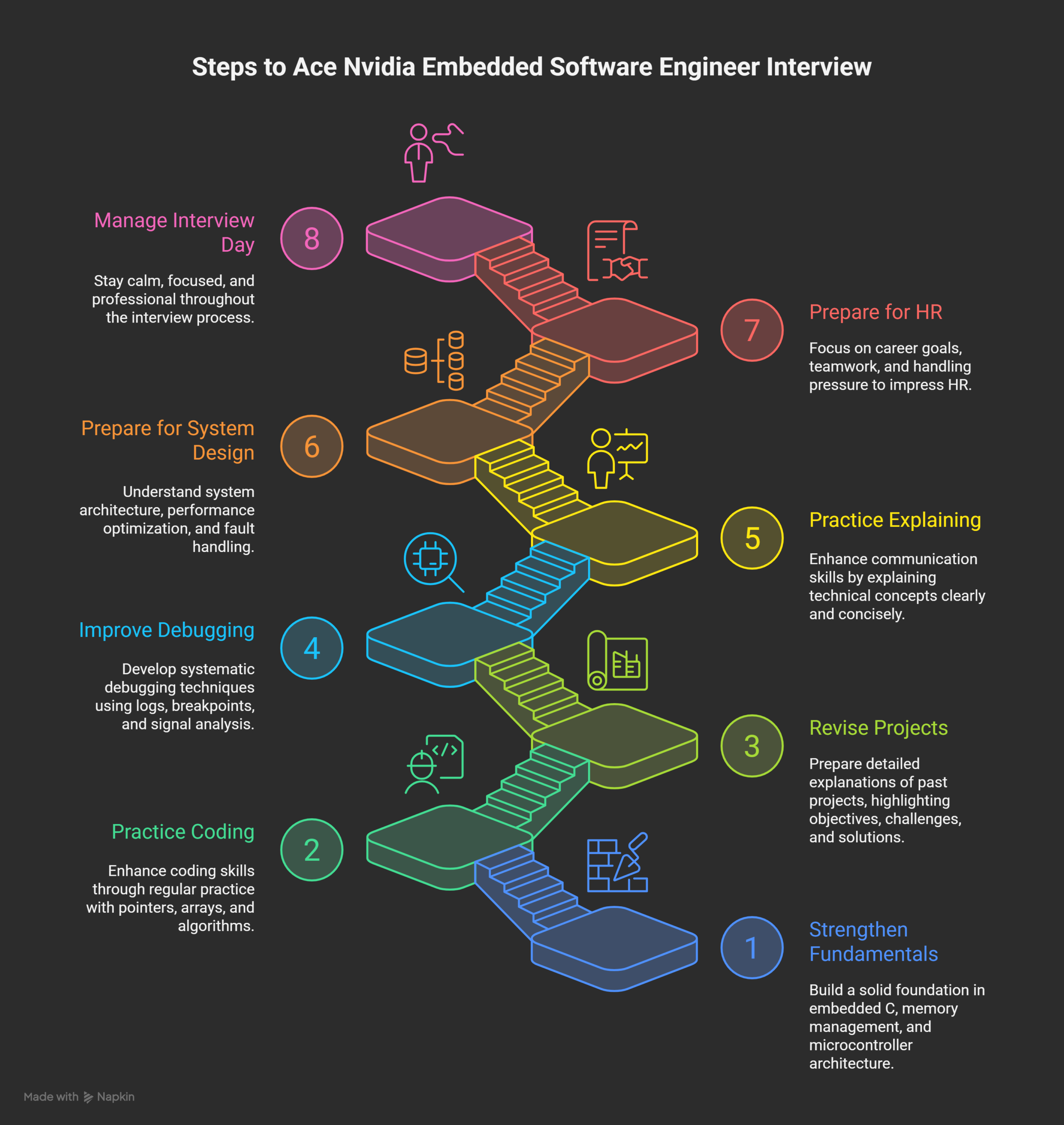
Strengthen Embedded Fundamentals Thoroughly
Embedded fundamentals form the interview foundation. Most interview questions originate from basic concepts. Weak fundamentals cause difficulty in advanced discussions.
Key Fundamental Areas to Revise
-
Embedded C programming basics
-
Memory management concepts
-
Microcontroller architecture fundamentals
-
Interrupt handling principles
-
Communication protocol basics
How to Strengthen Fundamentals
Revise concepts using simple explanations. Avoid memorizing definitions blindly. Understand why concepts exist practically. Relate concepts to real hardware behavior.
Practice Coding Regularly and Consistently
Coding ability is evaluated in multiple rounds. Interviewers observe logic clarity closely. Regular coding practice improves speed and accuracy.
Coding Topics to Practice Frequently
-
Pointer based programs
-
Array and string manipulation
-
Bit manipulation problems
-
Loop and conditional logic
-
Simple algorithmic problems
Best Coding Practice Approach
Write code without library functions initially. Focus on correctness before optimization. Practice explaining logic while coding. Review mistakes to avoid repetition.
Revise Projects in Complete Detail
Project discussion carries significant interview weight. Interviewers validate actual hands on experience. Poor project explanations reduce credibility.
What to Prepare for Each Project
-
Project objective and application
-
Hardware platform selection reasoning
-
Software architecture design
-
Communication protocols used
-
Major challenges faced
-
Solutions implemented successfully
Project Explanation Tips
Explain projects step by step clearly. Use simple language during explanations. Avoid exaggerating individual responsibilities. Honesty builds strong interviewer trust.
Improve Debugging and Problem Solving Skills
Debugging approach reflects engineering maturity. Interviewers value systematic troubleshooting methods. Random guessing indicates weak problem solving skills.
Debugging Skills to Develop
-
Log based debugging techniques
-
Breakpoint and register analysis
-
Signal analysis using tools
-
Root cause identification
How to Explain Debugging During Interviews
Describe issue identification clearly. Explain tools used for debugging. Show logical elimination of causes. Explain final fix implementation.
Practice Explaining Concepts Clearly
Clear explanations influence interviewer evaluation strongly. Technical knowledge alone is insufficient. Communication clarity differentiates strong candidates.
Explanation Practice Methods
- Practice explaining concepts aloud.
- Teach concepts to peers or friends.
- Simplify explanations without losing accuracy.
- Avoid unnecessary technical jargon.
During Interview Explanations
- Pause briefly before answering questions.
- Structure answers logically from basics.
- Use examples wherever possible.
- Maintain calm and confident tone.
Prepare for System Design Discussions
System design rounds test architectural thinking. Interviewers assess trade off understanding carefully. Preparation prevents confusion during open ended questions.
System Design Preparation Areas
-
Embedded system architecture design
-
Performance optimization strategies
-
Power management techniques
-
Reliability and fault handling
System Design Answering Strategy
Clarify requirements before starting design. State assumptions clearly upfront. Explain design components sequentially. Justify design trade offs logically.
Prepare for HR and Behavioral Questions
HR round influences final selection decisions. Technical strength alone is insufficient. Professional attitude matters significantly.
Behavioral Preparation Focus Areas
-
Career goals clarity
-
Teamwork experiences
-
Handling pressure situations
-
Learning from failures
HR Answering Tips
Answer honestly without exaggeration. Keep answers structured and concise. Maintain positive body language. Show willingness to learn continuously.
Manage Interview Day Effectively
Interview day performance depends on preparation discipline. Mental readiness impacts response quality.
Interview Day Best Practices
-
Revise basics lightly before interview
-
Avoid learning new topics last minute
-
Stay calm and focused
-
Listen carefully to each question
During the Interview
Ask clarifying questions when needed. Take short pauses before answering. Admit knowledge gaps honestly. Maintain professional demeanor throughout.
Final Advice for Success
Consistent preparation creates strong confidence. Strong fundamentals support advanced discussions. Clear explanations improve interviewer perception. Honesty builds credibility and trust. Calm thinking improves problem solving quality. Focused effort significantly increases selection chances.
Master Embedded Systems Programming!
Launch your tech career with our Embedded Systems Course in Kerala, designed for hands-on learning and industry readiness.
Know MoreConclusion
Success in the NVIDIA embedded interview comes from disciplined preparation. Strong fundamentals build confidence during challenging technical discussions. Practical understanding always outperforms memorized theoretical answers. Clear explanations help interviewers trust your engineering capability. Consistent effort transforms complex concepts into familiar strengths. Every interview question becomes manageable with structured preparation.
This interview is an opportunity to showcase real engineering potential. Challenges during preparation shape stronger problem solving skills. Each practice session moves you closer to technical excellence. Stay curious, calm, and confident throughout the process. Believe in your preparation and engineering mindset. Your focused effort can turn ambition into achievement.
Master Embedded Systems Programming!
Launch your tech career with our Embedded Systems Course in Kerala, designed for hands-on learning and industry readiness.
Know MoreFrequently Asked Questions
What does Nvidia look for in an Embedded Software Engineer interview?
In an Embedded Software Engineer interview, NVIDIA looks for candidates with strong practical engineering fundamentals rather than surface-level theoretical knowledge. Interviewers closely evaluate how well candidates understand embedded C, memory management, hardware–software interaction, and system-level behavior. Problem-solving approach, debugging methodology, and logical reasoning are given higher importance than speed or memorized answers. Candidates who can clearly explain why certain design decisions were made usually perform better. Calm communication under technical pressure is also an important evaluation factor.
How is the Nvidia Embedded Software Engineer interview process structured?
The Nvidia interview process is typically structured into multiple stages, each focusing on a different competency area. It usually begins with an online coding or written assessment that tests programming fundamentals such as C or C++. This is followed by one or more technical interview rounds that assess embedded systems knowledge, hardware understanding, and real-world problem-solving ability. Candidates then participate in a detailed project discussion round, where interviewers validate actual hands-on experience. Some roles also include a system design interview, and the process concludes with an HR or behavioral discussion.
Which programming languages should be prepared for Nvidia embedded interviews?
Embedded C is the most critical programming language to prepare for Nvidia embedded interviews. Candidates are expected to demonstrate deep understanding of pointers, memory usage, bit manipulation, and low-level programming concepts. C++ is also important, especially for roles involving system software, abstraction layers, or performance-critical modules. While scripting languages such as Python may be used internally for testing or automation, they are not the primary focus during interviews. Strong fundamentals in C and C++ remain essential for success.
What Embedded C concepts are most commonly asked during interviews?
Interviewers frequently ask questions related to pointer handling, arrays, structures, unions, and memory behavior in embedded environments. Topics such as the use of const and volatile keywords, static variables, and stack versus heap memory are common. Candidates should also be comfortable with bitwise operations and register-level programming. Many questions are scenario-based, requiring candidates to explain how C code interacts with hardware. Understanding the practical implications of these concepts is more important than recalling definitions.
How important is RTOS knowledge for Nvidia Embedded Software Engineer roles?
RTOS knowledge is highly valuable and often expected, especially for mid-level and senior roles. Interviewers assess understanding of task scheduling, priorities, context switching, and inter-task communication mechanisms. Concepts such as mutexes, semaphores, queues, and priority inversion are frequently discussed. Candidates who can explain real-time constraints and deterministic system behavior using examples from their projects stand out. Practical RTOS experience significantly strengthens a candidate’s interview performance.
Does Nvidia test Embedded Linux concepts during interviews?
Yes, Embedded Linux concepts are often tested, particularly for roles involving complex system software or SoC platforms. Interviewers may ask about the Linux boot process, including bootloaders, kernel initialization, and user space startup. Knowledge of device drivers, device trees, and kernel versus user space separation is important. Power management, performance tuning, and debugging Linux-based embedded systems may also be discussed. Hands-on Linux experience is considered a strong advantage.
What level of hardware knowledge is expected from candidates?
Candidates are expected to have a solid understanding of microcontroller or SoC architecture. This includes knowledge of CPU cores, memory maps, peripherals, interrupt controllers, timers, and DMA. Interviewers often test how software interacts with hardware registers and peripherals. Familiarity with ARM architecture, cache behavior, and clock domains is beneficial. Candidates with experience in board bring-up or low-level hardware debugging generally perform better.
Which communication protocols should candidates prepare for?
Common communication protocols tested include UART, SPI, I2C, and CAN. Interviewers expect candidates to understand how these protocols work internally, not just their definitions. Questions may involve timing, synchronization, addressing, arbitration, and error handling. Candidates are often asked to compare protocols and choose the appropriate one for a given application. Explaining real project usage of these protocols significantly strengthens answers.
How are project discussions evaluated during Nvidia interviews?
Project discussions are a critical part of the interview process and are used to validate real engineering experience. Interviewers focus on the candidate’s individual contribution rather than team-level descriptions. They evaluate understanding of system architecture, design choices, and trade-offs made during development. Debugging challenges, failures, and lessons learned are discussed in depth. Clear, honest explanations help build strong interviewer confidence.
How should candidates prepare to succeed in Nvidia Embedded Software Engineer interviews?
Successful preparation involves strengthening embedded fundamentals, practicing coding regularly, and revising projects thoroughly. Candidates should focus on explaining concepts clearly rather than memorizing answers. Developing a systematic debugging approach and system-level thinking is essential. Practicing mock interviews and explaining solutions aloud helps improve communication clarity. Consistent, structured preparation significantly increases the chances of success.