Table of Contents
Organizational leadership is all about guiding people, shaping a positive work culture, and helping a company move toward its goals with clarity and purpose. It goes beyond just managing tasks—organizational leadership focuses on inspiring teams, solving problems, and making decisions that create long-term success. Whether you’re a student, a professional, or someone exploring leadership roles, understanding how organizational leadership works can open the door to exciting career opportunities and personal growth.
Begin Your Personality Transformation- Enroll Today!
Introduction
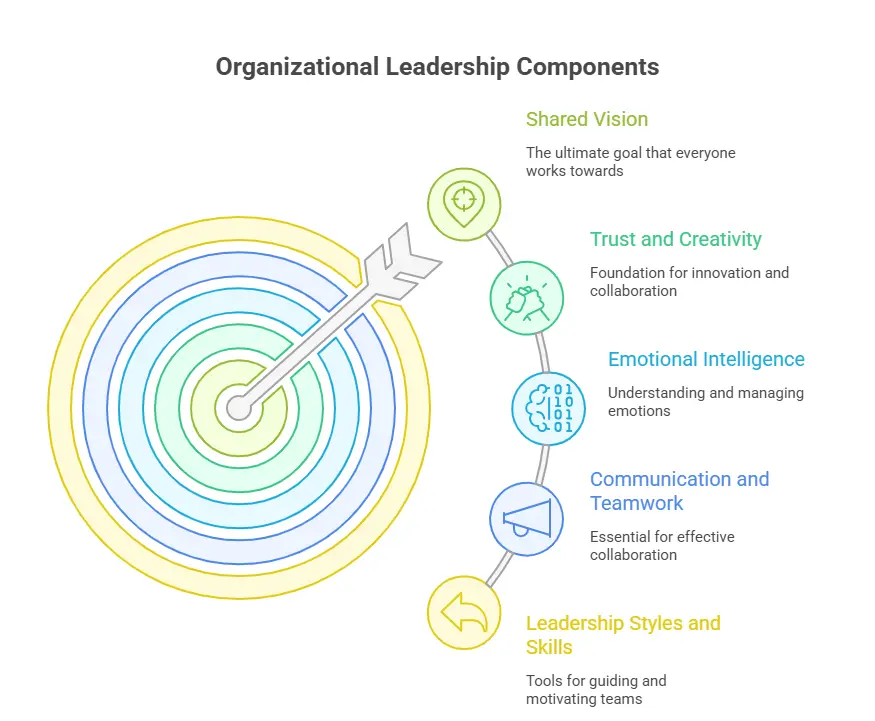
Organizational leadership is a modern approach to leading people and managing workplaces in a smarter, more meaningful way. In today’s fast-changing world, businesses need leaders who can think strategically, motivate employees, and create an environment where everyone works toward a shared vision. This is where organizational leadership becomes important.
Unlike traditional leadership—which often focuses on authority and task control—organizational leadership emphasizes communication, teamwork, emotional intelligence, and long-term planning. It’s about understanding how people behave within a company, what keeps them motivated, and how their strengths can be used to achieve success. Leaders in this field aim to build trust, encourage creativity, and guide teams through challenges with confidence.
Whether you’re leading a small team or managing an entire department, organizational leadership helps you make better decisions, improve work culture, and drive positive change. With the right mix of leadership styles, essential skills, and continuous learning, anyone can grow into a strong and effective organizational leader. This blog explores what organizational leadership really means, the different styles leaders use, the skills required, and the career paths available for those who want to build a future in this exciting field.
Understanding Organizational Leadership
Organizational leadership is the ability to guide people in a workplace toward shared goals in a positive and effective way. It focuses on helping teams work well together, making smart decisions, and creating a work environment where everyone feels motivated and supported.
1. Leadership Beyond Management
Organizational leadership is more than assigning tasks or supervising employees. It focuses on guiding, supporting, and motivating people so they can perform at their best. Instead of controlling work, leaders build strong relationships and create an environment where ideas and teamwork thrive.
2. The Human Side of Leadership
A major part of organizational leadership is understanding people — their strengths, challenges, motivations, and emotions. Leaders who recognize what their team needs can inspire trust, boost morale, and help employees feel valued and engaged.
3. Seeing the Bigger Picture
Organizational leaders are strategic thinkers. They plan for the future, analyze business challenges, and make decisions that help their teams and the company move forward. This big-picture thinking helps leaders guide teams through change with confidence.
4. Building a Healthy Work Culture
A positive workplace culture is essential for success. Organizational leaders focus on fairness, collaboration, and open communication. They create an atmosphere where employees feel safe to share ideas, solve problems, and grow professionally.
5. Encouraging Growth and Adaptability
Good leaders help teams improve continuously. They encourage learning, support new ideas, and guide employees during challenges. This mindset of growth and adaptability helps the organization stay strong even during fast-changing times.
Boost Your Skills & Kickstart Your Career!
Employability and Personality Development Course by Entri App: Enhance your communication, confidence, and job-ready skills to excel in your career.
Join Now!Key Styles of Organizational Leadership
1. Autocratic Leadership
Autocratic leaders make decisions on their own and expect others to follow instructions. They maintain full control and give clear, direct commands. This style is useful in situations where quick action is needed or when a team lacks experience. However, it can sometimes make employees feel unheard or restricted because there is little room for discussion or creativity.
When it works best: Emergencies, high-risk environments, or teams needing strong direction.
2. Democratic Leadership
Democratic leaders value teamwork and encourage employees to share ideas and opinions before making decisions. They believe that involving the team leads to better solutions and stronger commitment. This style creates a positive work culture where people feel respected and appreciated. However, decision-making can take longer since everyone is included in the process.
When it works best: Creative teams, group projects, or companies that prioritize innovation and collaboration.
3. Transformational Leadership
Transformational leaders focus on inspiring and motivating people to grow, think creatively, and work toward long-term goals. They create a strong vision for the future and energize the team with enthusiasm and support. These leaders encourage change, new ideas, and continuous improvement. However, this style requires strong communication skills and genuine passion.
When it works best: Fast-growing companies, organizations undergoing change, or teams that need inspiration.
4. Transactional Leadership
In this style, leaders use a system of rewards and consequences to guide performance. Employees know exactly what is expected, and they receive benefits like bonuses or recognition when they meet their goals. This approach works well in structured environments where tasks are clear. However, it may limit creativity because employees focus mainly on meeting targets.
When it works best: Sales teams, customer service roles, or tasks that require consistency.
5. Servant Leadership
Servant leaders prioritize the well-being and growth of their team above everything else. They believe that by supporting their employees—listening to their needs, removing obstacles, and providing resources—the team will naturally become more productive. This style builds strong trust and loyalty, but it may seem slow in very competitive environments.
When it works best: Nonprofits, educational institutions, or organizations that value empathy and teamwork.
6. Laissez-Faire Leadership
This hands-off leadership style gives employees lots of freedom to make decisions and manage their own work. It works best when the team is experienced, self-motivated, and skilled. However, without enough guidance, some employees may feel lost or confused, leading to delays or low productivity.
When it works best: Creative industries, research teams, or workplaces with highly skilled professionals.
7. Situational Leadership
Situational leaders adapt their leadership style based on what the team needs at a given moment. They may be firm and directive with new employees but more relaxed and supportive with skilled workers. This flexibility makes the leader effective in many situations, but it requires strong awareness and understanding of the team’s abilities.
When it works best: Dynamic workplaces, fast-changing industries, or teams with mixed skill levels.
Essential Skills for Effective Organizational Leaders
Organizational leaders are more than managers—they inspire, guide, and support their teams to achieve goals while creating a positive work environment. To do this effectively, certain skills are essential. Here’s a detailed look at the key skills every successful organizational leader should have:
1. Communication Skills
Effective leaders must be able to express ideas clearly and listen actively. Good communication helps in giving instructions, sharing vision, resolving conflicts, and building strong relationships. Leaders who communicate well create trust and reduce misunderstandings in the workplace.
Example: Explaining a project plan in simple terms so everyone understands their role.
2. Emotional Intelligence (EI)
Emotional intelligence is the ability to recognize, understand, and manage your own emotions while being aware of others’ feelings. Leaders with high EI can handle stressful situations calmly, empathize with team members, and resolve conflicts effectively.
Example: Comforting an employee going through a difficult time while keeping team morale high.
3. Decision-Making Skills
Leaders often face tough choices that affect their teams and the organization. Strong decision-making involves analyzing situations, weighing options, and choosing the best course of action. Good leaders make informed decisions that balance short-term and long-term goals.
Example: Choosing the best strategy to meet a tight deadline without overwhelming the team.
4. Strategic Thinking
Strategic thinking is the ability to see the bigger picture and plan for the future. Leaders with this skill anticipate challenges, identify opportunities, and align team efforts with organizational goals. It helps in making decisions that drive long-term success.
Example: Planning resource allocation for the next year to meet growth targets.
5. Adaptability and Flexibility
The business world is constantly changing. Leaders must be able to adapt to new situations, learn quickly, and guide their teams through change. Flexible leaders can adjust strategies, respond to unexpected challenges, and encourage their team to do the same.
Example: Shifting a marketing campaign strategy due to sudden market changes.
6. Conflict Resolution Skills
Conflicts are natural in any workplace. Leaders who can address disputes calmly and fairly maintain team harmony and productivity. Effective conflict resolution prevents misunderstandings from escalating and keeps the focus on goals.
Example: Mediating a disagreement between team members over responsibilities.
7. Delegation and Empowerment
Good leaders know they cannot do everything alone. Delegation involves assigning tasks based on employees’ strengths, while empowerment gives team members the confidence and resources to succeed. This not only improves efficiency but also motivates employees.
Example: Assigning a critical project to a capable team member and trusting them to handle it independently.
8. Problem-Solving Skills
Leaders face challenges regularly. Strong problem-solving skills allow them to identify issues, analyze causes, and find effective solutions quickly. This skill ensures smooth operations and keeps the team focused on achieving objectives.
Example: Resolving a technical issue that is delaying a project deadline.
9. Team-Building Skills
Effective leaders know how to create a cohesive and motivated team. They encourage collaboration, recognize achievements, and foster a sense of belonging. Strong teams perform better and are more resilient.
Example: Organizing team activities to improve cooperation and morale.
10. Vision and Goal Setting
Leaders must have a clear vision for their team and organization. They set achievable goals and guide their team toward them with clarity and motivation. A clear vision gives purpose and direction, inspiring employees to work together.
Example: Outlining a roadmap for a product launch and inspiring the team to meet deadlines successfully.
Begin Your Personality Transformation- Enroll Today!
Organizational Leadership vs Traditional Management
While the terms “leadership” and “management” are often used interchangeably, they are different approaches in how people guide and influence a team or organization. Understanding these differences helps individuals and companies develop a more effective work environment.
1. Focus and Approach
- Organizational Leadership: Focuses on inspiring, motivating, and guiding people. Leaders aim to create a shared vision, encourage teamwork, and develop employees’ potential. It’s more about people than processes.
- Traditional Management: Focuses on planning, organizing, and controlling tasks. Managers ensure that rules, procedures, and deadlines are followed efficiently. It’s more about processes and structure than people.
2. Goal Orientation
- Organizational Leadership: Works toward long-term growth and innovation, emphasizing vision, culture, and adaptability. Leaders think about how to inspire change and improve the organization over time.
- Traditional Management: Focuses on short-term results and task completion, ensuring that projects are done on time, within budget, and according to plan.
3. Decision-Making Style
- Organizational Leadership: Encourages collaboration and input from the team. Decisions are often based on discussion, creativity, and strategic thinking.
- Traditional Management: Decisions are top-down, made by managers or supervisors, and employees are expected to follow instructions.
4. Employee Engagement
- Organizational Leadership: Prioritizes employee growth, motivation, and engagement. Leaders mentor, coach, and empower team members to reach their full potential.
- Traditional Management: Focuses on task performance and compliance. Employees are often guided to meet expectations without necessarily developing new skills.
5. Flexibility and Innovation
- Organizational Leadership: Highly flexible, encourages innovation, new ideas, and adaptability. Leaders thrive in dynamic environments and embrace change.
- Traditional Management: More rigid, relies on rules, procedures, and standardized processes. Change is implemented slowly and cautiously.
6. Relationship with the Team
- Organizational Leadership: Builds trust, collaboration, and long-term relationships. Leaders listen, communicate openly, and value employees’ input.
- Traditional Management: Maintains a hierarchical relationship. Communication is often formal, and authority is emphasized.
| Aspect | Organizational Leadership | Traditional Management |
|---|---|---|
| Focus | People, vision, culture | Tasks, rules, procedures |
| Goal | Long-term growth and innovation | Short-term results |
| Decision-making | Collaborative, inclusive | Top-down, directive |
| Employee engagement | Motivation, development | Compliance, task completion |
| Flexibility | High, encourages innovation | Low, follows procedures |
| Team relationship | Trust and collaboration | Hierarchical and formal |
Boost Your Skills & Kickstart Your Career!
Employability and Personality Development Course by Entri App: Enhance your communication, confidence, and job-ready skills to excel in your career.
Join Now!Career Paths in Organizational Leadership
Organizational leadership is a dynamic field that offers exciting opportunities across industries. Leaders are needed in businesses, nonprofits, education, healthcare, and government. Pursuing a career in this area allows you to influence teams, shape organizational culture, and drive success. Here’s a detailed look at some common career paths:
1. Team Leader / Supervisor
This is often an entry-level leadership role where you oversee a small team, coordinate tasks, and ensure goals are met. Team leaders develop essential skills like communication, conflict resolution, and task management, which are crucial for growth.
Example roles: Project Team Leader, Department Supervisor, Shift Supervisor
2. Department or Functional Manager
Managers are responsible for specific departments or functions within an organization, such as marketing, operations, finance, or HR. They focus on strategy, resource allocation, and team performance. Leadership skills like decision-making, delegation, and strategic planning are critical here.\
Example roles: Operations Manager, Marketing Manager, HR Manager
3. Organizational Development Specialist
This role focuses on improving organizational effectiveness by designing training programs, improving processes, and guiding change initiatives. Professionals in this area combine leadership with analytical skills and a deep understanding of organizational behavior.
Example roles: Organizational Development Consultant, Training Manager, Change Management Specialist
4. Director / Senior Manager
Directors lead larger teams or entire departments, overseeing strategy, budgeting, and long-term goals. They are often involved in shaping company policies and mentoring mid-level managers. Strong vision, communication, and strategic thinking are key.
Example roles: Director of Operations, Director of Human Resources, Director of Sales
5. Executive Leadership / C-Suite Roles
At the top level, executives define the vision and strategic direction of the organization. They make high-level decisions that impact the entire company and represent the organization to stakeholders. This career path requires advanced leadership skills, experience, and the ability to inspire large teams.
Example roles: CEO (Chief Executive Officer), COO (Chief Operating Officer), CFO (Chief Financial Officer)
6. Entrepreneur / Business Owner
Organizational leadership skills are also essential for entrepreneurs. Leading a business involves setting a vision, building a team, and guiding growth, all of which require strong leadership, decision-making, and problem-solving abilities.
Example roles: Founder, Startup CEO, Business Owner
7. Nonprofit and Community Leadership
Leaders are also needed in the nonprofit and social sector, where they drive social change, manage volunteers, and coordinate programs. This path is ideal for those passionate about making a positive impact while applying leadership skills.
Example roles: Nonprofit Director, Program Manager, Community Outreach Leader
How to Develop Organizational Leadership Skills
Becoming an effective organizational leader doesn’t happen overnight. It requires continuous learning, self-awareness, and practical experience. Here’s a detailed guide on how to develop these essential skills:
1. Improve Communication Skills
Strong communication is the foundation of leadership. Leaders must clearly convey ideas, actively listen, and adapt their communication style to different team members.
Tips to improve:
- Practice active listening
- Give clear instructions and feedback
- Learn public speaking and presentation skills
2. Build Emotional Intelligence (EI)
Emotional intelligence helps leaders understand their own emotions and those of others, fostering empathy and better relationships. Leaders with high EI handle conflicts calmly and create a positive work environment.
Tips to improve:
- Reflect on your emotional responses
- Practice empathy and perspective-taking
- Learn to manage stress effectively
3. Strengthen Decision-Making and Problem-Solving
Leaders face challenges every day. Developing critical thinking, analytical skills, and confidence is key to making informed decisions.
Tips to improve:
- Analyze situations from multiple angles
- Weigh pros and cons before making decisions
- Learn from past successes and mistakes
4. Develop Strategic Thinking
Strategic leaders focus on the bigger picture and plan for long-term success. They anticipate challenges and identify opportunities for growth.
Tips to improve:
- Study your industry trends
- Set long-term goals for yourself and your team
- Practice scenario planning and risk assessment
5. Enhance Team-Building Skills
Strong leaders know how to bring people together, motivate them, and build trust. Team-building skills ensure collaboration and productivity.
Tips to improve:
- Encourage collaboration and idea sharing
- Recognize and reward team efforts
- Facilitate team activities to strengthen bonds
6. Gain Practical Leadership Experience
The best way to develop leadership skills is by taking on real responsibilities. Practical experience teaches you how to handle challenges and apply leadership principles.
Tips to improve:
- Volunteer for team lead roles or projects
- Mentor or coach junior colleagues
- Participate in leadership workshops or training programs
7. Embrace Continuous Learning
Leadership is a constantly evolving skill. Effective leaders adapt, learn, and grow with new experiences, technologies, and workplace dynamics.
Tips to improve:
- Read books or take courses on leadership
- Attend webinars and networking events
- Seek feedback and self-reflect regularly
8. Practice Adaptability and Resilience
Leaders often face uncertainty, challenges, and change. Being flexible and resilient helps leaders guide their teams confidently.
Tips to improve:
- Stay calm under pressure
- Adjust strategies when necessary
- Learn from failures and keep moving forward
Begin Your Personality Transformation- Enroll Today!
Conclusion
Developing strong organizational leadership skills is key to guiding teams, making informed decisions, and achieving long-term success. It’s not just about managing tasks—it’s about inspiring people, building trust, and creating a positive work environment. By improving communication, emotional intelligence, strategic thinking, and adaptability, anyone can grow into an effective leader. With continuous learning and practical experience, these skills become natural, helping you lead confidently and make a meaningful impact in any organization.
Boost Your Skills & Kickstart Your Career!
Employability and Personality Development Course by Entri App: Enhance your communication, confidence, and job-ready skills to excel in your career.
Join Now!Frequently Asked Questions
What is organizational leadership?
Organizational leadership is the ability to guide, inspire, and manage people within a workplace to achieve common goals. It focuses on building trust, motivating teams, making strategic decisions, and creating a positive work environment rather than just managing tasks.
How is organizational leadership different from traditional management?
While traditional management focuses on tasks, rules, and processes, organizational leadership emphasizes people, vision, and culture. Leaders motivate, mentor, and inspire employees, whereas managers ensure that work is completed efficiently according to procedures.
What are the key styles of organizational leadership?
The main leadership styles include:
- Autocratic: Leader makes decisions alone.
- Democratic: Decisions are made collaboratively with team input.
- Transformational: Inspires innovation and motivates growth.
- Transactional: Focuses on rewards and rules.
- Servant: Puts employees’ needs first.
- Laissez-Faire: Hands-off, giving employees freedom.
- Situational: Adapts style based on the team and situation.
What essential skills do organizational leaders need?
Effective leaders need:
- Strong communication and active listening
- Emotional intelligence and empathy
- Decision-making and problem-solving
- Strategic thinking and vision
- Team-building and delegation
- Adaptability and resilience
Can anyone become an organizational leader?
Yes. Leadership is a skill that can be learned and developed over time. With practice, continuous learning, and self-awareness, anyone can grow into an effective organizational leader regardless of their starting role.
What career opportunities exist in organizational leadership?
Organizational leadership offers roles such as:
- Team Leader / Supervisor
- Department or Functional Manager
- Organizational Development Specialist
- Director / Senior Manager
- Executive Leadership (CEO, COO, CFO)
- Entrepreneur / Business Owner
- Nonprofit or Community Leader
How can I develop my organizational leadership skills?
You can develop leadership skills by:
- Improving communication and emotional intelligence
- Gaining practical leadership experience
- Practicing decision-making and problem-solving
- Attending workshops and training programs
- Learning strategic thinking and team-building
- Being adaptable and resilient
Why is organizational leadership important for businesses?
Strong organizational leadership ensures high employee engagement, better teamwork, and long-term growth. Leaders guide the company through challenges, inspire innovation, create a positive culture, and help employees reach their full potential, which ultimately drives business success.