Table of Contents
Key Takeaways:
- Embedded engineering is one of the most promising and future-proof career options for CS graduates in 2025 and beyond.
- With IoT, robotics, AI, and automotive tech booming, demand for embedded engineers is rising globally.
- CS graduates already have strong programming fundamentals, making it easier to transition into embedded systems.
- Salaries, career growth, and opportunities in R&D are significantly higher in this domain.
- Courses like Entri Embedded Systems are the quickest way for CS students to bridge hardware gaps, gaining practical confidence and placement support.
- The future is not pure hardware or software; it’s a fusion, and CS graduates have the keys to unlock embedded innovation.
Introduction:
When people think of embedded systems, the silent computing brains behind smartwatches and medical devices to modern cars, they assume it’s an ECE (Electronics and Communication Engineering) domain. It’s true: ECE students spend semesters studying signal theory, circuit design, and microcontrollers, hours bent over breadboards and debugging electrical mishaps.
But when hiring managers in top tech companies review CVs and interview for embedded software engineering roles, a curious pattern emerges again and again. The ones who score highest, adapt fastest, and grow rapidly in embedded careers aren’t the ‘hardware wizards’; they’re Computer Science (CS) graduates, whose deeper coding foundation gives them a huge head start in this software-driven field.
Why is this? Here’s the real-world breakdown behind this surprise and why smart software engineers are being recruited and coveted for embedded roles.
Kickstart your embedded systems career and turn your tech passion into high-demand skills!
What is Embedded Engineering?
Embedded engineering is about designing software and hardware systems that make devices do specific things. Unlike general purpose software (like apps on your phone), embedded systems are designed to run on limited resources.
For example:
- A pacemaker uses embedded systems to regulate heartbeats.
- An autonomous car uses embedded engineering for sensors and navigation.
- Your washing machine has embedded software that optimizes wash cycles.
These examples show that embedded engineers work on real-world problem-solving with a huge impact.
Master Embedded Systems Programming!
Launch your tech career with our Embedded Systems Course in Kerala, designed for hands-on learning and industry readiness.
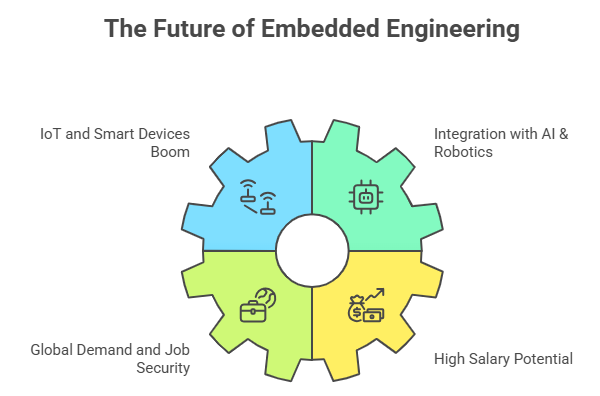
Know MoreWhy Embedded Engineering is the Future
1. IoT and Smart Devices Boom
IoT has changed industries. Every connected device, from Alexa to industrial robots, needs embedded systems.
- By 2025, IoT will be worth $1.5 trillion, making embedded engineers essential.
2. Integration with AI & Robotics
CS graduates dream of working in AI or robotics. But did you know AI needs embedded systems to run on edge devices? Robotics, drones, and autonomous vehicles need embedded engineers.
3. Global Demand and Job Security
Demand for embedded engineers is outstripping supply. Companies in USA, Germany and Japan are hiring big time, making this career recession-proof.
4. High Salary Potential
A generic software engineer might start with ₹4-6 LPA in India, an embedded engineer starts at ₹6-10 LPA and senior engineers earn ₹20-35 LPA globally.
The Core Skill Gap: Coding is Harder to Teach than Hardware
Walk into any electronics classroom in India, and you’ll find students surrounded by a mesmerizing tangle of wires, resistors, and capacitors. Labs focus on hands-on circuits, sensor experiments, and signal analysis, a rich preparation for hardware design. However, in most universities, only one semester is dedicated to C programming, and often just at an introductory level.
Contrast this to a CS curriculum, which builds coding proficiency over several years, covering data structures, algorithms, optimization, debugging, and multiple programming languages. CS students develop the kind of fluency in code that simply isn’t possible in a hardware-centric syllabus.
Hiring managers who’ve spent years testing candidates report a remarkable trend: when technical interview panels focus on software problems, whether in C, Embedded C, or logic design, almost 98% of non-CS students hit a wall. Many stumble over basic syntax, struggle with recursion, or fail to optimize code under hardware constraints. Conversely, CS grads breeze through, adapting quickly to hardware application needs.
Why does this matter?
The embedded industry is pragmatic. They need people who can build robust, efficient, and safe firmware to run physical devices. It’s far easier and faster to teach already-capable coders the essentials of hardware than the other way round. The demand is for well-rounded engineers, but if there’s a gap, it’s usually easier to cross from code to wires, not the reverse.
The “Lollipop Effect”: Interviews Reveal the Software Advantage
Ask hiring managers to describe interviews for embedded roles, and they’ll often mention the “lollipop effect”. Present a set of C programming questions to both CS and ECE candidates. CS grads handle these like warm-ups, sometimes wondering why they’re being asked such basic problems, it’s almost too easy.
This isn’t arrogance or an unfair advantage. It points to a fundamental difference in training. CS students spend their formative years mastering C, adapting to new compilers, and solving real-world algorithmic challenges. For them, controlling a microcontroller’s registers via code is a natural next step; for hardware-first candidates, it can be daunting.
Feedback from technical panels, hackathons, and competitive coding rounds confirm this: programming is the single biggest hurdle, not electronic theory. When companies choose, it’s just more efficient to start with those who comfortably manipulate logic, memory, and code, then expand into hardware topics.
In practice:
-
CS grads quickly grasp the quirks of compiler optimization, debugging, and safety standards (like MISRA C).
-
They adapt to new embedded languages faster and write scalable firmware with fewer bugs.
-
They learn hardware protocols and microcontroller interfaces by applying existing software concepts to a new context.
For more on this topic, check out industry interviews and hiring manager insights on YouTube:
Master Embedded Systems Programming!
Launch your tech career with our Embedded Systems Course in Kerala, designed for hands-on learning and industry readiness.
Know MoreThe Real Bridge: Application Software to Firmware
Where CS students shine is in application development, building mobile apps, web servers, and scalable backend services. Embedded systems require a pivot: shifting from “applications” to firmware, the logic and orchestration that controls hardware directly.
Here’s what CS graduates need to master for embedded roles:
-
Microcontroller Architecture: Understanding CPUs, memory blocks, registers, and hardware triggers.
-
Register-Level Programming: Writing code that interacts with hardware-specific instructions and memory spaces.
-
Embedded C Proficiency: Adapting code for constraints, limited memory, real-time deadlines, no operating system.
-
Industry Standards: Learning best practices (MISRA C, AUTOSAR) for safe, reliable, readable code in mission-critical environments.
-
Debugging Embedded Systems: Using JTAG, oscilloscopes, and simulation tools not typically covered in CS curricula.
But here’s the secret: these “hardware specifics” can be taught with hands-on project work and specialized, job-oriented training.
The Industry Reality: Blurred Lines and Explosive Demand
Gone are the days when embedded systems were “hardware only”. Today, even the world’s most famous hardware companies (think Apple, Tesla, Bosch) need engineers who can integrate AI, edge computing, and complex protocols, firmware is the invisible backbone. The industry lives and dies by its ability to iterate firmware, squash bugs fast, and integrate new features safely. That demands deep software talent.
CS grads can specialize in:
-
IoT and smart device development.
-
Automotive control systems, ADAS, and robotics.
-
Medical device firmware and wearable health tech.
-
Aerospace and defense systems.
-
Real-time OS and high-reliability software for industrial automation.
Success stories abound of CS grads who joined embedded teams as firmware engineers and quickly moved into team leadership because they could mentor their peers on code quality and scalable software practices.
Kickstart your systems career and turn your tech passion into high-demand skills!
Bridging the Gap: How Entri Embedded Systems Course Makes CS Graduates Job-Ready
Entri Embedded Systems Courses are designed with exactly these transitions in mind:
-
Embedded C Mastery: The course starts with what CS students excel at C programming, but pushes them into register-level control, interrupt management, and microcontroller interfaces.
-
Hardware Labs and Hands-On Projects: Students build and test real devices, learning PCB design, debugging, and system integration alongside embedded algorithms.
-
Microcontroller Architecture: Detailed modules cover ARM, PIC, and 8051 controllers, so software pros gain hardware confidence fast.
-
IoT and Real-Time Systems: CS grads get real-world exposure to protocols, sensors, and performance optimization, making their software skills relevant to the fast-growing IoT job market.
-
Industry Standards Training: Strict focus on safety guidelines, secure code, and efficient development processes.
-
Career Preparation: Resume, portfolio, and interview prep tailored to embedded job expectations, bridging the gap from app/software developer to embedded engineer.
-
Placement Support: Active networking with recruiters and access to internship/job leads.
Graduates of Entri’s course consistently report rapid onboarding, not just landing jobs, but thriving, thanks to their software edge. ECE students benefit too, but it’s the CS foundation that unlocks the biggest “potential leap.”
Career Spotlight: Real Embedded Engineers
Talk to young engineers in the industry and you’ll hear examples like these:
-
Ankush (CS, Bangalore): Landed a dream role at an automotive firm designing smart dashboard systems. Picked up hardware concepts over three months, but was already sailing through firmware problems from day one.
-
Priya (CS, Kochi): Joined an IoT startup as a junior developer, rapidly advanced to lead teams on device connectivity projects. Her software engineering skills meant she could scale and debug systems quickly, a huge benefit for product launches.
-
Raghav (ECE, Thiruvanthapuram): Had to do a crash course in programming before he could qualify for embedded jobs. Today works alongside CS grads, learning from their code and sharing hardware tips in return.
Conclusion
Are you a CS grad considering embedded systems? Start by sharpening your embedded C, take on hardware mini-projects, and join a focused course like Entri’s Embedded System Program for the confidence, mentorship, and placement support you need.
Ready to make embedded systems your next big leap? The new frontier is open, and CS is the fastest route in.
Master Embedded Systems Programming!
Launch your tech career with our Embedded Systems Course in Kerala, designed for hands-on learning and industry readiness.
Know MoreFrequently Asked Questions
What is the role of an embedded engineer for CS graduates?
An embedded engineer designs, develops, and optimises software and hardware systems for devices like IoT gadgets, automotive systems, and robotics.
Why should CS graduates consider embedded systems?
Their strong programming background aligns perfectly with embedded system development, opening doors to high-paying and future-proof jobs.
What industries hire embedded engineers?
Industries like automotive, consumer electronics, medical devices, robotics, and IoT are major employers.
What is the average salary of an embedded engineer in India?
Freshers earn between ₹6–10 LPA, while experienced professionals can make ₹20 LPA or more.
How can Entri Digital Course help CS graduates in embedded engineering?
Entri Digital Course provides structured training in embedded systems, bridging the gap between academic knowledge and industry requirements.
Is embedded engineering relevant in the AI era?
Absolutely. Embedded systems form the backbone of AI-driven devices, robotics, and IoT products.
Do CS graduates need hardware knowledge to start?
Basic hardware knowledge helps, but strong coding skills give CS graduates a head start.
What are the global opportunities for embedded engineers?
High demand exists in countries like the USA, Germany, Japan, and Singapore due to the IoT and automotive industries.