Table of Contents
In the world of smart, connected devices today, nearly every electronic product, your car’s infotainment system and your phone, for example, relies on embedded software. Behind the scenes, sometimes working anonymously to make all those perfect experiences just keep rolling, are embedded software developers who make sure it all gets done right and runs optimally. They walk that fine line between hardware and software, so they are mission-critical to sectors such as consumer electronics, automotive, healthcare, and aerospace. With organizations reversing the game by adopting IoT and AI, the need for embedded software engineers is on a meteoric ascent. But what do they do? In this blog, we will discuss an embedded software engineer’s work, where he is placed, what skill set is required of him, and what career growth he attains.
Kickstart your embedded systems career and turn your tech passion into high-demand skills!
What is Embedded Software?
Embedded software is a computer program for specific applications in hardware devices and systems. Different from typical desktop or laptop computers, embedded software is used to execute specific tasks in non-computers such as washing machines, clocks, car control modules, or medical devices. Embedded software is typically held in firmware in the appliance, on microcontrollers or microprocessors, and is performance-optimized, efficiency-optimized, and real-time optimized. Embedded software is closely coupled with the hardware that they run on and usually shares similarly adequate constraints like memory, processing, or power. Essentially, it is the “brain” responsible for electronic devices to perform their programmed purposes intelligently and efficiently.
Who is an Embedded Software Engineer?
An embedded software engineer develops, constructs, tests, and maintains embedded system software. These professionals ensure that hardware and software work in harmony by constant interaction with hardware engineers. They should know both hardware components as well as low-level programming languages such as C or assembly code. They are basically the connection that allows electrical devices to work and become “smart.”
Master Embedded Systems Programming!
Launch your tech career with our Embedded Systems Course in Kerala, designed for hands-on learning and industry readiness.
Know MoreKey Roles & Responsibilities
- Creating and designing embedded software for certain hardware configurations.
- Writing C, C++, or assembly code that is optimized and efficient.
- Using actual hardware platforms for software testing and debugging.
- Integrating software with device components in collaboration with hardware engineers.
- Ensuring the system’s dependability and functionality in real time.
- Putting safety and security procedures into action as needed.
- Use tools such as Git to carry out code reviews and version control.
- Drafting documentation for testing and development processes.
- Keeping software up to date for upcoming hardware releases.
Industries That Hire Embedded Software Engineers
Embedded software developers are most desired in numerous industries since they drive intelligent hardware devices. They design ADAS, ECUs, and infotainment systems for the automotive industry. Consumer electronics relies on them to design intelligent TVs, wearables, and home automation products. Aerospace and defense industries use them to develop software for drones, navigation, and avionics. The healthcare industry uses embedded solutions for medical imaging, monitoring devices, and implants. In industrial automation, they develop robotics software, PLCs, and factory equipment. Telecommunications also depends on them for routers, modems, and network-embedded devices. Their diversified work in these sectors makes embedded software engineering a future-oriented and indispensable career with massive career prospects.
Kickstart your embedded systems career and turn your tech passion into high-demand skills!
Required Skills
An embedded software programmer should have the following to be successful as an embedded software programmer:
- Good programming skills in assembly, C, or C++.
- Knowledge of microcontrollers and microprocessors.
- familiarity with real-time operating systems, or RTOS.
- Knowledge of circuit design and digital electronics.
- knowledge of debugging tools, like JTAG and oscilloscopes.
- knowledge of communication protocols, like CAN, SPI, I2C, and UART.
- problem-solving skills and attention to detail.
- Git and CI/CD practices are merely a few of the version control technologies.
- Cross-functional team working soft skills include communication and teamwork.
Master Embedded Systems Programming!
Launch your tech career with our Embedded Systems Course in Kerala, designed for hands-on learning and industry readiness.
Know MoreCareer Growth Path
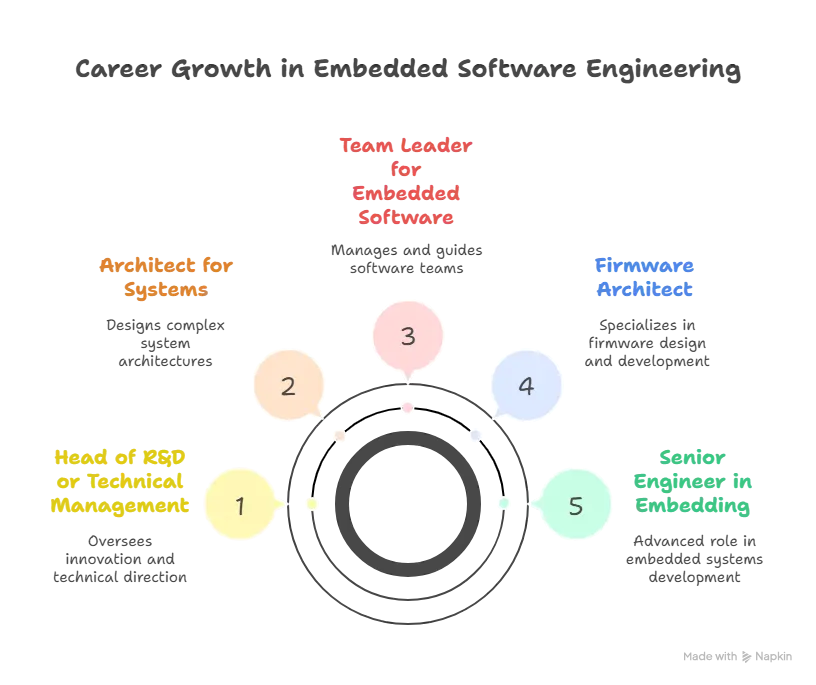
The work of an embedded software engineer usually begins at the junior level, with an emphasis on writing simple code and testing. With further experience, one can go to positions such as
- Developing Embedded Systems
- Senior Engineer in Embedding
- The Firmware Architect
- Team Leader for Embedded Software
- Architect for systems
- Head of R&D or Technical Management
Specialization in fields like automotive systems, IoT, robotics, or cybersecurity is another option available to engineers; each has its growth trajectory and set of difficulties.
Wrapping Up
The foundation of current intelligent systems and smart devices is embedded software developers. They are valuable to various companies due to their capacity to integrate knowledge of software and hardware. As technology is advancing quickly, especially in the areas of automation, artificial intelligence, and the Internet of Things, embedded software developers will play an increased role. Apart from offering technical expertise, this career gives young engineers the opportunity to be engaged in development projects that will shape how technology will change in the future.
Master Embedded Systems Programming!
Launch your tech career with our Embedded Systems Course in Kerala, designed for hands-on learning and industry readiness.
Know MoreFrequently Asked Questions
Which programming languages are used in embedded software development?
The most common languages are C, C++, and sometimes Assembly for low-level control. Python, Rust, or Embedded Java may also be used in higher-level or experimental cases.
Is embedded software engineering a good career?
Absolutely. With the rise of IoT, AI, and smart devices, the demand for embedded engineers is rapidly growing.
Can a fresher become an embedded software engineer?
Yes. With a strong foundation in C/C++, microcontrollers, and basic electronics, freshers can start in junior roles and grow quickly.
Do embedded software engineers need to know hardware?
Yes. While they primarily write software, they must understand the hardware to ensure seamless integration and system performance.
What is the difference between embedded software and regular software?
Embedded software is written for specific hardware and performs dedicated tasks, often with real-time constraints. Regular software (like apps or desktop programs) runs on general-purpose computers with broader functionality.