Table of Contents
Most of the electronic devices we all take for granted on a daily basis are embedded brains in embedded systems. From washing machines and traffic lights to cellphones and smart TVs, embedded systems accurately and reliably govern and regulate device operation. Even automobiles. Unlike general-purpose computers, we designed these systems to perform specific functions through combined hardware and software, often in real time. Typically based on microprocessors or microcontrollers, embedded systems are coded to optimize power usage, performance, and miniaturization. In the telecommunication, industrial automation, automotive, and medical industries, the ability to function independently and interface with the real world makes them invaluable. In this blog post, let’s discuss what are embedded systems , examine their applications in so many different industries, and see how they are changing the future of technology.
What is an Embedded System?
An embedded system uses a microcontroller or microprocessor to become part of a more extensive device and carry out a designated purpose. Embedded systems differ from desktop computers because they conduct specific processes precisely, reliably, and efficiently rather than serving broad usage.
Embedded systems monitor, control, or support equipment functioning by combining hardware (sensors, actuators, processors, etc.) with software (firmware written in languages such Embedded C). Many times restricted resources imply that they run with little memory, computing capability, and energy.
Features of embedded systems:
- Real-time functioning
- Low electricity consumption
- Efficient and reasonably priced
- Operate without human contact
- Dependable and receptive
Where Are Embedded Systems Used?
Almost every modern gadget has an embedded system that does certain jobs in the background. Because they are adept at doing specifically assigned tasks, they are perfect for many uses in many businesses. Embedded systems are a key part of making technology smarter, faster, and more reliable. We use them in everything from simple home items to complicated medical tools and car systems. Let’s look at some real-life examples of how different industries widely use these methods.
1. Consumer Electronics
These are things that we use every day.
- Smartphones: control sensors, how touchscreens work, and battery life
- Smart TVs can handle videos, accept remote controls, and run apps.
- Washing machines: To control the water level, processes, and motor speed, use built-in systems.
- Microwave Ovens: Set timers, manage hot elements, and set safety locks.
2. The automobile industry
These days, cars have a lot of built-in features.
- Anti-lock Braking Systems (ABS): Make sure you can stop safely
- Airbag Control Units set off airbags when a crash happens.
- Infotainment systems handle media, transportation, and talking to other people.
- Engine Control Units (ECUs): Keep an eye on and improve gas mileage
3. Medical tools
Embedded tools make sure that healthcare is accurate and safe.
- Pacemakers control the rate of heartbeats.
- With an insulin pump, you can control the dose and delivery times.
- MRI machines: Take care of the image and scanning processes
- Devices for monitoring patients— Keep an eye on vital signs in real time
4. Automation in Industry
These things help companies work better and safer.
- Programmable Logic Controllers (PLCs): These are machines and processes that you can control.
- Robotic arms: These are used on production lines.
- Sensors and Actuators: Keep an eye on things like movements, temperature, and pressure.
- SCADA systems enable you to monitor and control large industrial processes.
5. Telecommunications:
This is necessary for controlling networks and talking to people.
- Routers and modems handle the sending of data.
- Baseband Processing Units (BPUs) process signals in cell towers.
- Network switches: quickly route data packets
6. Defense and space
They need to be very precise and reliable.
- Flight control systems keep an airplane stable.
- Missile Guidance Systems: Navigation in real time
- Satellite Control Systems: Take care of activities and data
Kickstart your embedded systems career and turn your tech passion into high-demand skills!
Master Embedded Systems Programming!
Launch your tech career with our Embedded Systems Course in Kerala, designed for hands-on learning and industry readiness.
Know MoreFuture of Embedded Systems
Rapid growth in Artificial Intelligence (AI), Machine Learning (ML), and Internet of Things (IoT) is holding out a very promising future for embedded systems. Embedded systems are turning into intelligent decision nodes with learning and self-enhancement capabilities.
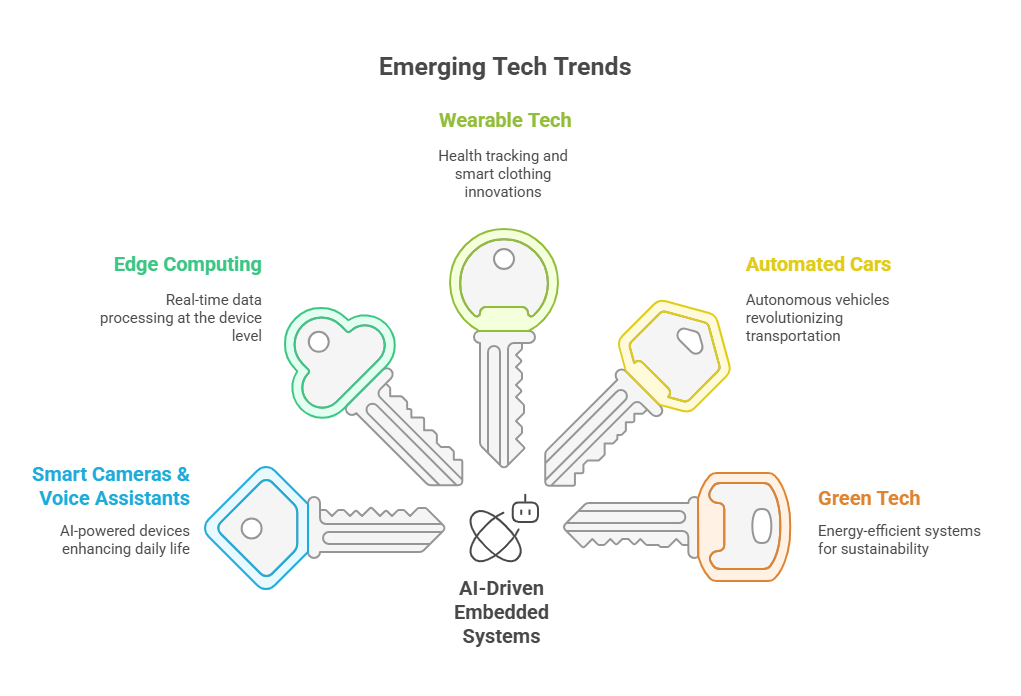
Watch out for these emerging trends:
- Smart cameras and voice assistants are just a few examples of AI-driven embedded systems.
- Edge computing – Doing things in real time at the device
- Wearable tech, such as tracking health and smart clothing
- Automated Cars—Embedded systems play a very significant role in autonomous technology.
- Green Tech: Energy-efficient systems for a greener future
Embedded systems will play a very significant role in smart cities, Industry 4.0, telemedicine, and space exploration because humans desire more automation and connectivity.
Final Thoughts
Embedded systems power thousands of products and systems behind the scenes today. They need them in most locations, from autonomous vehicles to advanced health devices, consumer electronics to consumer goods. Artificial intelligence (AI) and the internet of things (IoT) continue to improve, so integrated systems are becoming smarter, more connected, and more powerful. In the current digital age, knowing embedded systems can be the beginning of new ideas and many job opportunities, whether you are a student, an artist, or a professional expert.
Master Embedded Systems Programming!
Launch your tech career with our Embedded Systems Course in Kerala, designed for hands-on learning and industry readiness.
Know MoreFrequently Asked Questions
What skills are needed to work with embedded systems?
Basic knowledge of C/Embedded C programming, electronics, microcontrollers, and debugging tools is essential. Familiarity with real-time operating systems (RTOS) is also helpful.
What are some popular platforms for learning embedded systems?
Beginners can start with platforms like Arduino, Raspberry Pi, or ESP32, which are well-documented and supported by large communities.
Is Embedded C the only language used in embedded systems?
No. While Embedded C is the most common, other languages like Assembly, Python (MicroPython), and C++ are also used depending on the application and hardware.
What industries hire embedded systems engineers?
Industries such as automotive, aerospace, medical devices, industrial automation, consumer electronics, and telecommunications actively seek embedded systems engineers.
What are real-time embedded systems?
Real-time embedded systems are designed to respond to inputs or events within a strict time limit. Examples include airbag systems, pacemakers, and industrial robots where delays can lead to failure or danger.