Table of Contents
The modern automobile isn’t just a piece of metal and plastic; it’s a complex mix of hardware and software systems. The integrated system is one of the main things that makes this change possible. Embedded systems are very important for improving the speed, safety, and user experience of vehicles. They do a lot of things, from handling engine processes to letting cars drive themselves. Understanding how embedded systems work in the automobile world is important for engineers, coders, and tech fans as cars become smarter and more linked. This blog post will talk about what embedded systems are, what their parts are, how they are used in cars, their pros and cons, the challenges they bring, and the future trends that will shape this ever-changing field.
Kickstart your embedded systems career and turn your tech passion into high-demand skills!
What Are Embedded Systems?
An embedded system is a mixture of hardware and software that serves a dedicated purpose in a larger system. It is “embedded” within a finished device, usually with real-time computing requirements. Embedded systems, unlike general computers, are specifically programmed for a special operation like sensor monitoring, data processing, and actuator control. Embedded systems manage infotainment to engine timing and braking systems in the automotive industry.
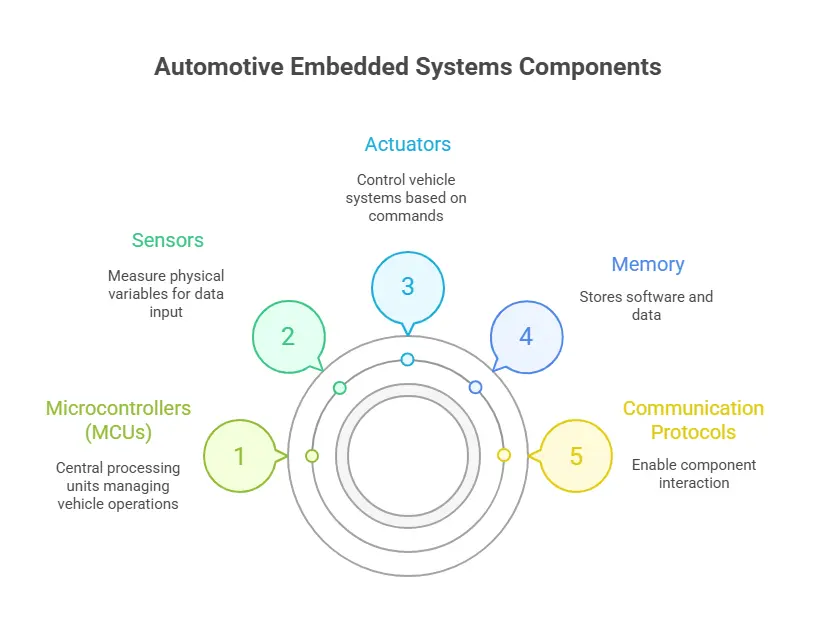
Key Components of Automotive Embedded Systems
- Microcontrollers (MCUs): Miniature computer chips called microcontrollers (MCUs) regulate many operations within a vehicle.
- Sensors: Instruments that measure actual physical variables, like proximity, speed, pressure, and temperature.
- Actuator: Equipment that regulates the brakes or the steering in response to commands from the control system is called an actuator.
- Memory: Software, logs, and real-time data are stored in memory, namely in flash and RAM.
- Communication Protocols: The components can reliably communicate with one another over the following protocols: CAN, LIN, FlexRay, and Ethernet.
- Software: The software used in automobiles includes real-time operating systems (RTOS) and firmware developed for particular uses.
Master Embedded Systems Programming!
Launch your tech career with our Embedded Systems Course in Kerala, designed for hands-on learning and industry readiness.
Know MoreBenefits of Embedded Systems in Automotive
Embedded systems have transformed the automotive industry by providing smarter, safer, and more efficient car features. Some of the primary advantages are discussed below:
1. Improved Safety and Car Handling
Embedded systems are utilized to provide the most critical contribution to the improvement of car safety. Anti-lock Braking Systems (ABS), Electronic Stability Control (ESC), Airbag Deployment, and Advanced Driver Assistance Systems (ADAS) rely on real-time computation to react in milliseconds, reducing accident risk and improving control overall.
2. Less Pollution
Lowering pollution is needed to protect the environment. These standards are met by embedded systems, which measure waste fumes and change how the engine works to make it better.
3. Higher fuel savings
Controlling engine parts like fuel injection, spark timing, and the ratio of air to fuel are some of the ways that embedded systems make burning better. This means that you’ll get better gas mileage and use less fuel.
4. Increased Comfort and Convenience
Modern vehicles offer automated climate control, smart infotainment systems, power seats, and keyless entry—all powered by embedded systems. These features make driving more comfortable and enjoyable.
5. Advanced Diagnostics and Predictive Maintenance
Embedded systems track the health of different components of the vehicle. On-board diagnostics (OBD) warns drivers of problems prior to their occurrence, and predictive maintenance systems can even book repair jobs prior to a breakdown.
6. Real-time Monitoring and Control
From tracking tire pressure to managing electric windows, embedded systems control multiple operations at once, with smooth and hassle-free operation in real-time.
7. Help with connecting and getting electricity
Electric and hybrid cars have integrated systems that handle the batteries, drive the electric motors, and collect energy. They also allow features like Bluetooth, GPS, and car-to-everything (V2X) connection to link to the car.
Master Embedded Systems and build the smart solutions of tomorrow!
Challenges in Automotive Embedded Systems
Embedded systems add knowledge and new ideas to modern cars, but they also come with some problems that engineers and makers need to solve:
1. Complexity of the system
There are 70 to 100 or more Electronic Control Units (ECUs) in modern cars. Each one controls a different function, such as the engine or the entertainment system. A big technical task is to make sure that these systems work well together and don’t interfere with each other.
2. Real-Time Performance Requirements
Many car features, such as deployment of the airbags or ABS, require responses on the order of milliseconds. Real-time operation in nearly all conditions, such as high temperatures and motions, requires hardware and software that are very stable and optimized.
3. Cybersecurity Risks
Cars may be vulnerable since they are becoming more networked (on Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, and V2X). If an untrusted user gains or has access to an embedded system, it can compromise the security and privacy of persons. It is extremely important to apply adequate security controls and encryption.
4. Trouble with power and space
Embedded gadgets need to be small, light, and energy-efficient. It is always hard to build and make things that work with these limitations while still having a lot of processing power. This is especially true for electric and hybrid cars that need to save battery power.
5. Pressures from cost and time to market
OEMs in the auto industry are under a lot of pressure to get new models out quickly and cheaply. It can be hard and risky to make stable embedded systems that meet these goals, especially as software gets more complicated.
6. Combining hardware and software
Hardware (sensors, motors, and controls) and software (firmware and running systems) must work together tightly, according to the developers. Mismatches of any size can cause systems to fail or work less well.
7. Following rules and safety procedures
Embedded systems in cars have to follow strict world rules, such as
- ISO 26262 is about functional safety.
- AUTOSAR helps with building software.
Meeting these rules demands more testing, paperwork, and approval work, which adds to the time it takes to create something.
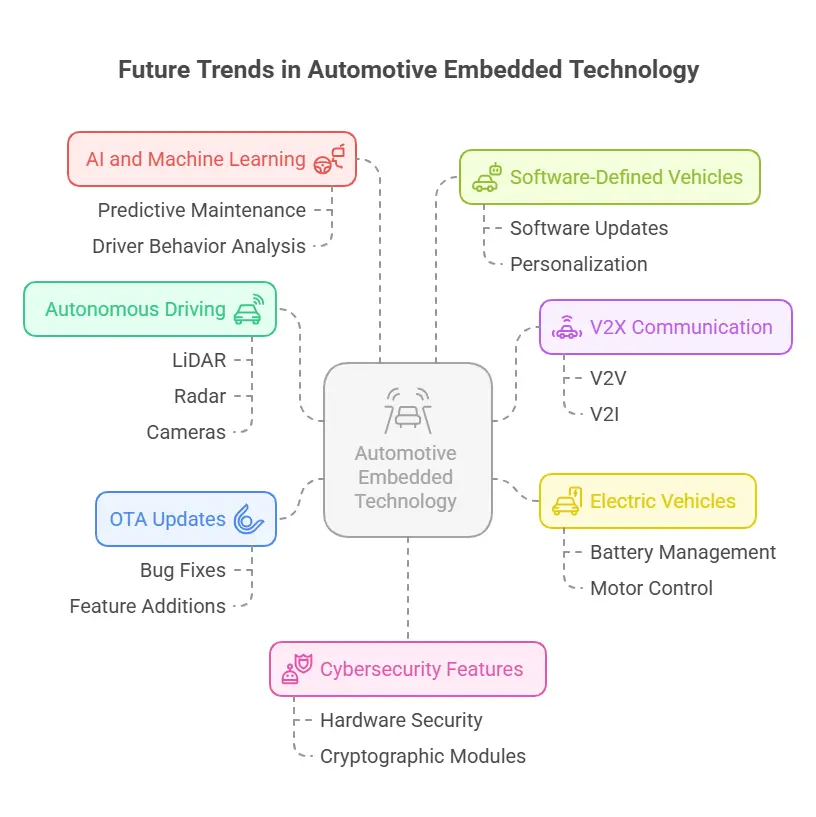
Future Trends
Master Embedded Systems Programming!
Launch your tech career with our Embedded Systems Course in Kerala, designed for hands-on learning and industry readiness.
Know MoreConclusion
Today’s smart and safe cars are made possible by subtle systems called embedded systems. As electric cars, self-driving cars, and cars that can connect to the internet get better, integrated systems will become more important to innovation. Not only do embedded systems make things faster and safer, but they also open the door to new technologies like self-driving cars and smart transport. Auto embedded systems are a fun and challenging job that people who are interested in electronics, programming, and cars can do.
Master Embedded Systems Programming!
Launch your tech career with our Embedded Systems Course in Kerala, designed for hands-on learning and industry readiness.
Know MoreFrequently Asked Questions
What programming languages are commonly used for automotive embedded systems?
Languages like C, C++, MATLAB/Simulink, and Assembly are widely used due to their efficiency and control over hardware. Python and Java may be used in higher-level or infotainment applications.
Are embedded systems used in electric vehicles (EVs)?
Yes, extensively. In EVs, embedded systems manage battery charging, temperature regulation, motor control, regenerative braking, and energy optimization to improve performance and efficiency.
Can a fresher get a job in automotive embedded systems?
Yes, with strong fundamentals in C/C++ and understanding of microcontrollers, real-time systems, and automotive protocols. Projects, internships, and certifications in AUTOSAR, CAN, or Embedded Linux boost employability.
What is ISO 26262?
ISO 26262 is a functional safety standard for automotive electrical/electronic systems. It defines a risk-based approach to ensure the safety of embedded software and hardware, especially in safety-critical functions like braking or steering.
Where do we find embedded systems in a car?
In engine control, airbags, automatic braking, GPS navigation, parking sensors, and even in the AC system.