Table of Contents
Everything from MRI machines to pacemakers now has an embedded system, and that has revolutionized the medical industry. Embedded in medical gadgets are small but sophisticated computers that carry out tests, monitor vital signs, and maintain life in real time. The importance of embedded systems in healthcare is growing, since their accuracy, efficiency, and ability to respond in real-time are crucial.
Intelligent gadgets that are safe, efficient, and dependable are essential in the medical industry. This void may be filled using embedded systems. Medical professionals are able to make better, more timely judgments with the help of embedded systems, which provide error-free communication between hardware and software. In this piece, we’ll define embedded systems, explore their importance in healthcare, and look at how they’re shaping future patient care.
Kickstart your embedded systems career and turn your tech passion into high-demand skills!
What Are Embedded Systems in the Medical Context?
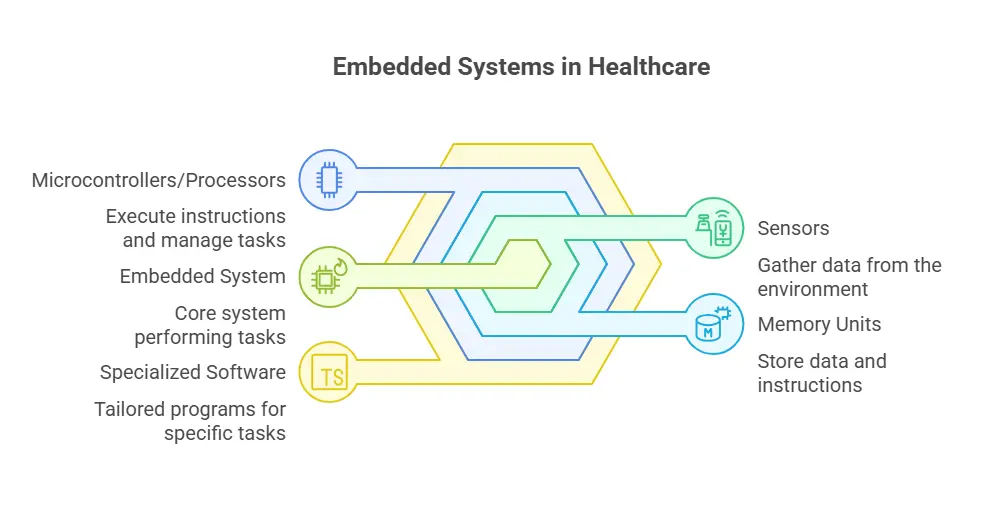
In healthcare, an embedded system is a computer system that is integral to a device for the purpose of performing a certain task. These systems are purpose-built for certain applications, as opposed to generic computers, and can do things like interpret images in diagnostic tools, monitor heart rates, or regulate medicine infusions.
In a typical embedded system, several components, such as sensors, memory units, microcontrollers or microprocessors, and specialized software, collaborate in real-time. They are perfect for wearable, implantable, and portable medical devices because of their small size, dependability, and data processing efficiency.
Why Embedded Systems Are Critical in Healthcare
Healthcare entails high reliability, speed, and accuracy, usually in life-critical circumstances. Embedded systems can facilitate this through the capability of real-time monitoring, control under automation, and medical device decision-making.
Embedded systems are crucial in:
- Continuous patient monitoring
- Reducing human error
- Facilitating personalized treatment
- Workload reduction for healthcare personnel
In high-risk environments such as ICU monitoring or surgery assistance, embedded systems ensure consistent performance, leading to improved patient outcomes and safety.
Master Embedded Systems Programming!
Launch your tech career with our Embedded Systems Course in Kerala, designed for hands-on learning and industry readiness.
Know MoreKey Components of Medical Embedded Systems
Medical embedded systems are built to perform with accuracy, reliability, and performance. Their parts work harmoniously to provide smooth data processing and real-time capabilities. The following are the main parts commonly included in medical embedded systems:
Microcontroller/Microprocessor
- Acts as the primary processor of the device
- Performs some control algorithms and data exchange management
- Mostly used: ARM Cortex, PIC, or AVR microcontrollers
Sensors
- Detect and quantify body signals such as heart rate, blood pressure, temperature, glucose level, or movement
- Translate physical signals into electrical signals to process
Memory
- Stores the system program, configuration information, and patient information
- Accommodates ROM (for system program) and RAM (for real-time program)
Communication Modules
- Allow data to be sent to outside devices or hospital networks
- Bluetooth, Wi-Fi, Zigbee, CAN bus, and USB are some examples.
Power Supply/Battery Management
- Guarantees fault-free functioning, particularly for wearable or implantable devices
- Can include battery backup provisions and energy-saving circuits
User Interface (Optional)
- Shows readings or warnings to healthcare professionals
- Can be constructed of LCD displays, touch screens, or warning LEDs
Embedded Software/Firmware
- Controls sensor data processing, real-time operations, and device functions
- Includes safety checks, error traps, and data encryption procedures
Applications of Embedded Systems in Medical Devices
In today’s healthcare, embedded systems are very important because they let a lot of different medical gadgets be precisely controlled and monitored in real time. These apps help with life-saving measures, better medical care, and better diagnoses. Here are a few noteworthy uses:
Tracking systems for patients
- Always keep an eye on your vital signs, like your breathing rate, heart rate, blood pressure, and oxygen saturation (SpO₂).
- In intensive care units, transports, and at home, they are used.
- For instance, bedside monitors and health apps that you wear
Implantable Devices
- Embedded systems control and watch how body processes are carried out by devices like pacemakers, defibrillators, and neurostimulators.
- Make sure that the body’s systems keep working on their own.
Therapeutic Devices
- Embedded systems are used to precisely handle things like IV pumps, ventilators, and dialysis tools.
- Assure proper drug transport and help for breathing
Wearable Medical Devices
- Smartwatches, fitness bands, ECG monitors, and glucose monitors all have built-in tools that let you track your health in real time.
- Allow tracking of patients from afar and preventive healthcare
Surgical and Robotic Tools
- Robotic operations and slightly invasive tools use them.
- Robotic arms and precise tools are controlled by embedded systems that also give haptic feedback.
Laboratory Equipment
-
Blood tests and centrifuges, for example, use built-in controls to process samples, keep track of time, and send reports.
Kickstart your embedded systems career and turn your tech passion into high-demand skills!
Benefits of Using Embedded Systems in Medical Devices
There are numerous advantages of embedded systems in the healthcare industry. They make instruments safer, more beneficial, and more dependable. These are some of the most important advantages:
Real-time tracking and reaction
Embedded systems can track body functions and other health indicators continuously in real time. This helps doctors treat patients at an early stage and enhance their performance.
Lots of accuracy and precision
In devices such as IV pumps, ECG monitors, and pacemakers, where minor errors are disastrous, they ensure controls and measurements to be accurate.
Small and portable structure
Due to their miniaturized size and low power use, embedded systems are best applied in medical devices that are to be implanted, carried in a pocket, or worn on the body.
Medical Process Automation
In order to make them work more efficiently and minimize errors, they automate activities like data collection, drug delivery, and diagnosis.
Made patients’ lives simpler and more convenient
Integrated devices that are wearable or home-based facilitate online monitoring, minimizing hospital visits and making care more patient-centered.
Master Embedded Systems Programming!
Launch your tech career with our Embedded Systems Course in Kerala, designed for hands-on learning and industry readiness.
Know MoreFrequently Asked Questions
Where are embedded systems used in healthcare?
They are used in devices like pacemakers, insulin pumps, MRI machines, ventilators, and patient monitors.
Are embedded medical devices safe?
Yes, but they must follow strict safety and government regulations to ensure they work reliably.
What skills are needed to work on embedded medical systems?
Knowledge of electronics, programming (C/C++), sensors, and basic healthcare standards is useful.
Why are embedded systems important in medicine?
They make devices smarter, safer, and faster, helping doctors make better and quicker decisions.
Are embedded systems expensive?
The cost depends on the device, but they often save money long-term by improving care and reducing hospital visits.