Table of Contents
Every stock market has its fair share of wild ups and downs. The flashy headlines earned by bull runs draw all the attention, while market crashes leave a lasting scar on history.
India’s stock market is one of the fastest growing in the world and has seen its fair share of sharp declines – each one has changed the way investors behave, shaped the regulatory policies and in fact, has had an impact on the economy itself.
In this blog, let’s take a good, hard look at the biggest stock market crashes in India – their causes, the impact they had and the lessons that can be learned from them.
What Is a Stock Market Crash?
A stock market crash is when stock prices tumble rapidly across all sectors in no time, wiping out a massive amount of market value.
It’s usually set off by economic shocks, financial swindles, political instability or a global contagion and gets magnified by fear-driven selling by investors.
Crashes aren’t just about numbers; they’re also a really good way to see where the system is weak – whether it’s in how companies are run, the state of investors’ minds, or the regulatory systems themselves.
The impact might only last for the short term, but the lessons that crises leave behind stick with you for a good long while.
The History of Stock Market Crashes
1: What is a stock?
You often end up hearing from your friends and family, “The Stock Market is a risky attempt, Beware!” Yes, it is something to be aware of, but not with all these fed fears. That’s where the real insight about the stock market can help you out. Know about the history, the pattern of the stock market crash, and the reasons for the crash. This can guide you in several ways and help you build a wall of security for your future investments. You will read some of the prominent stock market crashes from history and the necessary precautions needed to tackle them in the future in this article. Also, get to know why you shouldn’t worry about the crashes and learn the secret behind every stock crash and rise.
Major Stock Drops in the 21st century
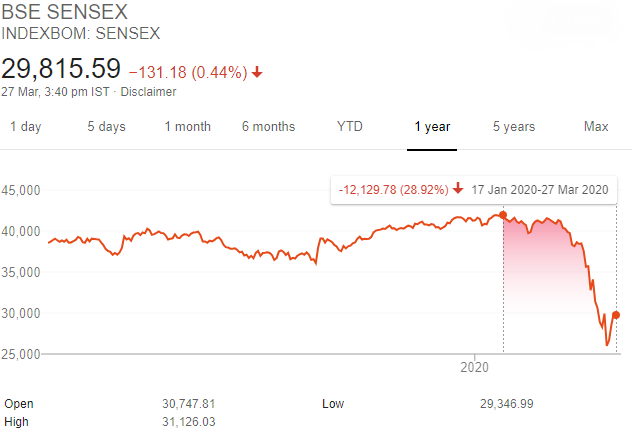
The 2020 COVID-19 Market Crash
The contemporary burst of COVID-19 that ended in a pandemic and lock downs throughout the globe led to a tremendous market crash in global and Indian markets. From the day the World Health Organization (WHO) announced the virus as a pandemic, the Sensex descended from 42,273 points to 28,288 points in a week. This corresponded with the Yes Bank emergency, generating the active BFSI division to drop crucial points too.
The display of the Union Budget on 1st February 2020 joined with the coronavirus panic drove the SENSEX to fall by 2%. Following, WHO listed Coronavirus as a dormant pandemic on February 28th, 2020 which directed to both the Nifty and the Sensex dropping with the most unfortunate weekly decline since 2009.
This was additionally supported by the shares of Yes Bank dropping on March 6th due to poor loans and one of the poorest NPA in the country. One of the patrons of Yes Bank was also caught in fraud custody. The recession after Yes Bank linked with the consequences of the Coronavirus in Europe and the US caused in the markets reaching 35,636 points
On 12th March the Sensex dropped by 8.18% as a consequence of WHO reporting corona a pandemic. As the pandemic further extended and the number of plights in India worsened, the stock Market fell 13.5% on March 23rd. Additionally, a countrywide lockdown of 21 days was declared by Prime Minister Narendra Modi beginning from midnight March 24th. The lockdown was an emergency to control the extent but it was the ultimate task the Indian economy needed in its attempts to make a rescue.
The period from 17th January 2020 to 27th March 2020 witnessed the SENSEX lose 12,129.75 points.
Check here for the Online Stock Market Trading Course @offer price
The 2015 China-Induced Crash
2015-16 was a difficult time for stock markets throughout the planet. In India, the Sensex advanced to fall. By February 2016 it had fallen almost 26% in just eleven months. This was essentially associated with Indian banks owning a lot of NPAs and overall global instability. By November 2016, there was wild traffic by people after the government split down on black money through the Demonetization drive heading to the Sensex falling by 6%. This held concurrent with declines in different Asian markets also.
While the markets gained from the significant downturn in 2008, on August 24, 2015, Sensex dropped 1624 points. This was associated with concerns of a possible slowdown in the Chinese market. This was because of the devaluation of the Chinese Yuan a few weeks before the wreck prompting a decline in the rates of other currencies and big selling volumes of stocks. In the Indian markets, this was worsened by a poor monsoon period in India and insufficient earnings in the first part of the Fiscal.
The 2008 Global Financial Crisis
The financial crisis of 2008 unfavorably affected businesses, economies, and stock markets. On January 21, 2008, the Sensex fell by around 1408 points, troubling the investor capital. This day is related to Black Monday and critics credited the decline to a range of speculations like the shift in the global investor faith, extensive doubt that the economy of the USA might go into bankruptcy, drop in the business degrees in the US etc.
By the close of 2008, the Sensex had fallen from nearly 20,465 points to 9716 points. The Sensex eventually passed the 20,000-mark repeatedly in September 2010.
The 2001 Ketan Parekh Scam
Fast forward to 2001, and history repeated itself. Ketan Parekh, a chartered accountant turned stockbroker, became infamous for rigging select technology and media stocks — dubbed “K-10 stocks.”
He borrowed heavily from banks and corporate funds to push stock prices upward.
When regulators started investigating, the bubble burst.
The Sensex fell nearly 20% in a single month, with IT and telecom shares losing 60–70% of their value.
The crash exposed how speculation without fundamentals can destroy investor confidence.
The 1992 Harshad Mehta Scam
The Harshad Mehta Scam is often called the “Big Bang” of Indian financial history.
In the early 1990s, stockbroker Harshad Mehta manipulated the stock market by exploiting loopholes in the banking system.
He used fake bank receipts to siphon money into the stock market, artificially inflating stock prices.
At one point, the Sensex skyrocketed by nearly 4x, driven by excessive speculation.
When the scam was exposed in April 1992, panic gripped Dalal Street. Within weeks, the Sensex crashed by over 55%, erasing crores in investor wealth. Financial markets need transparency and strong regulation. The scam led to the birth of the Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI) as a watchdog, making markets safer for future investors.
| Achieve Financial Freedom with these courses? | |
| Stock Market Trading Course | |
| Forex Trading Course | |
| Mutual Funds Course |
Why you Shouldn’t Worry About Stock Market Crashes?
Stock crashes are some of the worst shocks that investors fear. Even, there is a news related to the pathetic end of the investors, due to the stock market crashes. If your fear such crashes, here are some reasons not to fear
A stock market crash is not the end, wait for the recover
The stock market history has proved that, as there are crashes, there are recoveries too. The stock crash is not forever. You can be patient and wait for the recovery of the stocks.
Crashes are short term
If you are a long term investor, don’t worry about the short term falls. Keep your trust in the guts and wait for long term success.
Stock Crashes doesn’t come in a line!
Often when you look to history, you might have seen that the biggest crashes don’t come in a line. There are year lapses in between. So, keep your guts high and start investing.
Stock Market News Today!
BSE
| Company | Current Price | Prev Close
Date |
Change | Change % |
| GTL | 17.13 | 16.32
26-11-2021 |
0.81 | 4.96% |
| JCT | 4.87 | 4.64
26-11-2021 |
0.23 | 4.96% |
| National Oxygen | 68.80 | 65.55
26-11-2021 |
3.25 | 4.96% |
| SPML Infra | 19.92 | 18.98
26-11-2021 |
0.94 | 4.95% |
| Nagarjuna Fertilizer | 9.96 | 9.49
26-11-2021 |
0.47 | 4.95% |
| Shriram EPC | 6.79 | 6.47
26-11-2021 |
0.32 | 4.95% |
| Omkar SpecialityChem | 42.45 | 40.45
26-11-2021 |
2.00 | 4.94% |
| Kush Industries | 4.89 | 4.66
26-11-2021 |
0.23 | 4.94% |
| Amforge Inds. | 7.45 | 7.10
26-11-2021 |
0.35 | 4.93% |
| Poly Medicure | 1027.60 | 979.45
26-11-2021 |
48.15 | 4.92% |
| Viji Finance | 3.84 | 3.66
26-11-2021 |
0.18 | 4.92% |
| Shah Alloys | 45.90 | 43.75
26-11-2021 |
2.15 | 4.91% |
| Kilburn Engg. | 34.20 | 32.60
26-11-2021 |
1.60 | 4.91% |
| ISMT | 37.45 | 35.70
26-11-2021 |
1.75 | 4.90% |
| Sambhaav Media | 4.28 | 4.08
26-11-2021 |
0.20 | 4.90% |
| Super Spinning Mills | 11.59 | 11.05
26-11-2021 |
0.54 | 4.89% |
| Noida Toll Bridge | 7.72 | 7.36
26-11-2021 |
0.36 | 4.89% |
| A2Z Infra | 6.66 | 6.35
26-11-2021 |
0.31 | 4.88% |
| Oswal Agro Mills | 29.00 | 27.65
26-11-2021 |
1.35 | 4.88% |
| Praxis Home Retail | 46.30 | 44.15
26-11-2021 |
2.15 | 4.87% |
Get the latest daily stock market news and updates
NSE
| Company | Current Price | Prev Close
Date |
Change | Change % |
| Madhucon Projects | 6.70 | 6.10
26-11-2021 |
0.60 | 9.84% |
| HCL Infosystems | 16.25 | 15.10
26-11-2021 |
1.15 | 7.62% |
| Kridhan Infra | 5.00 | 4.65
26-11-2021 |
0.35 | 7.53% |
| Vodafone Idea | 11.65 | 10.85
26-11-2021 |
0.80 | 7.37% |
| PC Jeweller | 24.55 | 22.90
26-11-2021 |
1.65 | 7.21% |
| Raymond | 638.50 | 595.85
26-11-2021 |
42.65 | 7.16% |
| Dr Lal Pathlabs | 3898.00 | 3657.10
26-11-2021 |
240.90 | 6.59% |
| Bharat Dynamics | 412.55 | 387.45
26-11-2021 |
25.10 | 6.48% |
| Dynemic Products | 555.00 | 522.30
26-11-2021 |
32.70 | 6.26% |
| Poly Medicure | 1033.25 | 977.90
26-11-2021 |
55.35 | 5.66% |
| Surya Roshni | 585.60 | 555.65
26-11-2021 |
29.95 | 5.39% |
| Xpro India | 742.75 | 707.40
26-11-2021 |
35.35 | 5.00% |
| SAB Events & Governa | 6.30 | 6.00
26-11-2021 |
0.30 | 5.00% |
| PNB Housing Finance | 524.55 | 499.60
26-11-2021 |
24.95 | 4.99% |
| Panacea Biotec | 211.95 | 201.90
26-11-2021 |
10.05 | 4.98% |
| Automot. Stamp&Assem | 204.20 | 194.55
26-11-2021 |
9.65 | 4.96% |
| Aurionpro Solutions | 238.95 | 227.65
26-11-2021 |
11.30 | 4.96% |
| Goldstone Technology | 77.35 | 73.70
26-11-2021 |
3.65 | 4.95% |
| Morepen Laboratories | 53.00 | 50.50
26-11-2021 |
2.50 | 4.95% |
| ISMT | 37.20 | 35.45
26-11-2021 |
1.75 | 4.94% |
If you are looking forward for an online stock market course, you can download Entri App now! Check the latest Entri App’s stock market course here and make sure to get the whole study package in the offer price itself. Check out the limited offer and grab the whole stock market trading study materials Now! Hurry! Start trading with the expert advice Today!
Stock Market Training Reviewed & Monitored by SEBI Registered RA
Trusted, concepts to help you grow with confidence. Enroll now and learn to start investing the right way.
Know moreConclusion
From Harshad Mehta’s scam to the COVID-19 crash, India’s market history reflects both vulnerability and resilience. Crashes remind us that success in the stock market doesn’t come from luck; it comes from knowledge, patience, and strategy.
If you want to move beyond fear and trade confidently, start learning today.
Because the best investors aren’t those who avoid crashes, they’re the ones who know how to survive and thrive through them.
Stock Market Training Reviewed & Monitored by SEBI Registered RA
Trusted, concepts to help you grow with confidence. Enroll now and learn to start investing the right way.
Know moreFrequently Asked Questions
What is a stock market crash?
A stock market crash is a sudden and sharp decline in stock prices across sectors, often triggered by panic selling, economic shocks, or financial instability.
Which was the first major stock market crash in India?
The 1992 Harshad Mehta Scam crash was India’s first major post-liberalisation market collapse, caused by fraudulent use of banking funds for stock manipulation.
What caused the 2008 stock market crash in India?
The 2008 crash was triggered by the global financial crisis following the collapse of Lehman Brothers, leading to massive FII withdrawals and liquidity crunches in India.
How did the 2020 COVID-19 pandemic impact Indian markets?
In March 2020, the Nifty 50 and Sensex fell over 30% within weeks as global lockdowns disrupted businesses and investors feared a deep recession.
What was the 2001 Ketan Parekh scam?
Ketan Parekh manipulated select tech stocks using insider funding. When regulators intervened, overvalued tech shares collapsed, causing another market correction.
Did India face a crash after demonetisation in 2016?
Yes, short-term volatility followed demonetisation as liquidity tightened and cash-heavy sectors faced uncertainty, but markets stabilised within months.
What are the common causes of market crashes in India?
Crashes usually stem from speculative bubbles, corporate scams, policy shocks, or global contagion, often amplified by investor panic and leverage.
How do stock market crashes affect the Indian economy?
Crashes reduce investor wealth, lower consumer confidence, and may slow down capital investment, though long-term effects often fade as stability returns.
How can investors protect themselves during a crash?
Diversify your portfolio, maintain liquidity, avoid panic selling, and focus on fundamentally strong companies. Education through structured courses like Entri’s helps manage risk wisely.
What are the key lessons from India’s market crashes?
History shows that markets recover. Investors who stay disciplined, avoid speculation, and continuously upskill in market analysis ultimately outperform emotional traders.