Table of Contents
Smart devices are seamlessly integrated into our lives in this era, from advanced automotive systems to as simple as wearable fitness trackers. The professionals behind the design of these intelligent machines are none other than embedded software engineers. It is their work that makes modern machines intelligent and enables software to communicate directly with hardware. Therefore, we can say the demand for highly talented and knowledgeable embedded software engineers is on the rise. If you are a student looking to choose a career or a tech professional looking to transition into a new tech domain, understanding how to be an embedded software engineer can open many doors to the most innovative and impactful careers in technology.
Click here to register for the Entri Embedded system online certification course! Join now!
How to Be an Embedded Software Engineer: Introduction
The present-day world is increasingly driven by smart devices. Therefore, the role played by embedded software engineering is crucial in shaping the technology of today. Embedded software engineering gives “brains” to these machines, if we put it in the simplest words. This could range from the microcontroller in your washing machine to the advanced control system in an electric car. Are you fascinated by how software interacts with hardware? Do you like building such systems? Then embedded software engineering is the best career path for you. This blog will take you through all the important points that will answer the question in your mind, “How to Be an Embedded Software Engineer”.
What is Embedded Software Engineering?
The software must be efficient, reliable, and often run in real-time—meaning it must respond to events within strict timing requirements.
Embedded software engineering is one of the latest branches in the field of software development. It focuses on creating software that controls hardware. This is worlds apart from desktop or web applications that run on general-purpose computers. The embedded software runs on specialised computing devices designed for specific tasks. Such devices operate under many tight constraints, such as:
- Limited memory
- Limited processing power
- Limited energy availability
Therefore, they must be efficient, reliable, and often run in real-time. This means these devices have to respond to events within strict timing requirements. Some examples of Embedded Systems are:
- Smart thermostats
- Automotive ECU (Engine Control Unit)
- Wearable health devices
- Industrial automation controllers
- Drones and robotics
- Consumer electronics like TVs, microwaves, and cameras
Master Embedded Systems Programming!
Launch your tech career with our Embedded Systems Course in Kerala, designed for hands-on learning and industry readiness.
Know MoreWhat Does an Embedded Software Engineer Do?
The duties of an embedded software engineer are to do the following things to software that controls hardware devices.
- Designing
- Developing
- Testing
- Maintaining
Their daily responsibilities depend entirely on the industry in which they are employed. But generally, these include the following things.
| Key Responsibility | Description |
| Writing firmware | Developing low-level code that directly controls hardware components. |
| Working with microcontrollers (MCUs) and microprocessors (MPUs) | Programming and configuring embedded platforms for specific tasks. |
| Developing device drivers | Creating software interfaces that allow higher-level applications to interact with hardware. |
| Reading and interpreting hardware datasheets | Understanding specifications to configure peripherals like:
· ADCs · Timers · GPIOs |
| Debugging hardware-software integration issues | Using tools to identify and resolve issues. Some of them are:
· Oscilloscopes · Logic analyzers · JTAG debuggers |
| Testing and validating real-time performance | Ensuring the software meets timing and reliability requirements in embedded environments. |
| Collaborating with cross-functional teams | Working closely with hardware, mechanical, and systems engineers to ensure cohesive product development. |
| Working with communication protocols | Implementing and troubleshooting interfaces such as:
· I2C · SPI · UART · CAN · USB. |
How to Be an Embedded Software Engineer?
You cannot become an embedded system software engineer just by following any career path. In this section, we will give a clear and comprehensive answer to the question “How to Be an Embedded Software Engineer?”
Skills Required to Be an Embedded Software Engineer
If you want to be successful in your career as an embedded software engineer, then you should have:
- Programming skills
- Hardware understanding
- System-level thinking
Let us take a look at the technical skills you need to shine in this job.
| Category | Details |
| Programming Languages | · C: Core language for low-level programming
· C++: For OOP and RTOS-based systems · Assembly: For performance-critical tasks (optional) · Python: Useful for scripting, automation, and testing |
| Microcontrollers & SoCs | · STM32
· ESP32 · PIC · AVR · ARM Cortex-M series |
| RTOS | · FreeRTOS
· Zephyr · ThreadX · Embedded Linux |
| Hardware Communication Protocols | · SPI
· I2C · UART · PWM · CAN · Ethernet |
| Development Tools | · IDEs: Keil, MPLAB X, STM32CubeIDE, IAR
· Debuggers: JTAG, SWD, Segger J-Link · Diagnostics: Simulators, oscilloscopes |
| Version Control | · Git
· SVN |
Do technical skills alone guarantee career success? Never! Some essential soft skills that you need to work as an embedded system engineer are given below.
- Critical thinking and analytical skills
- Patience and perseverance during long debugging sessions
- Attention to detail
- Clear communication and collaboration
- Curiosity and eagerness to learn
Educational Background and Certifications
To put it simply, a degree in a technical discipline is the straight path to a career as an embedded system engineer. But sometimes we make wrong choices. In such cases, most often a professional certification is enough to reset your career path. A recognised certification, along with hands-on skills and a strong project portfolio, is just enough to overcome the hurdle created by the lack of formal education.
| Category | Details |
| Typical Degrees | · Bachelor’s in Electrical Engineering
· Bachelor’s in Electronics Engineering · Bachelor’s in Computer Engineering · Bachelor’s in Computer Science (with hardware-focused electives) |
| Certifications to Consider | · ARM Accredited Engineer
· IEEE Certified Embedded Systems Professional · Certified LabVIEW Developer · Vendor Training (Microchip, ST, NXP) · Online Courses: Embedded Systems Course by Entri Elevate |
Click here to get more information about the Embedded Systems Course by Entri Elevate!
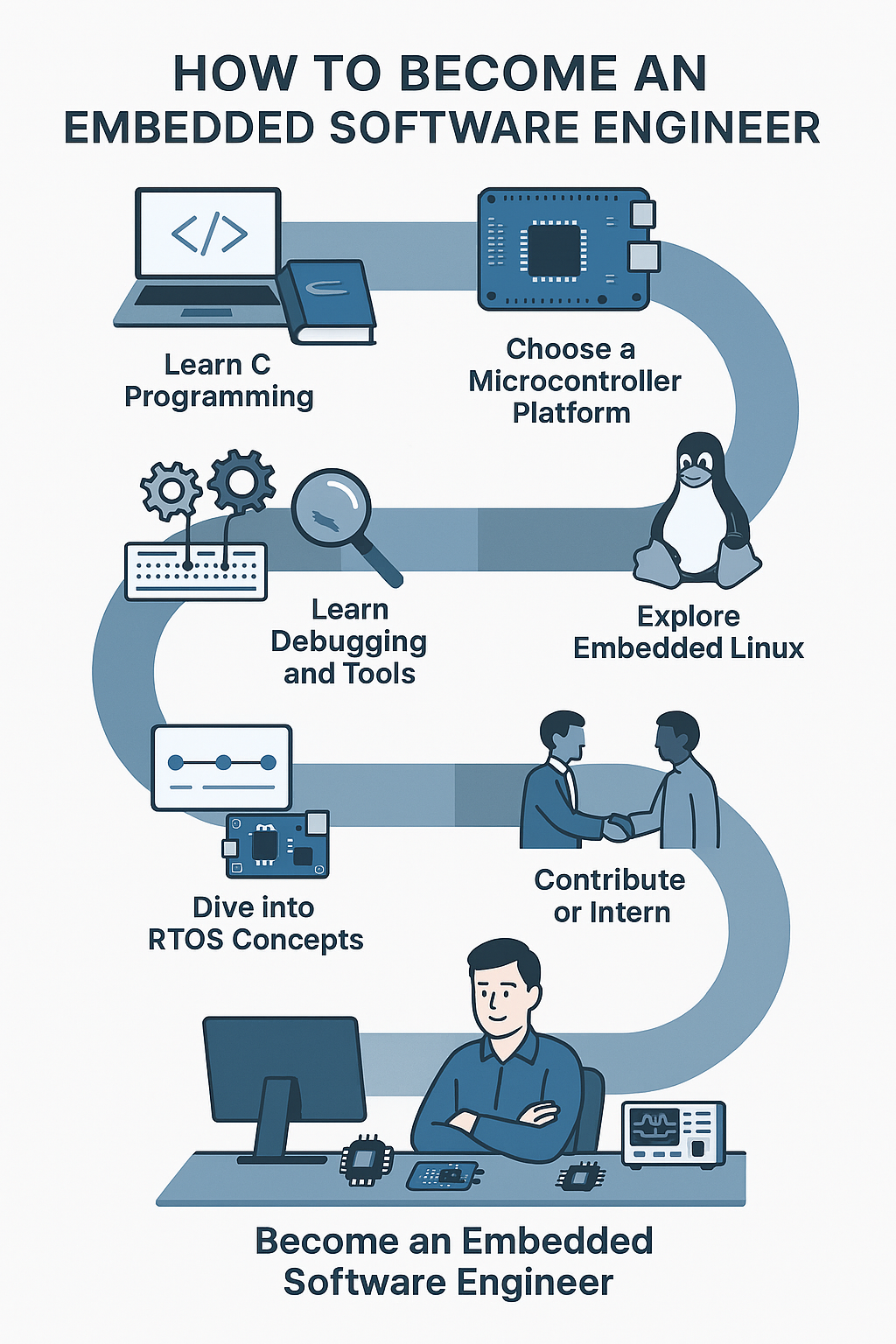
How to Get Started (Step-by-Step Roadmap)
A step-by-step roadmap to get into the career of an Embedded Software Engineer is given below. This will be more than enough to answer the question “How to Be an Embedded Software Engineer?’.
| Step | What to Do | Details |
| Learn C Programming | · Focus on C fundamentals
· Understand memory, pointers, and low-level operations |
· Essential for embedded development
· Practice writing efficient code for constrained systems |
| Choose a Microcontroller Platform | · Start with Arduino or STM32
· Use boards like Nucleo, Raspberry Pi Pico, ESP32 |
· Hands-on experience
· Learn to flash firmware and control peripherals |
| Build Mini-Projects | · Try simple projects: LED blink, sensor logger
· Work with LCDs, motors, and keypads |
· Reinforces learning
· Builds your portfolio and confidence |
| Learn Debugging and Tools | · Use simulators and real debuggers
· Study schematics and datasheets |
· Debug with JTAG, SWD, or logic analysers
· Understand hardware-software interaction |
| Dive into RTOS Concepts | · Learn tasks, semaphores, and interrupts
· Use FreeRTOS for real-time applications |
· Master multitasking and scheduling
· Understand real-time constraints |
| Explore Embedded Linux | · Learn about file systems and device drivers
· Build with Yocto or Buildroot |
· Required for complex systems
· Useful for advanced IoT or industrial devices |
| Contribute or Intern | · Join open-source projects on GitHub
· Apply for embedded internships |
· Gain real-world experience
· Expand your network and portfolio |
Master Embedded Systems Programming!
Launch your tech career with our Embedded Systems Course in Kerala, designed for hands-on learning and industry readiness.
Know MoreCareer Opportunities and Job Roles
The jobs that come under the career of embedded software engineering span a variety of industries. Look at the table below.
| Industry | Key Applications |
| Automotive | · ADAS (Advanced Driver-Assistance Systems)
· Infotainment systems · Battery management systems · Electric vehicle (EV) controllers |
| Aerospace and Defence | · Flight control systems
· Satellite and communication systems · Avionics and navigation modules |
| Consumer Electronics | · Smart TVs and appliances
· Digital cameras · Wearable tech (smartwatches, fitness bands) · Home automation devices |
| Healthcare | · Diagnostic equipment
· Patient monitoring systems · Implantable medical devices · Portable health scanners |
| Industrial Automation | · Robotics and robotic arms
· Programmable Logic Controllers (PLCs) · CNC machines · Smart manufacturing systems (Industry 4.0) |
Some job titles in these industries offered to an embedded software engineer are:
- Embedded Software Engineer
- Firmware Developer
- Systems Engineer
- IoT Developer
- Embedded Linux Engineer
- Controls/Automation Engineer
- Robotics Software Engineer
Salary Trends and Career Growth
Salary trends of an embedded software engineer are as listed in the table below.
| Level | Average Salary (USD) |
| Entry-Level | $60,000 – $80,000 |
| Mid-Level | $80,000 – $110,000 |
| Senior/Lead Level | $110,000 – $160,000+ |
As an embedded software engineer, you can choose either of the paths given below for your career growth,
| Career Path | Description |
| Technical Leadership | Lead engineering teams as a Principal or Staff Engineer. |
| Architecture Roles | Design the overall system or firmware as System/Firmware Architect. |
| Product Management / R&D Lead | Guide product development and research initiatives. |
| Consulting / Entrepreneurship | Start your own consultancy or create embedded products. |
Challenges and Rewards
Like any other job, becoming an embedded software engineer also comes with its challenges and rewards. Some of them are listed in the table below.
| Challenges | Rewards |
| Debugging is complex and time-consuming | Hands-on work with tangible, real-world outcomes |
| Limited system resources (memory, CPU) | High demand across many industries |
| Dependence on hardware slows development | Work on diverse applications—from wearables to spacecraft |
| Keeping up with rapidly changing platforms and tools | Balanced mix of hardware and software skills |
Want to be an embedded software engineer? Join Entri’s online certification course now!
How to Be an Embedded Software Engineer: Final Tips
We have discussed in detail the answer to the question “How to Be an Embedded Software Engineer?”. Some final points to keep in mind are mentioned below.
- Focus on building projects—it’s the best way to learn.
- Read datasheets thoroughly—they’re your guidebooks.
- Join communities like Reddit’s r/embedded, EEVblog forums, or Stack Overflow.
- Stay updated with blogs, books, and online courses.
- Keep your resume and GitHub updated with every project.
Master Embedded Systems Programming!
Launch your tech career with our Embedded Systems Course in Kerala, designed for hands-on learning and industry readiness.
Know MoreFrequently Asked Questions
Are there any good books to learn embedded systems?
Yes! There are many books that will help you in learning about embedded software. Some of them are listed below.
- “Embedded C Programming and the Atmel AVR” by Barnett, Cox, and O’Cull
- “Making Embedded Systems” by Elecia White
- “Programming Embedded Systems in C and C++” by Michael Barr
Can I work remotely in embedded systems?
Yes, especially in firmware development or simulation-heavy roles, though hardware testing often requires on-site presence.
Do embedded engineers need to know Assembly language?
It’s helpful for optimization and understanding what happens at the lowest level but not always required.
How long does it take to become job-ready?
With consistent effort and practical work, many learners become employable within 6–12 months.
Is embedded software engineering only for electrical engineers?
Not at all. While electrical engineers have an edge with hardware, computer science, or software engineers can thrive with enough hands-on practice.