Table of Contents
Java is an object-oriented programming language. Everything in Java is an object, all the programs, codes, and data reside within classes and objects. Inheritance, Polymorphism, Encapsulation, Abstraction, classes, and objects are few important concepts of Object-Oriented Programming. OOPs is a really important topic from an interview perspective.
As in real life, a child inherits some features from its parents; Similarly, in Object Oriented Programming language, a class may inherit from its parent class. In Java, every class has a superclass/parent class. The Object class is the root of the entire class hierarchy in Java.
This blog will discuss hybrid inheritance in Java in detail, along with codes and examples.
Inheritance
Inheritance is a crucial part of object-oriented programming. The process of inheriting the properties and behavior of an existing class into a new class is known as inheritance. We will reuse the original class methods and fields in a new class when we inherit the class. Inheritance may also be described as the Is-A relationship, also known as the parent-child relationship.
A real-world example of Inheritance is a relationship between a daughter and her Mother. A daughter inherits features from her mother, the mother, in turn, has inherited the features from her mother, and the cycle goes on. A technical example of inheritance is as follows: The Integer Class is the child class of the Number class. The Number class is the Child Class of the Object Class.
Learn Coding in your Language! Enroll Here!
Java supports the following types of inheritance:
- Single Inheritance
- Multi-level Inheritance
- Hierarchical Inheritance
- Hybrid Inheritance
- Multiple Inheritance(not support by using classes, but its possible using interfaces)
Hybrid Inheritance in Java
1: What is the default value of a boolean in Java?
Hybrid inheritance in Java is a combination of two or more types of inheritances. The purpose of using hybrid inheritance in Java is to modularize the codebase into well-defined classes and provide code reusability.
This blog will discuss hybrid inheritance in Java using a combination of the following inheritances:
- Hybrid Inheritance in Java using Single and Multiple Inheritance.
- Hybrid Inheritance in Java using Multilevel and Hierarchical Inheritance.
Hybrid Inheritance in Java using Single and Multiple Inheritance
Consider the following example wherein a combination of single and multiple inheritances is used to achieve hybrid inheritance in Java:
There is a HumanBody class that has some functionality like eating(), walking(), dancing(), etc., and some fields like bloodPressure, normalOxygenLevel, bonesCount, etc. There are two child classes of the HumanBody class, the Female and Male class. The Male class and the Female class will inherit all the functions and the fields of the HumanBody class. This is a simple example of Single Inheritance in Java.
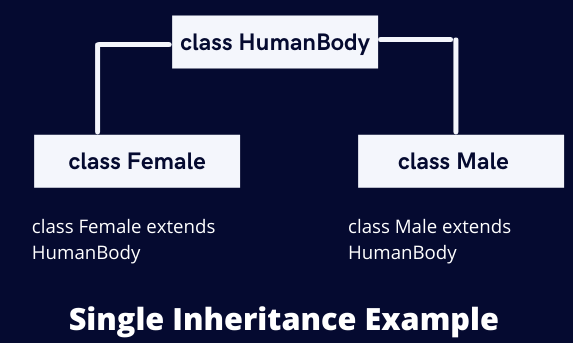
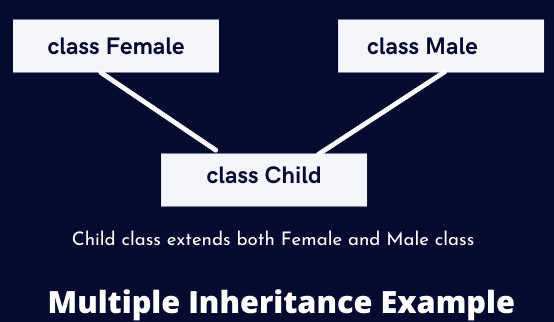
Now consider that the Male and Female classes have a child with the class name as Child. This is a simple example of multiple inheritances in Java. The relationship between the Male, Female, and Child classes is visualized below:
The combined relationship between the HumanBody, Male, Female, and Child classes is visualized below. It is an example of Hybrid Inheritance using the combination of Single and Multiple Inheritances.
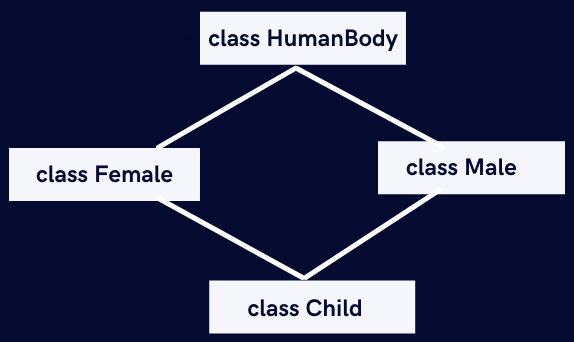
However, we know that multiple inheritances are not possible in Java. So this analogy has to be incorrect.
Well, the only incorrect thing is that, instead of classes, interfaces will be used to achieve multiple inheritances.
Syntax
public class A
{
// Methods and Fields of class A
}
public interface interfaceB
{
// Methods and Fields of InterfaceB
}
public interface interfaceC
{
// Methods and Fields of InterfaceC
}
public class D extends A implements InterfaceB,InterfaceC
{
// Implementation of the method defined in Interfaces, InterfaceB and InterfaceC
// Methods of class D
}The below program demonstrates hybrid inheritance using a combination of single inheritance and multiple inheritances using Interfaces.
class HumanBody
{
public void displayHuman()
{
System.out.println("Method defined inside HumanBody class");
}
}
interface Male
{
public void show();
}
interface Female
{
public void show();
}
// Single Inheritance is the relationship between Child // class and HumanBody class.
// Implementing Male and Female interface is Multiple // Inheritance
public class Child extends HumanBody implements Male, Female
{
public void show()
{
System.out.println("Implementation of show() method defined in interfaces Male and Female");
}
public void displayChild()
{
System.out.println("Method defined inside Child class");
}
public static void main(String[]args)
{
Child obj = new Child();
System.out.println("Implementation of Hybrid Inheritance in Java");
obj.show();
obj.displayChild();
}
}
The output of the above program is:
Implementation of Hybrid Inheritance in Java
Implementation of show() method defined in interfaces Male and Female
Method defined inside Child classHybrid Inheritance in Java using Multilevel and Hierarchical Inheritance
Hybrid Inheritance can also be achieved using a combination of Multilevel and Hierarchical inheritance. A real-world example will be, Son class inherits the Father class, Father class inherits the GrandFather class. This relation is of Multilevel inheritance. Likewise, A Daughter Class inherits the Father class, which in turn inherits the GrandFather class.
On the other hand, Son and Daughter both inherit Father class, and this relation is of Hierarchical Inheritance.
A combination of both the inheritance relation will make Hybrid inheritance.
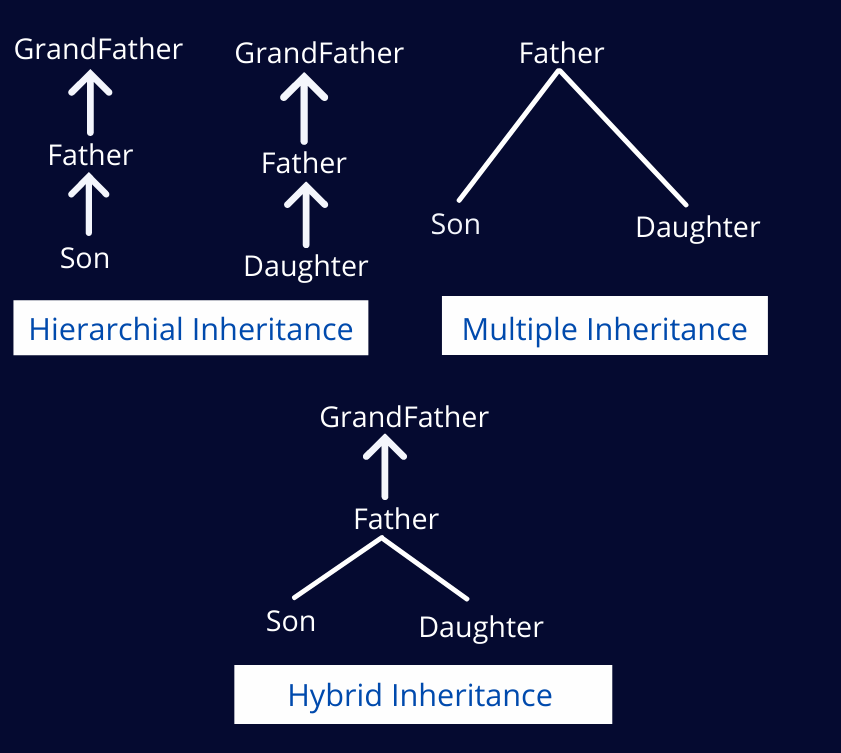
The below program demonstrates Hybrid inheritance using a combination of Multilevel and Hierarchical inheritance.
class GrandFather
{
public void printGrandFather()
{
System.out.println("GrandFather's class");
}
}
class Father extends GrandFather
{
public void printFather()
{
System.out.println("Father class has inherited GrandFather class");
}
}
class Son extends Father
{
public Son()
{
System.out.println("Inside the Son Class");
}
public void printSon()
{
System.out.println("Son class has inherited Father class");
}
}
class Daughter extends Father
{
public Daughter()
{
System.out.println("Inside the Daughter Class");
}
public void printDaughter()
{
System.out.println("Son class has inherited Father class");
}
}
public class HybridInheritance
{
public static void main(String[]args)
{
Son obj = new Son();
obj.printSon(); // Accessing Son class method
obj.printFather(); // Accessing Father class method
obj.printGrandFather(); // Accessing GrandFather class method
Daughter obj2 = new Daughter();
obj2.printDaughter(); // Accessing Daughter class method
obj2.printFather(); // Accessing Father class method
obj2.printGrandFather(); // Accessing GrandFather class method
}
}
The output of the above program is:
Inside the Son Class
Son class has inherited Father class
Father class has inherited GrandFather class
GrandFather's class
Inside the Daughter Class
Son class has inherited Father class
Father class has inherited GrandFather class
GrandFather's classFrequently Asked Questions
What are the different types of hybrid inheritance?
Hybrid Inheritance in Java is a combination of two or more inheritances. It can be done using a combination of the following inheritances.
1. Single and Multiple Inheritance
2. Multilevel and Hierarchical Inheritance
Grab the opportunity to learn Python with Entri! Click Here
Why is there no hybrid inheritance in java?
Java supports hybrid Inheritance. However, Java does not support Multiple Inheritance with classes, so in order to achieve hybrid inheritance, multiple inheritances with classes should not be used. Multiple Inheritance with Interfaces is possible.
What is hybrid inheritance?
The combination of two or more inheritances is called hybrid inheritance. It provides code reusability.
Why are pointers not used in Java?
Java is a highly secured programming language. Pointers provide direct access to a memory address, and an arbitrary memory location can be accessed, and read and write operations can be performed on it. For the purpose of security Java does not support Pointers.
Implementation of Hybrid Inheritance with Classes
public class ClassA
{
public void dispA()
{
System.out.println("disp() method of ClassA");
}
}
public class ClassB extends ClassA
{
public void show()
{
System.out.println("show() method of ClassB");
}
public void dispB()
{
System.out.println("disp() method of ClassB");
}
}
public class ClassC extends ClassA
{
public void show()
{
System.out.println("show() method of ClassC");
}
public void dispC()
{
System.out.println("disp() method of ClassC");
}
}
public class ClassD extends ClassB,ClassC
{
public void dispD()
{
System.out.println("disp() method of ClassD");
}
public static void main(String args[])
{
ClassD d = new ClassD();
d.dispD();
d.show();//Confusion happens here which show method to call
}
}
Output :
Error!!
We all know that we cannot extend ClassB and ClassC to ClassD at the same time but the point to be noted here is why it is not allowed. Since we have same show() method in both ClassB and ClassD compiler will not be able to differentiate which method to call whereas if we are using interface we can avoid that ambiguity.
Implementation of Hybrid Inheritance with Interfaces
public class ClassA
{
public void dispA()
{
System.out.println("disp() method of ClassA");
}
}
public interface InterfaceB
{
public void show();
}
public interface InterfaceC
{
public void show();
}
public class ClassD extends ClassA implements InterfaceB,InterfaceC
{
public void show()
{
System.out.println("show() method implementation");
}
public void dispD()
{
System.out.println("disp() method of ClassD");
}
public static void main(String args[])
{
ClassD d = new ClassD();
d.dispD();
d.show();
}
}
Output :
disp() method of ClassD show() method implementation
As we can see in the above code the ClassD has implemented both the interfaces InterfaceB and InterfaceC. In this case we didn’t have ambiguity even though both the interfaces are having same method.
Conclusion
Questions related to Inheritance are frequently asked in technical rounds of big companies.
Do not stop here !! Remember, Practice makes perfect !!
Hybrid Inheritance is a combination of both Single Inheritance and Multiple Inheritance. Since in Java , Multiple Inheritance is not supported directly we can achieve Hybrid inheritance also through Interfaces only.
As we can see in the above diagram ClassA is the Parent for both ClassB and ClassC which is Single Inheritance and again ClassB and ClassC again act as Parent for ClassC (Multiple Inheritance which is not supported by Java). Lets now see below code on what will happen if we go for implementing Hybrid Inheritance with both classes and interfaces.













