Table of Contents
Quantity surveying, an important aspect of the construction industry, plays a key role in ensuring construction projects are completed within budget and specifications. Quantity surveying is even more important in the UK, where building standards are high. This article examines the various measurement methods used in quantity surveying and shows how these techniques can contribute to the effective management of construction costs.
Key Takeaways:
- Methods of measurement provide structure and consistency in quantity surveying.
- Choose based on project type, location, and client standards.
- Learn at least three major methods to remain versatile as a professional.
- Always refer to the latest edition of the method you’re using.
- Accurate measurements lead to fair pricing, reduced disputes, and better project control.
Quantity Surveyor online certification course on Entri app! Join Now!
What is Measurement in Quantity Surveying?
Measurement in quantity surveying refers to the process of calculating and detailing the quantities of various construction materials, components, and work required in a construction project. This includes everything from concrete, steel, and bricks to painting, plumbing, and finishing works.
Accurate measurement ensures:
-
Fair contract pricing
-
Transparent billing and cost estimation
-
Effective budgeting and procurement planning
-
Reduced risk of disputes between contractor and client
Importance of Measurement in Quantity Surveying
1: What is the main purpose of a Bill of Quantities (BoQ)?
Using standardised methods ensures that:
-
Everyone speaks the same language, clients, contractors, consultants
-
There’s no ambiguity in pricing or quantities
-
Valuations, tendering, and billing are consistent
Without a unified standard, measurements could vary across projects, leading to misinterpretation and legal complications.
Master Quantity Surveying – Build a Rewarding Career Today!
Gain in-demand skills in cost estimation, project budgeting, and contract management with our Quantity Surveying Course. Learn from industry experts and boost your career in construction and infrastructure. Enroll now and take the first step toward success!
Know MoreMethods of Measurement in Quantity Surveying
The role of a quantity surveyor is deeply tied to how construction work is measured, described, and costed. Over the years, different countries and professional bodies have developed standardised methods of measurement to make cost estimating, tendering, and billing consistent and transparent.
Below is a detailed look at the top methods of measurement used worldwide, along with their relevance and application.
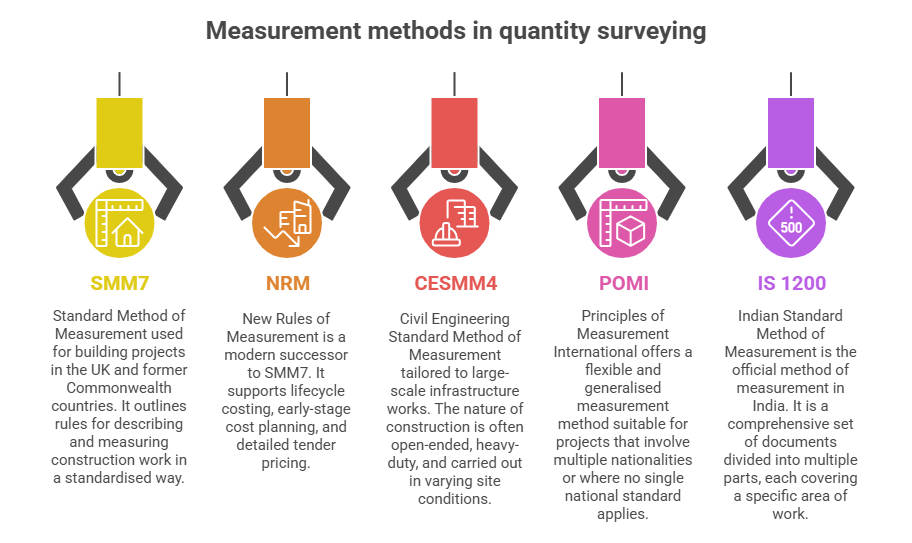
1. SMM7 – Standard Method of Measurement
Published by: Royal Institution of Chartered Surveyors (RICS), UK
Use case: Building projects in the UK and former Commonwealth countries
Overview:
SMM7 was once the most widely adopted method of measurement for building works in the UK. Though now largely replaced by NRM (New Rules of Measurement), it’s still used in many legacy projects and academic training. It outlines rules for describing and measuring construction work in a standardised way.
Structure:
SMM7 divides work into sections (e.g. substructure, superstructure, finishes), and defines how each component should be measured and presented in a BOQ.
Benefits:
-
Easy to follow for traditional construction work
-
Reduces scope misinterpretation
-
Offers uniformity in BOQ presentation
When to use it:
When working on older UK-based contracts or refurbishments that still refer to SMM7 specifications.
2. NRM – New Rules of Measurement
Published by: RICS (UK)
Versions:
-
NRM1 – Cost planning for capital building projects
-
NRM2 – Detailed measurement for BOQs
-
NRM3 – Costing of maintenance and refurbishment works
Overview:
NRM is designed as a modern successor to SMM7. It supports lifecycle costing, early-stage cost planning, and detailed tender pricing. It’s better aligned with BIM-based workflows and digital construction tools.
Highlights:
-
NRM1 helps during feasibility and cost estimation stages.
-
NRM2 focuses on precise BOQ preparation for tendering.
-
NRM3 is ideal for maintaining operational buildings.
Why it matters:
NRM allows QSs to offer value-based solutions to clients, especially where decisions about materials, construction methods, and maintenance affect overall costs.
Ideal For:
-
RICS-accredited professionals
-
Public and private sector building projects
-
Firms focused on cost management across the project lifecycle
3. CESMM4 – Civil Engineering Standard Method of Measurement
Published by: Institution of Civil Engineers (ICE), UK
Use case: Civil engineering projects like roads, bridges, pipelines, earthworks
Overview:
Unlike building measurement methods, CESMM4 is tailored to large-scale infrastructure works, where the nature of construction is often open-ended, heavy-duty, and carried out in varying site conditions.
Key Features:
-
Items are broken down into logical work sections
-
Includes extensive rules for earthworks, pipework, roadworks, and concrete structures
-
Often used in conjunction with FIDIC and NEC contracts
Benefits:
-
Simplifies complex civil engineering works
-
Reduces pricing ambiguity
-
Encourages a more detailed understanding of work scope
Ideal for:
QSs working in infrastructure development, highways, rail, energy, and marine works.
4. POMI – Principles of Measurement International
Published by: Chartered Institute of Building (CIOB)
Use case: International and cross-border construction projects
Overview:
POMI offers a flexible and generalised measurement method suitable for projects that involve multiple nationalities or where no single national standard applies.
Why it’s useful:
Unlike the rigid structures of NRM or CESMM, POMI is more adaptable. It is often adopted in Middle Eastern projects where the project teams comprise professionals from the UK, India, Philippines, Egypt, and other countries.
Features:
-
Divides construction works into trades
-
Provides consistent measurement rules without overcomplicating
-
Avoids excessive technicality, making it easier for global teams
Where it’s commonly used:
-
UAE, Qatar, Saudi Arabia
-
Multinational construction firms
-
Projects tendered by international consultants
5. IS 1200 – Indian Standard Method of Measurement
Published by: Bureau of Indian Standards (BIS)
Use case: Projects executed in India or funded by Indian organisations
Overview:
IS 1200 is the official method of measurement in India. It is a comprehensive set of documents divided into multiple parts (currently over 27), each covering a specific area of work ,like concrete, earthwork, steel reinforcement, etc.
Structure Example:
-
Part 1: Earthwork
-
Part 2: Concrete
-
Part 5: Formwork
-
Part 15: Painting
-
And more…
Why it’s important:
Most Indian tenders and public sector contracts strictly adhere to IS 1200. It ensures uniformity and legality in contract documentation and billing.
Benefits:
-
Nationally standardised for all project stakeholders
-
Widely accepted in CPWD, PWD, NHAI, and railway projects
-
Accepted by banks and legal authorities during dispute resolution
Tip:
As a QS in India, mastering IS 1200 is non-negotiable; it’s the standard against which you’re measured.
Quantity Surveyor Online Certification Course on Entri app! Join Now!
Types of Measurement in Quantity Surveying
There are generally three types of measurements done in QS:
| Type of Measurement | Description |
|---|---|
| Gross Measurement | Overall measurement of components without deductions for openings |
| Net Measurement | Includes exact dimensions and deducts voids/openings (e.g., windows, doors) |
| Detailed Measurement | Breaks down each element/component individually as per SMM or NRM standards |
A Bill of Quantities (BOQ) is a structured document that lists all construction items and their respective quantities, measured using one of the above standards.
BOQ Includes:
-
Description of work
-
Quantity
-
Unit of measurement
-
Rate per unit
-
Total cost
Why BOQ matters:
-
Acts as a pricing document during tendering
-
Enables contractor to plan manpower, materials, and machinery
-
Forms the basis for payment and project control
Tools & Software Used in Measurement
Modern QS professionals use advanced tools to enhance accuracy:
-
AutoCAD – For area and length calculations
-
Revit/BIM tools – For 3D measurement and clash detection
-
CostX – Digital take-off and BOQ preparation
-
Bluebeam – PDF markup and measurement
-
Excel – For quantity sheets and BOQ formatting
Quantity Surveyor online certification course on Entri app! Join Now!
Master Quantity Surveying – Build a Rewarding Career Today!
Gain in-demand skills in cost estimation, project budgeting, and contract management with our Quantity Surveying Course. Learn from industry experts and boost your career in construction and infrastructure. Enroll now and take the first step toward success!
Know MoreMeasurement in Pre- and Post-Contract Phases
Pre-Contract Phase:
-
Quantity take-offs from drawings
-
Cost planning and tender preparation
-
Preparing BOQs as per agreed standards
Post-Contract Phase:
-
Interim valuations and contractor payments
-
Variation orders and change management
-
Final account preparation
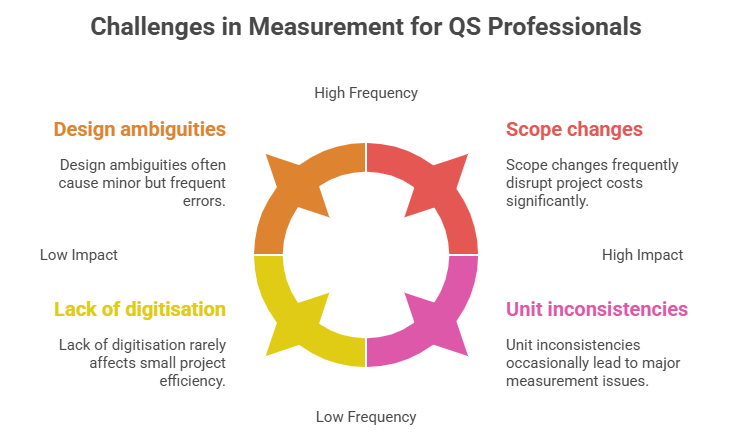
Challenges in Measurement
Despite standardisation, QS professionals face some challenges:
-
Design ambiguities: Poorly detailed drawings lead to quantity errors
-
Scope changes: Mid-project design modifications affect cost
-
Unit inconsistencies: Different standards use different units and formats
-
Lack of digitisation: Manual methods still common in small projects
Best Practices in Measurement
-
Always use the correct standard method based on project type and location
-
Maintain consistency in units and format
-
Cross-check with multiple drawings and specifications
-
Use technology tools for better accuracy
-
Collaborate closely with designers and contractors for updates
Conclusion
The methods of measurement in quantity surveying are fundamental to the financial and operational success of a construction project. They ensure transparency, accuracy, and consistency from estimation to execution. Whether you’re working on a residential tower, highway, or industrial facility, choosing the right method, be it NRM, CESMM, IS 1200, or SMM- can make or break your cost control efforts.
As the construction world moves toward automation and international collaboration, understanding and applying the correct method of measurement will remain a key skill for any successful quantity surveyor.
Master Quantity Surveying – Build a Rewarding Career Today!
Gain in-demand skills in cost estimation, project budgeting, and contract management with our Quantity Surveying Course. Learn from industry experts and boost your career in construction and infrastructure. Enroll now and take the first step toward success!
Know MoreFrequently Asked Questions
What is meant by methods of measurement in quantity surveying?
Methods of measurement in quantity surveying refer to the standardised guidelines or rules used to quantify building works. These help ensure consistency, clarity, and accuracy in preparing cost estimates, BOQs, and tender documents.
Why are standard methods of measurement important in construction?
They eliminate confusion and disputes by providing a common framework for measurement, ensuring all parties, clients, contractors, and consultants are on the same page regarding quantities and scope.
What is SMM7 in quantity surveying?
SMM7, or the Standard Method of Measurement 7, was widely used in the UK and Commonwealth countries to standardise measurement of construction works. Though now replaced by NRM, many QS professionals still reference SMM7 for legacy projects.
What is the difference between NRM and SMM?
SMM (like SMM7) focuses on the measurement rules for BOQs. NRM (New Rules of Measurement) is a more modern framework that covers the full lifecycle, cost estimating, cost planning, and BOQ production. NRM is better aligned with contemporary procurement practices and BIM.
Is CESMM used for building works or civil engineering?
CESMM (Civil Engineering Standard Method of Measurement) is primarily used for civil engineering projects such as roads, bridges, pipelines, and other infrastructure, not building construction.
Can different methods of measurement be used in the same project?
While not recommended, in some cases, different methods may be used for specific packages, such as NRM for buildings and CESMM for external civil works. However, consistency is key, and it’s best to define the standard clearly in contract documentation.
What is POMI in quantity surveying?
POMI stands for Principles of Measurement (International). It’s an internationally recognised standard developed by the Royal Institution of Chartered Surveyors (RICS) to provide a framework for international projects, especially when no local method exists.
How does a method of measurement affect cost estimation?
Accurate measurement based on standardised rules ensures reliable quantities, which directly influence cost estimates. Misinterpretation or incorrect application of measurement methods can result in significant cost variations or disputes.
Are methods of measurement used globally the same?
No, different countries and regions have their own standards. For instance, the UK uses NRM, the Middle East often uses POMI, while India follows IS 1200. It’s essential for QS professionals to adapt to local practices.
Where can I learn more about these measurement standards?
You can explore publications and guidance documents from professional bodies like RICS, ICE, CIQS, and national standard organisations. Enrolling in Entri’s Quantity Surveying course can also help you to learn all the concepts.