Table of Contents
Child-led learning is where children are encouraged to adopt self-directed learning. They decide what, how, and when they want to learn. Here, the parents play the role of a guide by not influencing the children too much but supervising them properly. If you wish to implement child-led learning in your household, great! You have come to the right place! In this article, we will learn what is child-led learning?, key principles of child-led learning, benefits of child-led learning, how to implement child-led learning at home, etc.
Start your journey to becoming a certified Montessori teacher! Get free Demo Here!
Introduction
Child-led learning is an educational approach that prioritizes a child’s interests, choices, and natural curiosity. Instead of following a rigid curriculum, this method allows children to explore topics that excite them, fostering deeper engagement and intrinsic motivation. Child-led learning aligns with developmental theories that emphasize autonomy, self-direction, and hands-on experiences, making learning more meaningful and enjoyable.
The Philosophy Behind Child-Led Learning
- Respect for Individual Pace:
- Supports learning at a comfortable speed.
- Recognizes unique development timelines.
- Intrinsic Motivation:
- Encourages curiosity-driven learning.
- Reduces dependence on rewards and punishments.
- Holistic Development:
- Focuses on intellectual, emotional, and social growth.
- Builds confidence, independence, and problem-solving skills.
How Child-Led Learning Differs from Traditional Education
- Flexible Learning Structure:
- Removes rigid schedules.
- Encourages spontaneous learning.
- Interest-Based Learning:
- Lessons stem from curiosity.
- Promotes deeper engagement.
- Active Participation:
- Encourages hands-on experiences.
- Develops critical thinking skills.
Role of Parents and Educators in Child-Led Learning
- Facilitators, Not Dictators:
- Provide resources and guidance.
- Let children lead their learning.
- Creating a Stimulating Environment:
- Offer books, art supplies, and hands-on tools.
- Encourage creativity and exploration.
- Encouraging Exploration:
- Support problem-solving and questioning.
- Incorporate outdoor and real-world experiences.
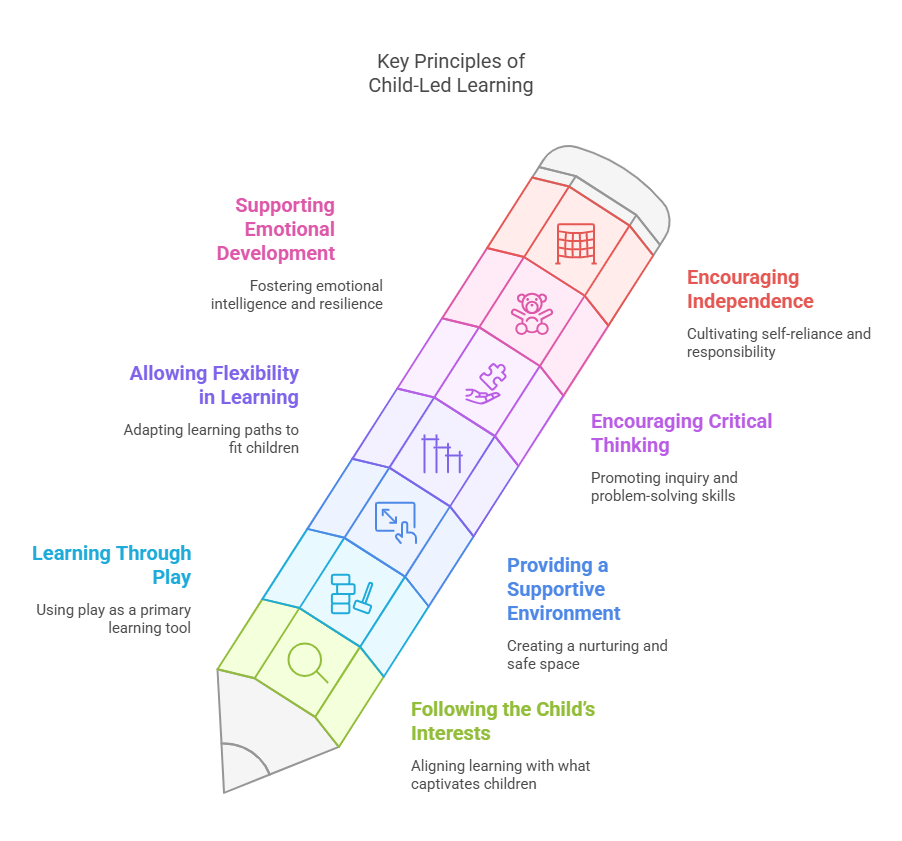
Key Principles of Child-Led Learning
1: What is the primary focus of the first plane of development in the Montessori method?
1. Following the Child’s Interests
- Encouraging exploration based on what fascinates the child.
- Allowing the child to dictate learning paths while offering gentle guidance.
| Aspect | Explanation |
|---|---|
| Interest-Driven | Children engage more when learning aligns with their passions. |
| Autonomy | Kids develop independence by choosing their learning focus. |
2. Learning Through Play
- Utilizing play-based activities as learning tools.
- Encouraging hands-on, experiential learning through:
- storytelling
- role-play
| Aspect | Explanation |
| Creativity Boost | Play fosters imagination and problem-solving skills. |
| Experiential Learning | Children learn by doing, which enhances retention. |
3. Providing a Supportive Environment
- Creating a resource-rich learning space with diverse materials.
- Ensuring:
- emotional safety
- encouragement for exploration
| Aspect | Explanation |
| Resource Accessibility | Books, art supplies, and tools should be within reach. |
| Emotional Security | A safe environment fosters confidence and willingness to learn. |
4. Allowing Flexibility in Learning
- Letting children learn at their own pace without external pressure.
- Adjusting approaches based on the child’s preferred learning style.
| Aspect | Explanation |
| Personalized Pacing | Allows children to grasp concepts without stress. |
| Adaptive Methods | Teaching strategies should suit each child’s needs. |
5. Encouraging Critical Thinking and Problem-Solving
- Asking open-ended questions that spark curiosity.
- Providing real-world problem-solving opportunities in daily activities.
| Aspect | Explanation |
| Inquiry-Based Learning | Encourages children to think deeply and analyze. |
| Real-Life Application | Helps children connect learning to everyday life. |
6. Supporting Emotional and Social Development
- Encouraging:
- self-expression
- communication
- Helping children navigate emotions and social interactions.
| Aspect | Explanation |
| Emotional Intelligence | Supports children in understanding and managing emotions. |
| Social Skills | Promotes collaboration, empathy, and teamwork. |
7. Encouraging Independence and Responsibility
- Allowing children to take responsibility for their learning choices.
- Teaching:
- self-regulation
- goal-setting
| Aspect | Explanation |
| Self-Directed Learning | Encourages children to take ownership of their education. |
| Decision-Making Skills | Helps develop confidence in making choices. |
Become a Early Childhood Care Educator! Get your diploma soon!
Get Certified & Start Your Montessori Career
Montessori Teacher Training Course by Entri App: Gain expert skills, earn certification, and kickstart your teaching career.
Join Now!Benefits of Child-Led Learning
1. Enhanced Motivation
- Learning is more enjoyable when driven by personal interest.
- Children are more likely to persist in learning activities they find meaningful.
| Aspect | Explanation |
| Intrinsic Engagement | Interest-driven learning sustains enthusiasm. |
| Long-Term Learning Habits | Encourages lifelong curiosity and commitment to learning. |
2. Improved Retention
- Children remember information better when they are actively engaged.
- Hands-on experiences solidify learning by making it tangible.
| Aspect | Explanation |
| Active Participation | Engaging experiences help retain knowledge. |
| Context-Based Memory | Learning through real-world application improves recall. |
3. Stronger Critical Thinking
- Encourages questioning and independent thought.
- Helps children:
- analyze information
- develop solutions
- make decisions
| Aspect | Explanation |
| Analytical Skills | Promotes deeper understanding through evaluation. |
| Problem-Solving Ability | Enhances logical reasoning and decision-making. |
4. Greater Creativity
- Allows room for:
- exploration
- imagination
- problem-solving
- Encourages experimenting with new ideas and perspectives.
| Aspect | Explanation |
| Innovative Thinking | Children develop originality through self-guided projects. |
| Expressive Freedom | Supports creative expression through various mediums. |
5. Higher Confidence
- Children feel empowered by taking charge of their learning.
- Encourages:
- self-assessment
- positive risk-taking
| Aspect | Explanation |
| Self-Efficacy | Kids build confidence by seeing their progress. |
| Resilience | Learning from mistakes fosters perseverance. |
6. Better Social Skills
- Encourages:
- communication
- collaboration
- negotiation
- Provides opportunities for:
- teamwork
- relationship-building
| Aspect | Explanation |
| Cooperative Learning | Kids learn to share ideas and work together. |
| Empathy Development | Encourages understanding of different perspectives. |
7. Personalized Learning Experience
- Adapts to each child’s unique learning:
- style
- pace
- Reduces stress associated with standardized education models.
| Aspect | Explanation |
| Tailored Instruction | Meets individual strengths and weaknesses. |
| Reduced Pressure | Allows natural progression without unnecessary competition. |
How to Implement Child-Led Learning at Home
1. Observe and Identify Interests
- Pay attention to what excites your child.
- Take note of recurring themes in their:
- play
- conversations
| Aspect | Explanation |
| Interest Discovery | Helps recognize patterns in a child’s curiosity. |
| Adaptive Exposure | Introducing new experiences broadens learning opportunities. |
2. Create an Enriching Learning Environment
- Provide access to:
- books
- art supplies
- building materials
- nature
- Arrange the space for easy exploration and self-directed learning.
| Aspect | Explanation |
| Accessible Resources | Ensures children can explore independently. |
| Stimulating Surroundings | A well-prepared environment encourages curiosity. |
3. Encourage Questions and Exploration
- Respond to questions with enthusiasm.
- Offer tools and resources to explore further.
| Aspect | Explanation |
| Open-Ended Inquiry | Encourages deep thinking and curiosity. |
| Resource-Rich Learning | Provides children with tools to seek answers. |
4. Support, Don’t Lead
- Guide without dictating.
- Offer suggestions without taking over.
| Aspect | Explanation |
| Child Autonomy | Encourages independence and confidence. |
| Guided Learning | Assists without overwhelming direction. |
5. Integrate Learning into Daily Life
- Use daily activities as learning opportunities (cooking, shopping, gardening).
- Encourage:
- storytelling
- journaling
- conversations
| Aspect | Explanation |
| Practical Applications | Connects learning to real-life experiences. |
| Conversational Learning | Encourages expression through dialogue. |
6. Be Flexible and Adaptable
- Recognize that interests may shift.
- Adjust resources and activities accordingly.
| Aspect | Explanation |
| Responsive Teaching | Adapts to the child’s changing needs. |
| Dynamic Learning | Encourages growth through evolving interests. |
Start your journey to becoming a certified Montessori teacher! Get free Demo Here!
Conclusion
Child-led learning fosters independence, creativity, and a lifelong love for learning. By observing, supporting, and providing a rich learning environment, parents and educators can help children develop essential skills naturally. While structured education has its place, incorporating child-led learning allows children to take ownership of their education, making learning a more enjoyable and meaningful experience.
Final Thoughts on Child-Led Learning:
- Personalized Growth:
- Encourages self-paced
- Allows independent learning
- Encourages Exploration:
- Extends learning beyond the classroom.
- Builds Resilience:
- Teaches adaptation
- Increases problem-solving skills
- Reduces Pressure:
- Removes stress from rigid curriculum.
- Prepares for the Future:
- Develops lifelong skills in critical thinking and adaptability.
By implementing child-led learning strategies, caregivers and educators can create a nurturing, engaging, and empowering educational experience that respects each child’s unique abilities and potential.
Get Certified & Start Your Montessori Career
Montessori Teacher Training Course by Entri App: Gain expert skills, earn certification, and kickstart your teaching career.
Join Now!Frequently Asked Questions
What is child-led learning?
Child-led learning is an educational approach where children take the lead in their learning journey based on their interests, curiosity, and pace. Instead of following a rigid curriculum, children explore topics they are naturally drawn to, fostering deeper engagement. Parents and educators act as facilitators, providing resources and guidance without dictating the learning process. This method encourages independent thinking, creativity, and self-motivation. It is widely used in homeschooling, alternative education models, and early childhood development.
How does child-led learning differ from traditional education?
Traditional education follows a structured curriculum with set lessons, timelines, and standardized assessments. In contrast, child-led learning allows children to explore subjects at their own pace based on personal interests. While traditional classrooms prioritize uniformity, child-led learning focuses on individual development and intrinsic motivation. It encourages exploration, critical thinking, and real-world application rather than rote memorization. Both methods have their benefits, but child-led learning fosters lifelong curiosity and adaptability.
What are the benefits of child-led learning?
Child-led learning enhances motivation, improves retention, and strengthens critical thinking. It allows children to develop creativity, problem-solving skills, and confidence by making their own learning choices. The approach also fosters independence and responsibility, encouraging children to take ownership of their education. Social skills improve as children engage in discussions and collaborative projects with peers and adults. Ultimately, child-led learning helps create self-motivated individuals who enjoy learning throughout life.
Can child-led learning work for every child?
Most children benefit from some level of child-led learning, but the effectiveness depends on their personality, environment, and support system. Some children thrive with complete freedom, while others may need more structure or guidance. Parents and educators should observe the child’s learning style and adapt the approach to ensure a balance between autonomy and necessary skill development. For children who prefer routine, integrating structured activities with self-directed exploration can be effective. Flexibility is key to making child-led learning successful for different learners.
How can parents support child-led learning at home?
Parents can support child-led learning by observing their child’s interests and providing resources that encourage exploration. Creating a stimulating environment with books, art supplies, and hands-on activities helps facilitate learning. Encouraging questions, discussions, and real-world experiences like field trips or experiments fosters deeper understanding. Instead of directing every lesson, parents should act as guides, helping children discover new concepts organically. A balance of support and independence ensures children stay engaged without feeling overwhelmed.
Is child-led learning the same as unschooling?
Child-led learning and unschooling share similarities, but they are not identical. Unschooling is a broader philosophy that rejects traditional schooling structures entirely, allowing children to learn exclusively through life experiences. Child-led learning, on the other hand, can exist within structured educational systems and still incorporate self-directed exploration. Some parents use a mix of both, combining formal education with child-led elements. Both approaches prioritize curiosity-driven learning but vary in the level of structure involved.
What if my child loses interest in a topic quickly?
It’s normal for children to shift interests frequently, as they explore different concepts and experiences. Instead of forcing continued engagement, parents should encourage natural curiosity by providing diverse learning opportunities. Observing patterns in their interests can help identify underlying themes, such as a love for storytelling, problem-solving, or building. Allowing flexibility ensures children stay engaged without feeling pressured. Revisiting topics later with new approaches can reignite curiosity in subjects they previously moved on from.
How do I balance academic essentials with child-led learning?
A balanced approach involves blending foundational academic skills with interest-driven exploration. Parents can incorporate reading, writing, and math into everyday activities, such as measuring ingredients while cooking or reading stories related to their child’s favorite topics. Offering structured lessons when needed while allowing self-directed learning keeps both academic growth and personal interests aligned. The key is to make essential subjects meaningful and relevant rather than separate from the child’s natural curiosity. Over time, children develop skills in a way that feels engaging rather than forced.
Does child-led learning prepare children for future careers?
Yes, child-led learning nurtures critical skills like problem-solving, adaptability, and independent thinking, which are essential for future careers. Many modern professions value creativity, self-motivation, and the ability to learn new skills on demand—qualities fostered through child-led education. Additionally, children who take ownership of their learning are more likely to develop lifelong learning habits, keeping them competitive in evolving job markets. While structured education provides foundational knowledge, child-led learning ensures children develop the curiosity and flexibility needed for long-term success. The combination of both approaches can be highly effective in career preparation.
Can child-led learning be used in traditional schools?
Yes, elements of child-led learning can be integrated into traditional schools through project-based learning, open-ended assignments, and student choice activities. Teachers can create flexible classroom environments that allow students to explore subjects based on personal interests while meeting curriculum requirements. Encouraging inquiry-based learning, hands-on experiments, and creative problem-solving fosters a more engaging educational experience. Schools that incorporate student-driven activities often see increased motivation and participation. While traditional schools have set guidelines, allowing student autonomy within those frameworks enhances learning outcomes.