Table of Contents
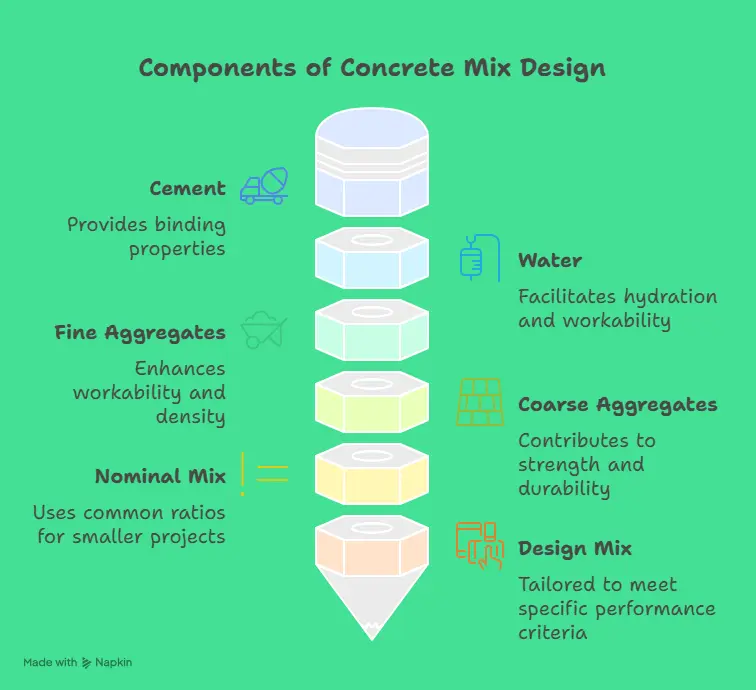
At this point in time, concrete is the most essential material for the production of everything. Additionally, this material is used in the construction of foundations, pavements, and bridges. The concrete mix design calls for a certain proportion of cement, sand, aggregates, and water to be included in the product. Concrete’s strength, durability, and general quality are all significantly impacted by these quantities to a significant degree. For the purpose of ensuring that buildings are not only safe but also inexpensive and durable for a long period of time, it is necessary for engineers, builders, and those who want to do it themselves to have knowledge on how to manufacture concrete mixes, including standard ratios and best practices.
Start Your Journey To A Prosperous Career ! Study Quantity Surveying With Professional Mentors!
What is Concrete Mix Design?
In order to create concrete that is durable, long-lasting, and simple to work with, the process of building a concrete mix entails selecting the appropriate elements and determining the appropriate amount of each item to utilize. For the purpose of meeting certain performance criteria, it is necessary to determine the appropriate quantities of cement, water, fine aggregates (such as sand), and coarse aggregates to be used.
When it comes to concrete, a proper mix ensures that
- Strong enough to support weights in a secure manner
- The capacity to withstand the effects of the elements
- The ability to work, allowing for simple positioning and compacting
- Reduction in material waste, which results in cost-effectiveness
The nominal mix, which is used for smaller projects and makes use of common ratios, and the design mix, which is built to fulfill specific requirements for strength and durability, are the two kinds of concrete mix designs. For the purpose of constructing structures that are secure, reliable, and long-lasting, the mix design has to be correct.
Standard Concrete Mix Ratios
1: What is the main purpose of a Bill of Quantities (BoQ)?
The proportions of cement, sand (fine aggregate), and coarse aggregate that are involved in the production of concrete are denoted by the concrete mix ratios. To achieve the desired level of strength, several ratios are used, depending on the kind of structure being utilized. The ratios of cement, sand, and aggregate in concrete are what determine the amount of each that is blended in order to reach the required level of strength and workability. Below is a table of mix ratios that are often used:
| Mix Ratio (Cement : Sand : Aggregate) | Grade of Concrete | Typical Strength (MPa) | Common Uses |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 : 3 : 6 | M10 | 10 MPa | Used for simple, non-structural works like leveling and flooring. |
| 1 : 2 : 4 | M15 | 15 MPa | Ideal for pathways, plain concrete flooring, and small foundations. |
| 1 : 1.5 : 3 | M20 | 20 MPa | Commonly used for structural elements such as slabs, beams, and columns. |
| 1 : 1 : 2 | M25 | 25 MPa | Used in high-strength structural works and reinforced concrete. |
| Custom Design Mix | M30 and above | 30–60 MPa | Used for high-rise buildings, bridges, and heavy-duty structures. |
Master Quantity Surveying – Build a Rewarding Career Today!
Gain in-demand skills in cost estimation, project budgeting, and contract management with our Quantity Surveying Course. Learn from industry experts and boost your career in construction and infrastructure. Enroll now and take the first step toward success!
Know MoreHow to Calculate Concrete Mix Ratios
Cement, sand, aggregates, and water must be proportioned accurately to provide the requisite strengths and workability. The technique includes selecting the slope, water-cement ratio, and proportions according to the project’s requirements and location.
Calculation of Concrete Mix Ratio
-
It is important to comprehend the function of the concrete.
A foundation, a slab, or a walkway are all examples of potential applications for concrete. The first step is to consider where the concrete will be utilized. To determine the mix ratio, you will need to consider the strength and durability requirements.
-
Make a selection of the concrete grade that you want.
The project’s strength requirements should guide the selection of the grade (such as M15, M20, etc.). A predetermined ratio of cement, sand, and aggregate is used in the production of each grade.
-
Determine Each of the Essential Components
Cement, fine aggregate as sand, coarse aggregate as gravel, and water are the primary components of the material. There are occasions when admixtures are introduced in order to increase the workability or strength of the combination.
-
Use the Standard Mix Proportions as a reference.
To determine the general percentage for the grade you have selected, you may make use of standard criteria such as IS 10262 or ACI standards. This will provide you with a position to begin.
-
Adjust in accordance with the practicability
You may make the mixture more workable by making a minor adjustment to the amount of water or sand that is present, depending on how easy you need the mixture to be while pouring or putting it.
-
Establish the Water-to-Cement Coefficient
It is via this ratio that the concrete’s strength and durability are directly influenced. A lower water-to-cement ratio results in increased strength but might result in decreased workability; it is important to achieve the optimal balance.
-
Verify the amount of moisture present in the aggregates.
Considering that sand and gravel often contain moisture, it is necessary to modify the amount of water being used in order to keep the appropriate proportion.
-
Perform a Test Mixing
Start with a small batch and mix it according to the quantities you estimated. It is important to pay attention to its uniformity, workability, and finish.
-
Examine and Modify the mix
After curing, the sample mix should be evaluated for its strength. Make some little adjustments to the mixture and give it another go if it does not match your desired level of strength or workability.
Types of Concrete Mix
Based on the project requirements and the method used to determine the proportions of the ingredients, many kinds of concrete mixes are available. You may get the desired level of strength, workability, and durability by selecting the right mix.
1. Nominal Mix
Construction projects that are deemed moderate or regular utilize a predetermined mix ratio.
Two examples of ratios are the 1:1 ratio and the 1:2:4 pattern. 2.3, 1.3, and 6
For simple tasks that do not need a lot of power, such as installing flooring, sidewalks, or small foundations, this material is ideal.
Keep in mind that the batching volume determines the strength, which in turn varies since the components are not constant.
2. A Combination of Designs
To get a certain level of strength and performance, a “bespoke combination” has been tested in a laboratory.
Constructing massive structures like bridges, skyscrapers, and columns that can hold a lot of weight is their intended use.
The usage of cement is made more precise, quality control is improved, and money is saved.
Think about the M25, M30, M40, and subsequent variants as an example.
3. RMC, or Ready-Mix Concrete
What we mean when we say “cement that is ready to use” is concrete that has been mixed and then brought to the site from a central place.
Use: It’s a great tool for big tasks that need to be done quickly and efficiently every time.
It guarantees consistent performance, for one thing, and cuts down on the amount of work and time needed, too.
4. Super-Duty Concrete (SDUCC)
A unique blend of concrete that is easier to work with, lasts longer, and is more durable than regular concrete.
Use: Made use of in construction projects, such as bridges, dams, and skyscrapers.
Additives like fly ash, silica fume, or superplasticizers may improve performance.
Quantity Surveyor online certification course on Entri app! Join Now!
Factors Affecting Concrete Mix Ratios
When it comes to the proportions of cement, sand, additives, and water that are used in the production of concrete, there are a lot of factors that might alter. Through the acquisition of knowledge about these aspects, it is possible to enhance the strength, durability, and workability of concrete.
- The amount of water that is present in the cement, the kind of cement that it is, and the quality of the cement.
- Aggregates Coming in a Variety of Forms and Dimensions
- The quantity of moisture present in the aggregate, the manner in which it ought to be combined, and the length of time that it ought to be mixed for.
- Both the current status of the environment and the manner in which combinations are used.
Tips for Effective Concrete Mix Design
It is necessary to have thorough planning, exact proportioning, and severe quality control in order to produce a concrete mix that is both long-lasting and of high quality. When engineers and builders follow to mixing design principles that have been shown to be beneficial, they are able to achieve consistent strength, workability, and long-term performance in every project that they undertake.
1. Make sure you choose supplies of high quality
Put cement to use in conjunction with things that are fresh, clean, and well-organized. For concrete, the materials that are utilized to manufacture it have an effect on both its strength and its durability. There are notable differences in the strengths of various materials.
2. Make certain that the ratio of water to cement is always of an appropriate value
Both the concrete’s durability and its workability would suffer if an excessive amount of water was added to the recipe. You should always make sure that the ratio of water to cement is exactly where it should be for the greatest possible workability and power. Between 0.40 to 0.55 is the typical range for this value.
3. Ensure that everything is well combined
The uniformity of the mixing operations will not be affected in any way, nor will there be any fluctuation in the quality of the finished product. For more extensive operations, it is recommended to use motorized mixers in order to guarantee standardization.
4. Conduct a test of the concrete mix
Before pouring the large batch of concrete, it is essential to conduct a test on a fraction of the mixture. We can be certain that the combination will be robust enough and practical enough if we proceed in this manner. Adjustments to the numbers are permitted if you believe that they are required.
5. Rely on additives with extreme care
To make a combination simpler to work with, to set more quickly, and to give it more durability, chemical additives such as superplasticizers, retarders, or boosters may be added to the mixture. For all intents and purposes, however, the directions provided by the manufacturer must be strictly followed.
6. Determine the Scrubbing Environment and Regulate It
Once the concrete has had the opportunity to harden, it is quite unlikely that it would be able to break under normal circumstances. This would make the concrete completely impervious to harm. It is essential to ensure that the concrete remains moist for the first seven to fourteen days after it has been placed onto the ground.
7. Observe the Guidelines That Are Already in Effect
By adhering to national and international standards such as IS 10262, ACI 211, or BS 8500 throughout the manufacturing process, a mix may be guaranteed to be acceptable and safe for use.
Master Quantity Surveying – Build a Rewarding Career Today!
Gain in-demand skills in cost estimation, project budgeting, and contract management with our Quantity Surveying Course. Learn from industry experts and boost your career in construction and infrastructure. Enroll now and take the first step toward success!
Know MoreKey Takeaways
- The strength, durability, and workability of concrete are all evaluated based on the design of the concrete mix.
- The ratios 1:2:4 and 1:1.5:3 are examples of standard ratios that are used for general and structural purposes.
- In order to achieve the necessary level of concrete quality, the water-to-cement ratio is an extremely important factor.
- Concrete performance may be affected by a variety of factors, including the quality of the materials used, the conditions of the environment, and the mixing processes.
- Before using the product on a wide scale, doing trial mixes ensures that it is accurate and consistent.
- Establishing concrete buildings that are not only safe but also cost-effective and long-lasting may be accomplished by adhering to best practices and standards.
Final Thoughts
In the process of developing the optimal concrete mixture, both science and art are engaged in the whole process. When it comes to determining whether or not a structure will last for decades or finally fall down, the amounts of cement, sand, aggregates, and water that are used in its construction might be the decisive factor. When we pay attention to the details, such as using high-quality materials, keeping a water-to-cement ratio that is under control, and testing our mixes, we not only create structures that are more durable, but we also imbue people with confidence in the job that we do. Creating a concrete mix that is well-designed is the first stage in the process of developing structures that are safe, long-lasting, and beneficial to the environment in the future.
Master Quantity Surveying – Build a Rewarding Career Today!
Gain in-demand skills in cost estimation, project budgeting, and contract management with our Quantity Surveying Course. Learn from industry experts and boost your career in construction and infrastructure. Enroll now and take the first step toward success!
Know MoreFrequently Asked Questions
Why is concrete mix design important?
It ensures that concrete is strong, workable, durable, and cost-effective, reducing material waste and structural failures.
What affects the concrete mix ratio?
Factors include material quality, aggregate size, moisture content, temperature, and mixing methods.
What is ready-mix concrete?
Ready-mix concrete (RMC) is prepared in batching plants and delivered ready to use, ensuring consistency and saving time.
What happens if too much water is added to the mix?
Excess water weakens the concrete, reduces strength, and increases the risk of cracking and shrinkage.
What are common mistakes in concrete mix design?
Using poor-quality materials, incorrect ratios, inadequate mixing, or insufficient curing are the most common errors.
How long should concrete be cured?
Concrete should be cured for at least 7 to 14 days to achieve optimal strength and prevent surface cracks.
How can I ensure the best concrete mix design for my project?
Follow standard guidelines (like IS 10262 or ACI 211), perform trial mixes, and adjust ratios based on test results and site conditions.