Table of Contents
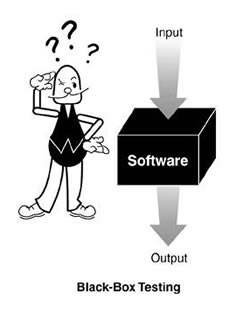
Black Box Testing is a software testing method in which the functionalities of software applications are tested without having knowledge of internal code structure, implementation details and internal paths. Black Box Testing mainly focuses on input and output of software applications and it is entirely based on software requirements and specifications. It is also known as Behavioral Testing.
The above Black-Box can be any software system you want to test. For Example, an operating system like Windows, a website like Google, a database like Oracle or even your own custom application. Under Black Box Testing, you can test these applications by just focusing on the inputs and outputs without knowing their internal code implementation.
White Box Testing
White Box Testing is a testing technique in which software’s internal structure, design, and coding are tested to verify input-output flow and improve design, usability, and security. In white box testing, code is visible to testers, so it is also called Clear box testing, Open box testing, Transparent box testing, Code-based testing, and Glass box testing.
It is one of two parts of the Box Testing approach to software testing. Its counterpart, Blackbox testing, involves testing from an external or end-user perspective. On the other hand, White box testing in software engineering is based on the inner workings of an application and revolves around internal testing.
The term “WhiteBox” was used because of the see-through box concept. The clear box or WhiteBox name symbolizes the ability to see through the software’s outer shell (or “box”) into its inner workings. Likewise, the “black box” in “Black Box Testing” symbolizes not being able to see the inner workings of the software so that only the end-user experience can be tested.
Types of White Box Testing
White box testing encompasses several testing types used to evaluate the usability of an application, block of code or specific software package. There are listed below —
- Unit Testing: It is often the first type of testing done on an application. Unit Testing is performed on each unit or block of code as it is developed. Unit Testing is essentially done by the programmer. As a software developer, you develop a few lines of code, a single function or an object and test it to make sure it works before continuing Unit Testing helps identify a majority of bugs, early in the software development lifecycle. Bugs identified in this stage are cheaper and easy to fix.
- Testing for Memory Leaks: Memory leaks are leading causes of slower running applications. A QA specialist who is experienced at detecting memory leaks is essential in cases where you have a slow running software application.
Learn Coding in your Language! Enroll Here!
Types of Black Box Testing
1: What is software testing?
There are many types of Black Box Testing but the following are the prominent ones –
- Functional testing – This black box testing type is related to the functional requirements of a system; it is done by software testers.
- Non-functional testing – This type of black box testing is not related to testing of specific functionality, but non-functional requirements such as performance, scalability, usability.
- Regression testing – Regression Testing is done after code fixes, upgrades or any other system maintenance to check the new code has not affected the existing code.
Difference between White-box and Black-box Testing
Black Box testing is also known as behavioral testing, data driven testing or closed box testing. It is the process of giving input to the system and checking the output of the system without considering on ‘how the output was generated’.
Black box testing is a testing strategy solely based on requirements and specifications. It requires no knowledge of internal paths, structures, or implementation of the software on the applications that are being tested. However, this strategy minimizes the tester’s approach on finding the errors or defects in the testing program. Also, the defects are not corrected because of lacking internal application knowledge of the tester.
Black box testing is done at an outer level of the system; it simply checks if the output is correct for the given input. The functionalities of the application are checked and tested. Also, user knowledge on the internal flow or design of the system are not required, as they simply test the system without any information on how the system is made.
White-box Testing is also known as structural, open box, clear box or glass box testing. It is the process of giving input to the system and checking how the system processes the given input by generating the given output.
White-box testing is a testing strategy based on internal paths, code structures, and the implementation of the software being tested. It generally requires detailed programming skills. This strategy helps in quickly finding the bugs and defects as compared to other methods. It gives a complete testing coverage by ensuring exactly what to test in an application.
White-box testing involves thorough testing of the application. It typically includes checking with the data flow, exceptions, and errors. It also checks the defect handling and compares the results to the written code. It refers to a testing team or system with full knowledge, along with, it accesses to all the source codes and other architectural documents. They test the internal logics and applications of the code.
Learn to code from industry experts! Enroll here
Comparison between White-box and Black-box Testing
|
White-box Testing |
Black-box Testing |
|
| Definition | It is a software testing method in which the internal structure, design and implementation of the program is known to the tester. | It is a software testing method in which the internal structure, design and implementation of the program are not known to the tester. |
| Tested by | It is done by software developers. | It is done by a professional testing team. |
| Coding knowledge | This requires knowledge of internal coding. | This does not require knowledge of internal coding. |
| Concern | It is concerned with testing the implementation of the program. | It does not concern with the structure of the program. |
| Testing | It is mainly applicable to lower level of testing such as:
|
It is mainly applicable to higher level of testing such as:
|
| Knowledge | Implementation knowledge is required for testing. | Implementation knowledge is not required for testing. |
| Test basis | Test cases are based on detail design. | Test cases are based on required specifications. |
| Time | It is time consuming and exhaustive. | It is less time consuming and exhaustive. |
| Algorithm test | It is suited for algorithm testing. | It is not suited for algorithm testing. |
| Testing method | Data domain and internal boundaries are better tested. | This can only be done by trial and error method. |
| Advantages |
|
|
| Disadvantages |
|
|






.jpg)









