Table of Contents
Java continues to be one of the most widely used programming languages of 2025 thanks to its unparalleled flexibility and decades of tried-and-tested reliability. Used to run enormous business systems, Android applications, and scalable web apps, Java is applied across almost every major industry. Backed by solid frameworks such as Spring Boot, massive following, and platform agnosticism, Java has turned out to be a favorite among developers. While newer languages are trending, Java remains future-oriented with newer innovations such as virtual threads and improved cloud integration, demonstrating that it’s not only timely but still sought after for creating applications with a future. In this article, we are discussing Java as a career path.
Eager to master Python? Enroll in our free demo now!
Why Choose Java as a Career?
Java is a robust and future-proof platform for those eager to take up a career as software professionals. Here’s why:
- Timeless Strength: Java is well above 25 years old and still growing, proof that it has timeless strength within the ever-changing, ever-shifting world of technology.
- Industry Adoption: Finance, banking, insurance, and government are some of the big industries that make heavy usage of Java in their backends and mission-critical applications.
- Android App Development: Java is still one of the key languages in which Android apps can be developed with a huge potential for mobile app development.
- Open Source Platform & Community: Java boasts a huge gigantic ecosystem and extensive global developer base for support and knowledge-sharing with Spring and Hibernate toolkits and Maven and Jenkins build toolchains.
Together, they make up Java as a safe and lucrative career option with vast potential to enhance.
Java Career Path Overview
The Java career path promises consistent growth, from code writing to heading large-scale engineering teams. Here is an overview of every one of the main roles, required skills, and the typical salary brackets in both Indian and international environments:
| Role | Experience | Role Description | Expected Skills | Avg. Salary (India) | Avg. Salary (Global) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Junior Java Developer | 0–2 years | Assists with bug fixes, writing test cases, and small development tasks under guidance | Core Java, OOP, Git, Basic SQL, IDEs (Eclipse/IntelliJ) | ₹3.5L – ₹5.5L per year | $40,000 – $60,000 |
| Java Developer | 2–5 years | Develops backend modules, builds APIs, and collaborates with team members | Core Java, Spring Boot, REST APIs, Maven, SQL | ₹6L – ₹10L per year | $60,000 – $90,000 |
| Senior Java Developer | 5–9 years | Designs features, mentors juniors, optimizes performance, and ensures code quality | Microservices, CI/CD, Docker, Kafka, Advanced Java | ₹12L – ₹20L per year | $90,000 – $130,000 |
| Java Architect / Technical Lead | 9–12+ years | Leads architecture design, ensures scalability and performance, and sets technical direction | System Design, Cloud (AWS/GCP), Security, DevOps | ₹20L – ₹35L+ per year | $130,000 – $180,000 |
| Engineering Manager / VP Engineering | 12–20+ years | Manages teams, aligns tech with business goals, oversees large projects and budgets | Leadership, Strategic Planning, Architecture Oversight | ₹35L – ₹60L+ per year | $180,000 – $250,000+ |
Junior Java Developer (less than two years)
Here you become a Java newbie or new employee. Your role as a programmer is to do nothing but some minor tasks like bug fixing, test case writing, and submitting code for optimization under supervision.
- Skills: You must have Java basics, object-oriented programming, SQL, Git, and IDEs such as IntelliJ
- Salary: Ranges from ₹3.5L to ₹5.5L in India and $40,000 to $60,000 in the US and other nations.
Java developer (2–5 years)
Work closely with teams from different departments to build modules, APIs, and back-end programming as a mid-level skilled Java developer.
Skills: Core Java, Spring Boot, REST APIs, unit testing, Maven/Gradle, and MySQL/PostgreSQL are all necessary skills.
Salary: The pay range in India is between 6 and 10 lakh rupees. It ranges from $60,000 to $90,000 in the US and throughout the world.
Senior Java Developer (5–9 years)
They write the code for the systems, make sure they run as well as they can, and help train new personnel.
They make style decisions and other decisions most of the time.
- Skills: Some of the skills that you must possess at this level are microservices, CI/CD, Docker, message suppliers (Kafka and RabbitMQ), and accelerating performance.
- Salary: ₹12L to ₹20L in India, $90,000 to $130,000 in the US, and globally
Java Architect or Technical Lead (9–12 years or more)
Java architects are responsible for several tasks, including the design of big systems, technology selection, and code quality and adaptability assurance. Programmers’ technological needs are also the purview of tech leaders.
- Skills: Proficient in system architecture, growth patterns, security, DevOps, and cloud platforms (AWS/GCP).
- Salary: 20–35 Lakh in India, 130–180 K in the US/worldwide.
VP engineering or manager (12–20 years or more)
Leading entails overseeing a team, completing tasks, allocating funds, and ensuring that technological objectives are in line with operational requirements. The design level remains quite high.
Skills: Ability to lead, organize projects, hire, communicate with stakeholders, and create at a high level are all essential talents.
Salary: A salary ranging from ₹35L to ₹60L+ in India and $180,000 to $250,000+ in the US and worldwide
Explore Free Courses!
Explore Free Courses! Dive into a world of knowledge with our curated selection of free courses designed to help you learn new skills, advance your career, or simply explore your passions.
Start Learning!Popular Job Roles for Java Professionals
Java is a versatile language that can be used to build many types of applications in any sector. Here are a few of the most lucrative fields that will be using Java in 2025, along with brief descriptions of each:
Java Backend Developer
A Java backend developer’s primary job is to create the logic and APIs that make online and mobile programs work.
- Some of the tasks include building RESTful APIs, working with databases, managing business logic, and making sure everything is safe and can grow.
- Cloud deployment basics, MySQL/PostgreSQL, Docker, Hibernate, REST APIs, and Java are all skills you need.
- There is a lot of demand in the platters, e-commerce, banking, and software as a service.
Android Application Developer
Most of the time, Android app developers code in Java or Kotlin.
- Responsible for building Android app features, working with user interface components, calling backend APIs, and making sure everything runs as well as possible.
- You require Java, the Android software development kit (SDK), Jetpack libraries, SQLite, and UI/UX design.
- The market is always becoming bigger since Android is utilized all around the globe.
Full Stack Developer (Java + Frontend)
To design web applications that are fully functional, this role demands backend Java proficiency as well as frontend.
- Server and client-side feature design and integration, API usage management, and responsiveness of the design are all the responsibilities.
- All these techniques, Angular, JavaScript, HTML, CSS, Spring Boot, REST APIs, and Java, are needed.
- Startups and product companies are looking eagerly for one-stop developers, and that is creating industry demand.
DevOps Engineer (with Java-based apps)
DevOps engineers work to make the development and deployment of applications and microservices better, with a concentration on Java.
- To make sure that things are always available, automate builds and deployments, keep focus on Java programs, and manage continuous integration and continuous delivery pipelines.
- You need to know how to use cloud systems like AWS and GCP, as well as Git, Kubernetes, Jenkins, Maven/Gradle, Docker, and Java (for app context).
- There is a lot of demand in the sector, particularly for commercial settings and cloud-native development.
QA Automation Engineer (using Java in Selenium/TestNG)
These experts use Java to make sure that software products are of high quality by automating testing.
- Writing and running automatic test scripts, doing beta testing, and putting tests into CI/CD processes are some of the things that you need to do.
- You need to know how to use Java, Selenium WebDriver, TestNG, JUnit, and Maven and have a general idea of how web features work.
- Demand: High in businesses that want quick and steady releases.
Big Data Developer (Hadoop with Java)
Hadoop and other similar tools are used by Big Data Developers to work with big datasets.
- Writing Map Reducing jobs, designing and implementing big data processing systems, and improving speed are some of the things that you need to do.
- Java, Hadoop, Apache Spark, Hive, HDFS, and knowledge of how to handle data are skills that are needed.
- Analytics, IoT, and data-driven businesses are using it more and more.
Get hands-on with our python course – sign up for a free demo!
Industries That Hire Java Developers
Java is the best programming language for many tasks because it is safe, effective, and easy to expand. The main places that need Java writers the most are these:
IT Services and Consulting
Lots of big IT service and consulting firms use Java to make apps and business solutions just for their clients, as well as to keep old systems running for clients all over the world.
- Some companies that do this are Infosys, TCS, Wipro, and Accenture.
- So why Java? Because it’s safe, easy to use, and adaptable to different jobs and people.
Banking, Financial Services, and Insurance (BFSI)
Java is used by the BFSI sector to make safe, fast systems for online banking, trade sites, payment methods, and insurance handling.
- JPMorgan Chase, HDFC Bank, ICICI, and Goldman Sachs are some examples.
- Why Java? Because it has strong support for handling transactions, security, and multiple threads.
E-commerce
Many of the core systems in e-commerce sites run on Java. These systems show products, process orders, authenticate users, and connect payments.
- Amazon, Flipkart, Myntra, and Shopify are some examples.
- Why Java? Frameworks like Spring Boot make it scalable and stable even when there is a lot of traffic.
Telecom
Java is used by telecom companies to manage big amounts of customer data, payment tools, and platforms for providing services.
- Airtel, Jio, Vodafone Idea, and Ericsson are some examples.
- Why Java? Because it can be used for real-time processing and system interaction.
Government & Public Sector
It is used by government agencies and public service platforms for e-governance, ID systems (like Aadhaar), and big citizen-service apps.
- NIC, UIDAI, and the Indian Railways are some examples.
- Why Java? It’s open source, safe, works on any device, and is great for long-term projects.
Top Skills Needed for a Java Career
Proficiency in the core and new tools is required for a prosperous Java professional in 2025. These are the things you can do if you are a Java professional:
Java Core (OOP, Collections, Multithreading)
All that a Java employee should know essentially lies here.
- By learning to apply classes, objects, inheritance, and polymorphism to structuring your code, you will be in a position to make it simple to reuse repeatedly and alter.
- Learn how to store and manage data efficiently using collections with lists, sets, maps, and queues.
- Multithreading is applied in high-performance and real-time systems because of the reason that it enables programmers to develop programs that can do multiple things simultaneously.
Spring/Spring Boot
Spring is the most popular Java framework for building backend applications.
- Spring Boot simplifies building production-grade apps with less configuration.
- It takes care of aspects such as dependency injection, security, and building REST APIs in an efficient manner so that development is easier and quicker.
Hibernate
If you are a Java programmer, Hibernate is a helpful tool to deal with databases.
- It is an object-relational mapping tool, so rather than SQL, you can use Java objects to handle databases.
- It simplifies CRUD operations and also manages links, transactions, and database connections easily.
REST APIs
With REST APIs, various internet-based systems can communicate to each other.
- You’ll often be a Java worker who makes RESTful web services that other apps, like front-end or mobile apps, will use.
- To make, test, and describe APIs, you’ll use tools like Spring Boot.
SQL/Database Management
Databases are often used by Java apps to store and get info.
- You should know how to make simple SQL queries, join tables, and set up databases so that they work well and are safe.
- MySQL, PostgreSQL, and Oracle are all databases that are often used.
Git/GitHub
All software development jobs need to keep track of versions.
- If you need to, Git lets you go back to earlier versions of your code, work with other teams, and keep track of changes to your code.
- When you store your code on GitHub, you can handle problems and add to projects online.
Basic Frontend (HTML, CSS, JS—for full-stack roles)
Full-stack Java developers must have hands-on experience with frontend technology.
- HTML/CSS: Layout and design the web page structure.
- JavaScript: Introduce interactivity to websites (forms, buttons, etc.).
- Although frontend is not your area of expertise, possessing this knowledge allows you to bridge the Java backend and the user interface.
Explore Free Courses!
Explore Free Courses! Dive into a world of knowledge with our curated selection of free courses designed to help you learn new skills, advance your career, or simply explore your passions.
Start Learning!Java Career Growth Timeline (Sample Path)
For most Java professionals, their career path is one of steady growth. This is how your job might change over time:
Year 0-2: Junior Java Developer
During this part of learning, you build a strong base.
- Help with writing, solving bugs, and testing while being supervised.
- Key Skills: Core Java, basic SQL, Git, version control, and knowing how projects are put together.
Year 3–5: Mid-Level Java Developer
You take responsibility for features and make contributions on your own.
- Develop modules, write APIs, take part in code reviews, and make sure speed is at its best.
- Focus on Spring Boot, REST APIs, database design, and the basics of deployment.
Year 6–9: Lead or senior developer
During this time, technical decisions and guidance are made.
- Lead teams, help younger developers, check code for errors, and make sure systems can grow as needed.
- Focus on CI/CD, Docker, message queues, microservices, and design models.
Year 10+: Java Architect/Manager
As time goes on, you start to think about bigger issues like system design and team planning.
- Define design, pick platforms, lead teams or partners, and make sure that technology fits with the goals of the business.
- Focus Areas: AWS and Google Cloud Platform (AWS/GCP), system scaling, leadership, budgets, and planning.
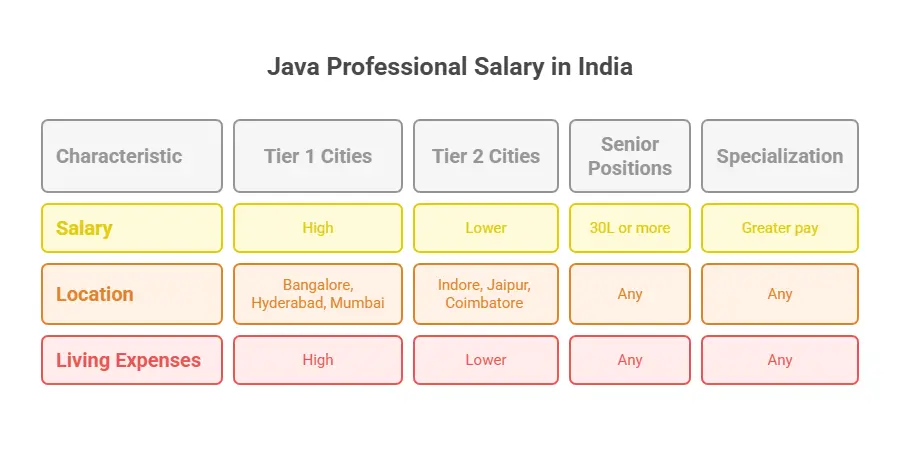
Salary Trends In India (2025)
Java professionals in India are well paid, and their salary increases significantly as they gain experience and progress in their career. Your salary will also vary based on whether you reside in a Tier 1 or Tier 2 city.
| Role | Tier 1 Cities (₹/year) | Tier 2 Cities (₹/year) |
|---|---|---|
| Junior Java Dev | ₹3.5L – ₹5.5L | ₹3L – ₹4.5L |
| Java Developer | ₹6L – ₹10L | ₹5L – ₹8L |
| Senior Java Dev | ₹12L – ₹20L | ₹10L – ₹15L |
| Architect/Lead | ₹20L – ₹35L+ | ₹18L – ₹28L+ |
- Good compensation is offered in Tier 1 cities like Bangalore, Hyderabad, and Mumbai, with numerous large-scale IT companies and foreign technology parks.
- Tier 2 cities like Indore, Jaipur, and Coimbatore offer lower pay but at much lower living expenses.
- Preparation-level positions like Java Architect or Lead Developer can offer 30L or more in large MNCs or product companies.
- Its specialization in a specific field (say telecommunication or banking), licensure, or cloud integration expertise can also result in greater compensation.
Certifications That Boost Your Java Career
Obtaining a certification not only makes your resume look prettier, but it can also assist you in getting a better job, career growth, and salary increment. In order to make your Java career stronger in 2025, the below four crucial certifications can back you up:
Oracle Accredited Cloud Associate
Skill level: Entry-level
Java 8 or higher developers should target this entry-level certification.
- What you will prove: You’ve got a good grasp on the fundamentals of Java, object-oriented programming, data types, loops, classes, methods, and exception handling.
- Best suited for: Starting Java programmers or new entrants.
- Benefits: Get a good foundation for higher-level certifications and increase your likelihood of securing your first job for Java with these advantages.
Oracle Certified Professional (OCP)
Skill level: Upper-level
An advancement from OCA, the OCP exam delves deeper into Java’s capabilities.
- Validation Requirements: Extensive understanding of Java APIs, threads, JDBC, file I/O, NIO, collections, and security.
- These developers should have a minimum of two years of expertise with Java.
- Advantages: Establishes your credentials as a dedicated Java developer and is highly esteemed in corporate environments.
Spring Professional Certification
It is provided by VMware
This proves that you have mastered the Spring and Spring Boot frameworks, which are popular tools for developing microservices and Java web apps.
- Skills in REST APIs, testing, security, and Spring Data, as well as Spring Boot and Spring Core, are shown.
- Apps built for the cloud and Java backend developers are the target audience.
- Advantages: Raises your marketability as a full-stack or backend developer, which is particularly important for product firms and startups.
AWS Certified Developer – Associate
Targeted at the cloud-based application
Although this certification is not exclusive to Java, it is very useful for Java developers who are working on cloud-based application development and deployment.
- The ability to deploy Java projects using CI/CD technologies and leverage AWS services like Lambda, S3, and DynamoDB is what it proves.
- Java developers specializing in cloud, DevOps, or distributed system development will find this ideal.
- Boosts your cross-functional value and looks good on a CV for cloud-native developer jobs.
Final Thoughts
Java programming remains one of the safest and most rewarding career options in the technology industry. Java will remain one of the most sought-after choices for developers in 2025 because of its ability to withstand future trends such as microservices, cloud computing, and mobile app development, and also because of its continued relevance in industries such as banking, e-commerce, telecom, and government. Java offers a strong platform for diverse professional prospects, from entry-level jobs to higher levels, due to strong frameworks such as Spring Boot, greater cloud platform interfacing, and a huge open-source community.
Get hands-on with our python course – sign up for a free demo!
Explore Free Courses!
Explore Free Courses! Dive into a world of knowledge with our curated selection of free courses designed to help you learn new skills, advance your career, or simply explore your passions.
Start Learning!Frequently Asked Questions
Is Java still relevant in 2025?
Absolutely. Java remains one of the most widely used languages in enterprise, Android, backend development, and government systems. With new features like virtual threads and cloud-native support, it continues to evolve and stay modern.
Can a Java developer become a full-stack developer?
Yes. If you learn frontend technologies like HTML, CSS, JavaScript, and frameworks like React or Angular, you can transition into a full-stack developer role using Java for the backend.
Which is better: Java or Python for a career?
Both are excellent, but Java has the edge in enterprise environments, Android development, and large-scale systems. Python is popular in data science and scripting. Your choice depends on your career goals.
How long does it take to become a Java developer?
If you study consistently and work on projects, you can become job-ready within 4–6 months. For mid- to senior-level roles, hands-on experience of 2–5 years is typically expected.
Can I start a career in Java without a computer science degree?
Yes! While a degree can help, many successful Java developers are self-taught or come from non-CS backgrounds. What matters most is your understanding of Java, problem-solving skills, and practical experience through projects or internships.