Table of Contents
Key Takeaways:
- Programming languages like Python, C, JavaScript, and SQL are essential tools for cybersecurity professionals.
- Scripting languages such as Bash and PowerShell enhance your ability to automate security tasks and manage systems efficiently.
- Low-level languages like C and C++ provide a deep understanding of system vulnerabilities and malware behavior.
- Mastering these languages opens up a variety of career paths including ethical hacking, penetration testing, and security analysis.
- Following a practical learning roadmap, combined with expert guidance like Entri’s Cybersecurity course, can accelerate your skill development and job readiness.
Introduction
Cybersecurity remains one of the fastest growing fields globally, with predictions indicating 3.5 million cybersecurity job openings worldwide by 2025 (source). As cyber threats grow more complex, mastering the best programming languages for cybersecurity in 2026 has never been more critical.
Languages such as Python, C, JavaScript, and SQL consistently top the list due to their roles in automation, threat detection, penetration testing, and secure software development. These skills not only boost your career prospects but also equip you to actively defend and fortify digital environments.
Why Programming Languages Matter in Cybersecurity
-
Automation and Scripting: Automate repetitive security checks and streamline incident response.
-
Malware and Exploit Analysis: Decode malicious software and system vulnerabilities.
-
Building Security Tools: Develop scripts and applications to test and strengthen systems.
-
Incident Forensics: Analyze logs and create tools for detailed investigations.
-
Job Market Demand: Programming skills are required in 60%+ of cybersecurity job listings
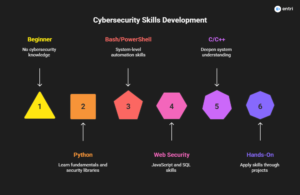
Top Cybersecurity Languages to Learn
1. Python
Python’s clear syntax and powerful libraries like Scapy and Requests make it perfect for automation, penetration testing, and malware analysis. Given its accessibility and applicability, Python tops the cybersecurity language charts.
-
Used in building SIEM tools, network scanners, and exploit frameworks.
-
Ideal for beginners learning cybersecurity programming.
-
Employ it in real-world tasks such as scripting ransomware detection.
-
Try hands-on projects like building a network packet sniffer in Python.
2. C and C++
C and C++ offer close-to-the-hardware control, helping cybersecurity pros understand buffer overflows, rootkits, and kernel exploits.
-
Crucial for reverse engineering malware and exploits.
-
Many core OS components and security tools are written in these languages.
-
Combine with Assembly language for comprehensive malware analysis.
-
Build a small program that handles memory operations to feel the power and risks of low-level programming.
3. JavaScript
JavaScript is essential for tackling web application vulnerabilities like Cross-Site Scripting (XSS).
-
Most modern web apps and browsers rely heavily on JS.
-
Understand common web attacks and defend client-side environments.
-
Learn to write safer front-end applications and browser extensions.
-
Practice live debugging and XSS attack demonstration on controlled test sites.
4. SQL
Databases lie at the heart of most applications, making SQL indispensable for cybersecurity.
-
Master SQL to detect and prevent SQL injection, one of the most common causes of data breaches.
-
Use it to analyze and audit database permissions and vulnerabilities.
-
Experiment with injection attacks in safe lab environments to understand risks.
5. Bash / Shell Scripting
Useful for automating Linux and Unix system tasks, Bash scripts simplify incident detection and response.
-
Automate processes like log file analysis and system backups.
-
Facilitate quicker, repeatable security audits and penetration testing.
-
Write shell scripts to scan for vulnerabilities or monitor system health.
6. PowerShell
PowerShell remains vital for Windows environments—key for system automation and forensic analysis.
-
Manage Windows system configurations and security policies programmatically.
-
Develop scripts that detect suspicious activity and unauthorized changes.
-
Use PowerShell scripts to perform audit logging and malware detection on Windows servers.
Tips to Choose the Right Programming Language
-
Start with Python, given its versatility and beginner-friendly nature.
-
Align your learning with your career focus: web security leans on JavaScript and SQL, while malware analysis demands C/C++ and low-level knowledge.
-
Use scripting languages like Bash and PowerShell to enhance your operational efficiency.
-
Participate in Capture The Flag (CTF) challenges to apply your coding skills in practical cybersecurity contexts.
-
Keep current with evolving threats, programming trends, and security technologies.
Practical Cybersecurity Languages Learning Roadmap
Building expertise in cybersecurity programming languages is best achieved through a well-structured learning plan. Here’s a detailed roadmap to help you progress effectively and maximize your chances of success in this competitive field.
Step 1: Master Python Fundamentals and Security Libraries
Python is widely recognized for its simplicity and power, making it the ideal starting point.
-
Begin with Python basics: syntax, data types, control flow, and functions.
-
Progress to libraries essential for cybersecurity such as Scapy (for network packet manipulation), Requests (for HTTP requests), and Socket (for network communications).
-
Practice writing small scripts that automate simple security tasks:
-
Scanning open ports on a network.
-
Automating log analysis.
-
Writing simple brute-force or password cracking scripts for learning purposes.
-
-
Experiment with open-source Python security tools like Paramiko for SSH, or Impacket for network protocols.
-
Engage with interactive platforms or courses offering real-life scenarios and coding challenges.
Tip: Join Capture The Flag (CTF) challenges or online platforms like Hack The Box, TryHackMe to apply Python scripting in cybersecurity problem-solving.
Step 2: Learn Bash or PowerShell for System-Level Automation
Understanding scripting for operating system environments is crucial for penetration testing and incident response.
-
Bash (for Linux/Unix):
-
Learn scripting basics such as creating shell scripts, using command-line utilities, and automating system administration tasks.
-
Develop scripts that monitor system logs, automate backups, or scan for vulnerabilities.
-
Familiarize yourself with common Linux security tools (e.g., Nmap, Netcat) and how to script their execution.
-
-
PowerShell (for Windows):
-
Understand PowerShell commands and scripting to automate Windows system administration.
-
Write scripts for event log analysis, user account audits, and malware detection.
-
Learn how PowerShell integrates with Windows security frameworks.
-
Tip: Practice writing scripts that combine multiple commands and handle error-checking, which mirrors real cybersecurity automation needs.
Step 3: Build Web Security Skills with JavaScript and SQL
Web applications are a favorite target for attackers, so proficiency here is invaluable.
-
JavaScript:
-
Learn core JavaScript concepts: variables, functions, DOM manipulation, and asynchronous operations.
-
Study common web vulnerabilities like Cross-Site Scripting (XSS) and understand how malicious JavaScript exploits these.
-
Practice manually identifying and fixing vulnerabilities in sample web projects.
-
-
SQL:
-
Understand SQL basics and how databases manage data.
-
Learn about SQL injection, one of the most widespread web vulnerabilities, by practicing simulated attacks in a safe environment.
-
Get proficient at writing secure SQL queries to prevent injections.
-
Tip: Use platforms like OWASP Juice Shop to practice finding and mitigating web vulnerabilities with JavaScript and SQL knowledge.
Step 4: Deepen System Understanding with C and C++
For advanced cybersecurity roles such as malware analyst or exploit developer, low-level languages are essential.
-
Start learning C fundamentals: pointers, memory management, and data structures.
-
Explore C++ features like object-oriented programming that power complex system applications.
-
Study how vulnerabilities such as buffer overflows and memory leaks occur in C programs.
-
Practice reading and analyzing open-source security tools written in C/C++.
-
Learn basics of Assembly language for reverse engineering and malware dissection.
Tip: Set up a safe lab environment with virtual machines to compile and test C/C++ programs, learning how exploits operate at the system level.
Step 5: Apply Your Skills Through Hands-On Projects and Challenges
Theory is important, but real learning happens when you build and break things.
-
Participate in Capture The Flag (CTF) competitions, which simulate real-world cybersecurity challenges.
-
Develop small security tools or scripts automating vulnerability scans or log analysis.
-
Contribute to open-source cybersecurity projects to gain practical exposure.
-
Use platforms like Hack The Box or TryHackMe to simulate penetration testing and defensive operations.
-
Create a personal portfolio of projects showcasing your scripting and programming skills in cybersecurity.
Tip: Regular challenges help solidify concepts and prepare you for interviews and real job tasks.
Step 6: Stay Updated and Continue Learning
The cybersecurity landscape is constantly shifting with new technologies and threats.
-
Follow cybersecurity news portals, blogs, and forums for the latest trends and vulnerabilities.
-
Refresh your knowledge with advanced courses, certifications, and workshops.
-
Network with professionals through conferences and online communities for shared learning and mentorship.
-
Experiment with emerging languages or frameworks that gain relevance to cybersecurity.
Tip: Schedule regular self-study sessions focused on emerging tools and exploits to keep your skills sharp.
Also read: Cybersecurity Career Path
Conclusion
Mastering the right programming languages is key to thriving in the cybersecurity domain. Languages like Python, C, JavaScript, and SQL provide the tools to automate, investigate, and defend digital environments. Scripting languages like Bash and PowerShell complement your skillset by enabling automation and system control.
Ready to transform your coding skills into a cybersecurity career? Join Entri’s Cybersecurity course to gain expert-led, hands-on training, practical projects, and mentorship designed to help you become job-ready in this fast-growing field. Secure your future by learning the languages that matter most in cybersecurity today!
Frequently Asked Questions
Are these languages the best to learn for cybersecurity in 2026?
Yes, Python, C/C++, JavaScript, SQL, Bash, and PowerShell are consistently rated among the best due to their broad applications in current cybersecurity roles.
Do I need to learn all these languages?
Not necessarily all—choose based on your career goals. Python and Bash are excellent starting points, while specialized roles might require C/C++ or web-focused JavaScript and SQL.
How quickly can I become proficient in these languages?
Python basics can be learned within months; mastery comes through projects and practice. Other languages like C/C++ may require longer learning curves.
Can programming alone make me a cybersecurity expert?
Programming is crucial but should be complemented with knowledge of networks, protocols, threat intelligence, and ethical hacking concepts.
How can I practice these languages effectively?
Engage in Capture The Flag competitions, build personal projects, contribute to open-source security tools, and enroll in structured courses with hands-on labs.