Table of Contents
Preparing for a BIM Specialist role? This guide covers the most common BIM Specialist interview questions that recruiters ask across architecture, engineering, and construction firms. Whether you’re just starting out or have years of BIM experience, these questions help you showcase your technical knowledge, coordination skills, and project insight. From Revit workflows and clash detection to ISO standards and model management, we’ve got you covered. Use this resource to build your confidence and prepare for any challenge that comes your way.
BIM Specialist Interview Questions & Answers
Introduction
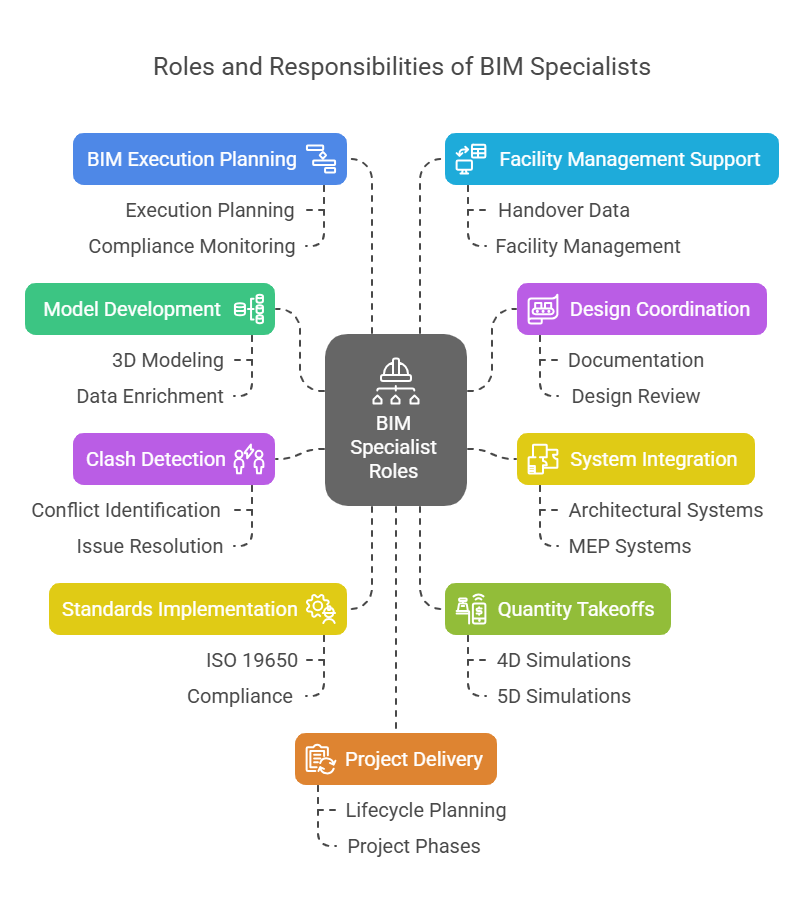
BIM Specialists are essential in leading digital transformation within architecture, engineering, and construction. They ensure accurate model creation, maintain project data integrity, and facilitate collaboration across all disciplines.
Why BIM Specialists are essential:
-
Develop smart, data-rich 3D models
-
Streamline design coordination and documentation
-
Integrate architectural, structural, and MEP systems
-
Conduct clash detection and issue resolution
-
Implement standards like ISO 19650
-
Automate quantity takeoffs and 4D/5D simulations
-
Lead BIM Execution Planning and compliance
-
Support handover with data for facility management
-
Promote lifecycle-based project delivery
-
Collaborate across multiple platforms and stakeholders
This guide includes 30 BIM Specialist interview questions and answers divided into Basic, Intermediate, and Advanced sections to help you prepare effectively.
Get Career-Oriented BIM Certification Course with Expert Mentors! Get a free demo here!
Master BIM and Elevate Your Career – Enroll Today!
Stay ahead in the construction and design industry with our comprehensive BIM Course! Learn Building Information Modeling (BIM) from experts, gain hands-on experience with top software, and boost your career prospects. Join now and become a certified BIM professional!
Know MoreBIM Specialist Interview Questions and Answers: Basic Level
1. What is BIM (Building Information Modeling)?
-
A digital process for creating and managing building data
-
Represents both physical and functional characteristics
-
Supports planning, design, construction, and operations
-
Centralizes data for improved collaboration
-
Enhances decision-making through 3D visualization
2. What does a BIM Specialist do?
-
Manages BIM workflows and modeling standards
-
Coordinates interdisciplinary models for clash detection
-
Supports Revit, Navisworks, BIM 360, and related tools
-
Leads quality control and BIM data validation
-
Guides project teams in BIM adoption and best practices
3. What are the key benefits of BIM?
-
Enhances collaboration and communication
-
Reduces design errors and construction rework
-
Improves visualization and simulation
-
Speeds up approvals with accurate models
-
Supports better asset and facility management
4. What is the difference between CAD and BIM?
| Feature | CAD | BIM |
|---|---|---|
| Output | 2D drawings | Data-rich 3D models |
| Focus | Drafting | Modeling + coordination |
| Intelligence | Lines and shapes only | Parametric elements with data |
| Collaboration | Limited | Real-time, cloud-based |
| Lifecycle Coverage | Design stage only | Entire building lifecycle |
5. What is a BIM Execution Plan (BEP)?
-
A roadmap for implementing BIM on a project
-
Defines roles, responsibilities, and deliverables
-
Establishes modeling standards and data workflows
-
Specifies software platforms and naming conventions
-
Ensures alignment across the project team
6. What is LOD (Level of Development)?
-
Indicates the detail and accuracy of model elements
-
LOD 100: Conceptual
-
LOD 200: Approximate geometry
-
LOD 300: Precise geometry and location
-
LOD 400: Fabrication-ready detail
-
LOD 500: As-built and operational data
7. What is parametric modeling?
-
Uses constraints and parameters to drive model geometry
-
Ensures model elements update automatically when changed
-
Enables reusable components with adjustable settings
-
Supports consistency and design efficiency
-
Reduces manual drafting
8. What is Revit used for in BIM?
-
Authoring 3D architectural, structural, and MEP models
-
Generating 2D drawings and construction documents
-
Creating and modifying parametric families
-
Extracting schedules and quantities
-
Coordinating models and performing clash checks
9. What are families in Revit?
-
Predefined elements grouped by behavior and parameters
-
System Families: Walls, floors, roofs (built-in)
-
Loadable Families: Windows, furniture (custom)
-
In-place Families: Unique elements made in the project
-
Enable component standardization and reuse
10. What is a Central Model in Revit?
-
The main model stored on a server for team collaboration
-
Enables multiple users to work via local copies
-
Sync with Central keeps models updated
-
Ensures consistency and version control
-
Supports project-wide data sharing
BIM Specialist Interview Questions and Answers: Intermediate Level
11. What is clash detection?
-
Identifies conflicts between model elements (e.g., pipe through a beam)
-
Hard Clashes: Physical interferences
-
Soft Clashes: Clearance issues
-
Tools: Navisworks Manage, Revit Interference Check
-
Helps reduce errors during construction
12. How are linked models managed in Revit?
-
Link models separately by discipline (Architectural, Structural, MEP)
-
Use Worksets for visibility control
-
Maintain consistent naming conventions
-
Update links frequently
-
Avoid excessive nesting of links
13. What is Worksharing in Revit?
-
Allows multiple users to collaborate on one project
-
Uses Central and Local files
-
Sync with Central to share changes
-
Reload Latest to get team updates
-
Assign Worksets to divide model components
14. What is COBie?
-
Construction-Operations Building Information Exchange
-
Transfers building asset data to facility managers
-
Includes data like equipment tags, maintenance info
-
Delivered in spreadsheet or IFC format
-
Supports post-construction operations
15. What is a Shared Parameter?
-
Custom parameter used across multiple projects/families
-
Stored in an external .txt file
-
Enables consistent tagging and scheduling
-
Essential for company-wide standards
-
Supports COBie and IFC exports
16. What is a Section Box in Revit?
-
3D tool to crop and isolate specific model areas
-
Improves model navigation and visualization
-
Helps inspect detailed zones (e.g., riser shafts)
-
Reduces view clutter
-
Enhances performance in large models
17. What is a View Template?
-
Preset settings applied to multiple views
-
Controls scale, detail level, visibility, filters
-
Ensures documentation consistency
-
Saves time in creating standard views
-
Improves quality assurance
18. How do you ensure model accuracy?
-
Follow modeling standards and BEP guidelines
-
Conduct regular model audits and health checks
-
Run clash detection and interference reviews
-
Resolve Revit warnings
-
Keep models organized and purged
19. What is 4D and 5D BIM?
-
4D: Adds scheduling data to 3D models
-
Used for sequencing and simulation
-
-
5D: Adds cost data to models
-
Used for quantity takeoffs and budgeting
-
-
Helps with project planning and forecasting
20. What are Revit Phases?
-
Used to manage project timelines (e.g., renovation stages)
-
Typical Phases: Existing, Demolition, New Construction
-
Enables filtered views by phase
-
Supports phased documentation
-
Tracks design progress
Get Career-Oriented BIM Certification Course with Expert Mentors! Get a free demo here!
BIM Specialist Interview Questions and Answers: Advanced Level
21. How do you manage large Revit models?
-
Divide into linked models by zone or discipline
-
Use Worksets for better control
-
Purge unused elements and views
-
Minimize file size with model audits
-
Limit detailed 3D views and sheets
22. What is ISO 19650?
-
International standard for BIM information management
-
Sets naming conventions and data workflows
-
Defines roles and responsibilities
-
Promotes lifecycle-based project delivery
-
Ensures consistency across platforms and teams
23. How do you collaborate with other disciplines?
-
Link discipline-specific models (e.g., MEP with architecture)
-
Use common platforms like BIM 360 or ACC
-
Conduct weekly coordination meetings
-
Share clash detection reports
-
Document workflows and approvals
24. What is a Custom Family?
-
Tailor-made model component for specific project needs
-
Created when standard libraries don’t suffice
-
Enables detailed representation and accurate data
-
Used for unique furniture, equipment, façade elements
-
Should be performance-optimized
25. What is IFC?
-
Industry Foundation Classes – open BIM data format
-
Ensures interoperability between BIM software
-
Used for model exchange across platforms
-
Supports long-term data preservation
-
Essential for regulatory and client deliverables
26. What is a View Filter?
-
Tool to customize visibility based on element parameters
-
Used for highlighting system types or statuses
-
Helps in quality checks and plan reviews
-
Enhances drawing clarity and control
-
Applied via View Templates
27. How do you perform clash detection in Navisworks?
-
Append or merge Revit/IFC models
-
Use Clash Detective tool
-
Define clash sets and tolerances
-
Group and assign issues
-
Export reports for resolution tracking
28. How do you manage BIM 360 projects?
-
Create project folders and set permissions
-
Upload models with consistent file naming
-
Assign roles to project members
-
Use issues and markup tools for collaboration
-
Maintain version control with published models
29. What is the importance of naming conventions?
-
Ensures model clarity and traceability
-
Helps organize sheets, views, and families
-
Prevents confusion during file exchanges
-
Supports automation and scripting
-
Required for ISO 19650 compliance
30. What makes a successful BIM implementation?
-
Clear project goals and BIM uses
-
Well-documented BEP
-
Skilled team with proper training
-
Regular coordination meetings
-
Strong leadership and communication
Master BIM and Elevate Your Career – Enroll Today!
Stay ahead in the construction and design industry with our comprehensive BIM Course! Learn Building Information Modeling (BIM) from experts, gain hands-on experience with top software, and boost your career prospects. Join now and become a certified BIM professional!
Know MoreConclusion
BIM Specialists are much more than modelers — they are leaders in digital project delivery. Mastering the tools is important, but knowing when and how to apply them is key.
Final Tips:
-
Know your software inside-out: Revit, Navisworks, BIM 360
-
Follow standards like ISO 19650 and LOD definitions
-
Communicate clearly across disciplines
-
Always keep models clean, efficient, and coordinated
-
Focus on workflows, not just tools
Keep practicing, stay updated, and you’ll be ready to impress in your next BIM Specialist interview.
Master BIM and Elevate Your Career – Enroll Today!
Stay ahead in the construction and design industry with our comprehensive BIM Course! Learn Building Information Modeling (BIM) from experts, gain hands-on experience with top software, and boost your career prospects. Join now and become a certified BIM professional!
Know MoreFrequently Asked Questions
What does a BIM Specialist do in a typical project?
A BIM Specialist is responsible for managing and coordinating Building Information Modeling processes throughout a project’s lifecycle. Their role includes creating and maintaining BIM models, ensuring data accuracy, setting up project templates, and collaborating with multiple disciplines. They also ensure that all BIM deliverables meet project standards and requirements. A BIM Specialist bridges the gap between design and construction by facilitating coordination, clash detection, and data integration. Their work improves project efficiency, accuracy, and team collaboration.
What is the difference between a BIM Specialist and a BIM Coordinator?
While both roles are closely related, a BIM Specialist typically focuses on the technical aspects of modeling and documentation, while a BIM Coordinator takes a more strategic and managerial role. A BIM Specialist builds families, sets up views, prepares documentation, and performs model cleanups. In contrast, a BIM Coordinator oversees collaboration between disciplines, sets BIM execution strategies, ensures adherence to standards, and leads clash detection meetings. BIM Specialists often report to BIM Coordinators in larger projects.
What skills should a BIM Specialist have to succeed in interviews?
To succeed in a BIM Specialist interview, candidates should demonstrate strong technical knowledge of software like Revit, Navisworks, and BIM 360. They should understand BIM execution plans, Level of Development (LOD), clash detection, and model coordination. Communication and collaboration skills are also essential, as BIM Specialists interact with architects, engineers, and contractors. Familiarity with international standards such as ISO 19650 and file naming conventions is important. Employers also look for attention to detail and a proactive approach to problem-solving.
How should I prepare for a BIM Specialist interview if I’m new to the role?
If you’re new to the BIM Specialist role, start by mastering core BIM tools like Revit and Navisworks. Learn about BIM standards, templates, worksets, and collaboration workflows. Create sample projects that showcase your modeling and coordination skills. Review basic concepts like parametric modeling, family creation, LOD, and shared parameters. Practice explaining your process clearly. Understand how BIM supports construction sequencing (4D) and cost estimation (5D). Employers value both software skills and the ability to apply them in real project scenarios.
What types of projects do BIM Specialists typically work on?
BIM Specialists work on a variety of construction projects, including residential buildings, commercial complexes, hospitals, educational facilities, transportation hubs, and industrial plants. They may also be involved in infrastructure projects such as roads, bridges, and railways. In all cases, they help teams visualize the project in 3D, detect potential issues, and manage data across disciplines. Depending on the organization, a BIM Specialist may support multiple projects simultaneously or focus deeply on one large-scale development.
What is your role during coordination meetings?
During coordination meetings, the BIM Specialist plays a critical role in identifying and resolving clashes between models from different disciplines. They present issues using Navisworks or other coordination tools, propose solutions, and track issue resolution. They also prepare coordination views, snapshots, or reports for meetings. BIM Specialists ensure that models are updated regularly and remain aligned with the project’s latest revisions. Their active involvement helps prevent costly errors and supports better on-site construction planning.
Can you explain the significance of LOD in BIM?
Level of Development (LOD) defines the detail and reliability of model elements at different project stages. For example, LOD 100 refers to a conceptual representation, while LOD 400 includes fabrication-level detail. BIM Specialists must understand when and how to apply each LOD level, ensuring models are not over- or under-detailed. LOD also affects scheduling, budgeting, and construction decisions. During interviews, it’s helpful to discuss how you’ve used LOD to align expectations between stakeholders and improve project outcomes.
How do you ensure model integrity and accuracy over time?
Maintaining model integrity requires ongoing checks and quality control. BIM Specialists regularly audit models for errors, clean up unused families, and manage file sizes. They follow project-specific modeling standards and use tools to identify warnings or conflicts. Shared parameters and naming conventions ensure consistency. Using model health check tools or add-ins also helps identify performance issues. Clear documentation, frequent syncing, and coordination with team members contribute to accurate and reliable BIM models throughout the project lifecycle.
What is your experience with BIM standards and ISO 19650?
BIM Specialists are expected to understand and apply standards like ISO 19650, which outlines principles for managing information throughout the asset lifecycle. This includes naming protocols, file structures, and data exchange practices. Knowledge of the Common Data Environment (CDE) is essential, as is understanding how to deliver BIM data according to employer’s information requirements (EIR) and project BIM execution plans (BEP). During interviews, discussing your experience aligning projects with ISO standards shows your awareness of best practices and global benchmarks.
What tools do you use for clash detection and reporting?
Clash detection is a core responsibility of BIM Specialists, and the most commonly used tool for this task is Navisworks Manage. Within Navisworks, BIM Specialists run clash tests between disciplines such as MEP, structure, and architecture. They group clashes, assign them to relevant team members, and export clash reports. Additional tools like BIM Track or Revizto may be used to manage issue tracking and communication. Revit’s built-in Interference Check is also useful for quick internal checks. Reporting clashes in a clear, actionable format is a key part of the coordination process.