Table of Contents
Many students wonder about type of accounting in demand. The industry keeps evolving with new expectations. Businesses now need smarter financial minds every day. Companies look for experts who guide smart decisions. Accountants today do more than basic reporting. They help reduce risks and improve company performance. They support leaders with accurate financial insights. This blog helps you understand these rising trends.
This blog shows you which roles lead today. You will learn different accounting specialisations clearly .Each section explains what skills employers prefer. You will see why some fields grow faster. We also highlight country-wise and industry-wise demand. You will find helpful answers to common questions. This guide prepares you to choose the right path.
Become an Accounting Pro – Learn from Industry Experts!
Introduction
Accounting careers evolve with business changes. Companies expect stronger financial understanding today. They want experts who support smart decisions. These companies value professionals who ensure clear financial reporting. They need talent that manages risk and compliance. These expectations push some fields faster. They create rising demand for specialised accountants.
This blog helps you understand these shifts. It explains which roles grow fastest now. It shows why businesses prefer certain specialisations. This blog also highlights skills needed for future success. It also covers global demand variations. Each section offers clear and useful guidance. You get insights that support better career choices.
Key points covered:
-
Types of accounting growing quickly today
-
Factors driving higher demand across roles
-
Top specialisations companies hire actively
-
Skills needed for long-term stability
-
Industry-wise and region-wise trends
-
Simple FAQs for quick understanding
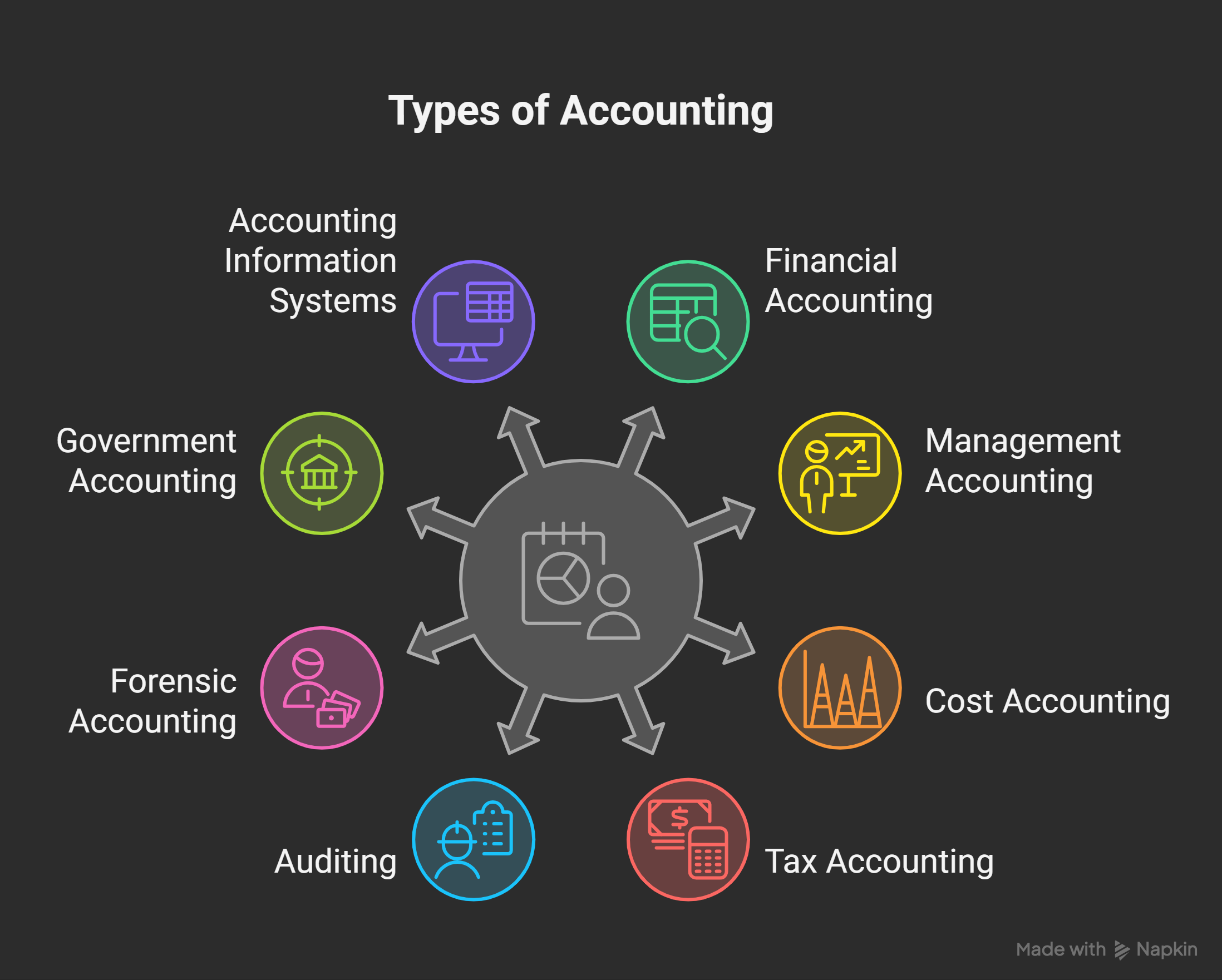
Overview – Main Types of Accounting
1: Accounting provides information on
Understanding the main accounting types helps you see the field clearly. Each branch supports different business needs. Each role uses unique skills and methods. Together, they build a complete financial system. This overview explains these core branches. It helps you understand their purpose. It also shows how each branch functions.
1. Financial Accounting
Financial accounting focuses on correct financial reporting. It records daily financial transactions carefully. It prepares statements for external users. These users include investors and lenders. This field follows strict reporting rules. These rules ensure clarity and consistency.
Key tasks include:
-
Preparing balance sheets and statements
-
Recording transactions correctly
-
Following accepted reporting standards
Common users include:
-
Investors checking financial health
-
Banks assessing credit position
-
Partners reviewing yearly performance
2. Management Accounting
Management accounting supports internal decision-making. It gives managers useful financial insights. This accounting focuses on planning and control. It looks at future financial outcomes. It improves internal workflows and operations.
Important responsibilities:
-
Analysing budgets across teams
-
Tracking internal financial performance
-
Supporting short-term and long-term planning
Useful outputs:
-
Cost reports for quick decisions
-
Performance summaries for managers
-
Forecasts for future projects
3. Cost Accounting
Cost accounting studies production-related costs. It helps businesses track spending accurately. It examines materials, labour, and overheads. This accounting supports efficiency and resource planning. It helps control unnecessary expenses.
Main elements:
-
Direct material calculations
-
Labour cost breakdowns
-
Overhead allocation steps
Key advantages:
-
Better spending control overall
-
Improved pricing decisions
-
Stronger operational planning
4. Tax Accounting
Tax accounting deals with tax obligations. It ensures correct tax calculations. It handles required annual filings. Tax accounting helps avoid unwanted penalties. It follows rules by authorities.
Core activities:
-
Preparing tax-related documents
-
Filing returns on time
-
Checking compliance with rules
Areas of focus:
-
Income tax requirements
-
Indirect tax guidelines
-
Deduction and exemption checks
5. Auditing
Auditing examines financial accuracy carefully. It checks the reliability of records. It reviews internal systems thoroughly. Auditing ensures correct financial controls. It identifies weaknesses in processes.
Types of audits:
| Audit Type | Purpose |
|---|---|
| Internal Audit | Reviews internal systems |
| External Audit | Checks overall financial accuracy |
| Compliance Audit | Verifies rule adherence |
Benefits include:
-
Stronger record reliability
-
Better internal system control
-
Reduced financial risk overall
6. Forensic Accounting
Forensic accounting investigates financial issues closely. It identifies wrongdoing through analysis. It supports cases with clear evidence. This accounting uses detailed financial examination techniques. It assists legal teams effectively.
Important tasks:
-
Investigating suspicious transactions
-
Reviewing records for fraud clues
-
Preparing detailed investigation reports
7. Government Accounting
Government accounting manages public financial records. It follows rules set by authorities. It ensures correct public fund handling. This accounting supports transparent record maintenance. It focuses on public financial responsibility.
Core functions:
-
Recording government expenditures
-
Managing public revenue records
-
Maintaining budget transparency
8. Accounting Information Systems
AIS combines accounting and technology. It uses software to manage data. AIS also supports quick financial processing. It improves information accessibility greatly. It enhances accuracy in daily tasks.
Main components:
-
Data input tools
-
Processing systems
-
Reporting modules
Placement Oriented PWC Business Accounting Course
PWC Certified Business Accounting Course by Entri App: Master in-demand skills, ace interviews, and secure top-tier jobs.
Join Now!Factors That Decide “Demand”
Understanding demand factors helps you see hiring patterns clearly. Each factor influences career opportunities differently. Some factors shift slowly with time. Others change quickly with business needs. Together, they guide overall market demand. This section explains these major influences. It helps you see their direct impact.
1. Market Growth Trends
Market growth directly shapes accounting needs. Growing businesses require more financial support. Expanding firms increase their financial tasks. These movements create steady role demand.
Key points:
-
Growth increases daily transactions
-
Companies expand reporting requirements
-
New operations increase financial responsibilities
Additional insights:
-
Rising activity needs accurate records
-
Expanding teams require stronger structure
-
New units need financial tracking
2. Regulatory and Legal Requirements
Regulations strongly influence accounting tasks. New rules increase required documentation. Firms must follow guidelines carefully. This drives need for trained professionals.
Important areas:
-
Reporting rules across sectors
-
Compliance checks for activities
-
Documentation guidelines for operations
Regulation impact table
| Regulatory Aspect | Effect on Demand |
|---|---|
| New reporting rules | More compliance support |
| Stricter audits | Higher verification needs |
| Updated tax laws | Increased specialist roles |
Regulation highlights:
-
Rules increase checking work
-
Compliance needs trained staff
-
Documentation accuracy becomes essential
3. Technology Adoption Levels
Technology changes accounting processes quickly. Automation reduces repeated tasks. New systems improve accuracy levels. Skilled roles remain very important.
Influencing elements:
-
Digital tools support financial work
-
Software upgrades improve workflows
-
Data systems enhance reporting
Technology highlights:
-
Tools require trained handling
-
Systems need correct data
-
Technology improves overall visibility
4. Business Complexity Levels
Complex business structures increase accounting needs. Larger units require organised tracking. Multiple functions need coordinated reporting. Complex models demand deeper understanding.
Key indicators:
-
More teams need financial inputs
-
Larger structures increase activities
-
Diverse functions require oversight
Complexity highlights:
-
Detailed records become essential
-
Cross-team coordination improves accuracy
-
Internal workflows need alignment
5. Economic Conditions
Economic shifts affect hiring patterns. Strong economies increase financial activity. Weak periods change accounting focus. Both conditions drive specific roles.
Primary factors:
-
Growth increases tracking needs
-
Slowdowns require careful planning
-
Shifts alter budget priorities
Economic highlights:
-
Cash flow needs close monitoring
-
Cost planning becomes important
-
Forecasting needs become stronger
6. Industry-Specific Requirements
Industries follow different financial patterns. These patterns shape required roles. Each sector demands unique skills.
Industry examples:
-
Manufacturing focuses on cost tracking
-
Banking depends on detailed checks
-
Retail requires sales monitoring
Industry table
| Industry | Key Focus Area |
|---|---|
| Manufacturing | Cost systems |
| Banking | Record checks |
| Retail | Transaction tracking |
Highlights:
-
Sector needs shape responsibilities
-
Patterns guide required expertise
-
Skills differ across industries
These factors together shape accounting demand everywhere.
Become an Accounting Pro – Learn from Industry Experts!
Top 3–5 Most In-Demand Types of Accounting
Understanding high-demand accounting fields helps you choose suitable paths. Each field grows for different business reasons. These roles support essential financial needs. They also offer strong long-term stability. This section explains these leading fields. It shows what makes them valuable. It also highlights their key responsibilities.
1. Management Accounting
Management accounting supports internal business planning. It helps teams understand financial direction. It focuses on short-term and long-term performance. This accounting provides insights for everyday decisions. Many companies depend heavily on this role.
Key responsibilities:
-
Preparing structured internal reports
-
Reviewing performance across departments
-
Supporting planning for future goals
Why demand is strong:
-
Managers need clear financial visibility
-
Businesses prefer data-backed decisions
-
Teams require constant performance updates
Summary table
| Aspect | Importance |
|---|---|
| Planning support | Helps guide decisions |
| Performance tracking | Improves internal focus |
| Forecast preparation | Supports future goals |
2. Tax Accounting
Tax accounting deals with mandatory tax work. It handles yearly filing requirements. This ensures correct calculations always. It helps avoid unwanted legal issues. This field stays relevant continuously.
Core tasks:
-
Preparing tax documents properly
-
Checking rule changes regularly
-
Handling returns for businesses
Why demand is consistent:
-
Tax rules change frequently
-
Companies must follow authorities
-
Filing errors create heavy penalties
Highlights:
-
Strong need during tax periods
-
High value in every industry
-
Constant updates keep roles important
3. Financial Accounting
Financial accounting builds accurate financial statements. It tracks transactions daily. This accounting organises financial information clearly. It ensures records remain fully reliable. Every business needs this function.
Key duties:
-
Preparing major financial statements
-
Recording transactions systematically
-
Ensuring clean financial records
Why demand stays stable:
-
All firms require reported results
-
Lenders check company statements
-
Investors depend on accurate information
Financial focus table
| Output | Purpose |
|---|---|
| Balance sheet | Shows financial position |
| Income statement | Shows business performance |
| Cash flow report | Shows cash movement |
4. Auditing
Auditing checks financial accuracy carefully. It examines internal systems thoroughly. Auditing ensures records stay trustworthy. It reviews processes for weaknesses. Many sectors rely on audit support.
Key responsibilities:
-
Reviewing internal activities carefully
-
Checking record accuracy regularly
-
Assessing control systems fully
Why demand increases:
-
Businesses need stronger controls
-
Authorities enforce strict checks
-
Companies require verified records
Audit insights:
-
Helps reduce financial errors
-
Improves system accountability
-
Strengthens organisational trust
5. Forensic Accounting
Forensic accounting investigates financial concerns. It identifies irregular activity clearly. This accounting helps organisations understand hidden issues. It provides detailed findings for review. Many sensitive cases need this role.
Primary duties:
-
Examining suspicious financial data
-
Identifying fraudulent patterns
-
Preparing investigation reports
Why demand rises:
-
Growing concerns about fraud
-
Higher scrutiny in major firms
-
Sensitive cases need accurate analysis
Key strengths:
-
Strong analytical approach
-
High importance in disputes
-
Direct value in risk situations
These fields represent today’s strongest accounting opportunities.
How Demand Changes by Country & Industry
Demand varies across regions and industries. Each location follows unique financial patterns. Each sector uses different accounting strengths. These variations shape hiring priorities everywhere. Understanding these differences improves career planning. It helps you choose suitable environments. It also supports better long-term decisions.
Demand Differences by Country
Different countries follow unique financial systems. These systems influence accounting priorities. Some countries require specialised knowledge. Others need broad financial understanding. These differences shift demand levels.
1. United States and Canada
These countries follow strong reporting systems. They value detailed financial accuracy. These countries focus heavily on compliance checks. They also expect strong analytical ability.
Key observations:
-
Complex rules create steady opportunities
-
Reporting needs increase hiring demand
-
Accuracy expectations improve role importance
2. United Kingdom and Europe
These regions follow international reporting frameworks. They maintain structured financial environments. These countries expect clean and consistent statements. They also value process reliability.
Important points:
-
Clear standards create consistent roles
-
Strong systems improve career opportunities
-
Reporting accuracy remains highly important
3. Middle Eastern Countries
These regions saw rising financial regulations. Many countries introduced new tax systems. These shifts created major skill needs. Accounting teams expanded quickly.
Regional highlights:
-
Tax systems increased demand
-
Compliance needs created opportunities
-
Financial oversight improved significantly
4. India and South Asia
These regions show strong business growth. Small firms expand financial operations. Digital systems grow across sectors. These shifts increase accounting activity.
Key patterns:
-
Growing firms need structured reporting
-
Digital tools improve accounting roles
-
Expanding markets create new opportunities
Demand Differences by Industry
Industries follow different financial patterns. These patterns shape role expectations. Each industry requires specific accounting strengths. These needs create varied hiring trends.
1. Manufacturing Sector
Manufacturing depends on cost understanding. It needs accurate spending assessment. This sector requires structured production tracking. It values strong cost systems.
Industry traits:
-
Spending control remains essential
-
Production needs clear cost analysis
-
Processes require timely assessments
2. Banking and Financial Services
This sector requires deep record review. It handles sensitive transactions daily and follows strict internal procedures. It demands careful financial analysis.
Key elements:
-
Detailed checks remain crucial
-
Accurate records support decisions
-
Verification tasks stay important
3. Retail and E-commerce
These sectors focus on transaction volume. They track daily sales movements. These sectors require strong data visibility. They manage constant financial activity.
Important features:
-
Sales records need quick processing
-
Inventory influences financial reports
-
Daily activity increases workload
4. Technology and Startup Sector
Startups grow at fast speeds. They need structured financial clarity and rely on digital financial tools. They expect flexible financial support.
Sector highlights:
-
Fast growth increases tracking needs
-
Digital systems support quick reporting
-
Scaling teams need organised processes
Summary Table: Country vs Industry Influence
| Area | Main Demand Driver |
|---|---|
| Countries | Regulatory structures |
| Regions | Financial practices |
| Industries | Operational patterns |
| Sectors | Process requirements |
Placement Oriented PWC Business Accounting Course
PWC Certified Business Accounting Course by Entri App: Master in-demand skills, ace interviews, and secure top-tier jobs.
Join Now!Frequently Asked Questions
Which accounting field offers the strongest long-term career stability?
Management-focused roles and financial reporting positions offer strong long-term stability because organisations continuously require accurate performance insights, planned budgets, and reliable statements to support decision-making, annual evaluations, and growth analysis. Even when technology automates repetitive tasks, these functions remain essential since companies still need professionals who can design reports, interpret numbers, evaluate risks, and guide strategic planning in clear and practical ways.
Do specialised accounting certifications improve job prospects?
Yes, certifications such as CA, CPA, CMA, ACCA, and CISA significantly improve job prospects because they validate advanced technical knowledge, demonstrate strong commitment to the profession, and make candidates more competitive for specialised and higher-level roles. Employers value certified professionals because they can handle complex responsibilities, maintain accuracy under strict regulations, and contribute deeper financial insight during audits, planning, or compliance work.
Can beginners enter high-demand accounting roles without experience?
Beginners can enter these roles, but they must build strong fundamentals in accounting concepts, reporting standards, and essential software tools before moving into specialised positions. Many companies hire entry-level candidates for junior tasks, and as beginners gain experience, learn relevant systems, and improve analytical skills, they can move into planning roles, auditing functions, tax-focused positions, or reporting responsibilities that offer better long-term growth.
How important is software knowledge for modern accounting careers?
Software knowledge is extremely important because most organisations rely on digital systems, ERP platforms, automated tools, and data-driven dashboards to manage daily financial tasks, reduce errors, generate quick reports, and streamline overall performance monitoring. Accountants who understand tools like SAP, Tally, QuickBooks, Oracle, or advanced Excel can work faster, solve problems quickly, and manage larger volumes of information with greater accuracy, which makes them far more valuable to employers.
Will automation reduce the number of accounting jobs?
Automation will change the nature of accounting jobs, but it will not reduce opportunities because automated systems handle only repetitive tasks such as basic entries, rule-based checks, or standardised calculations, while accountants remain responsible for interpretation, judgement, planning, and risk evaluation. As a result, demand increases for professionals who understand both accounting principles and digital tools, and these professionals are needed to oversee systems, validate outputs, manage exceptions, and translate data into meaningful guidance for business decisions.