Table of Contents
Material Requirement Planning (SAP MRP) is a tool that helps in planning the quantity requirements and schedules of a given material. It not only ensures the availability of the material for which the MRP is being done, but also ensures the availability of the components (of all BOM levels) further down in the BOM structure.
In addition to ensuring material availability, MRP also performs purchase quotation planning using lead times for materials/components. When the material is an internally produced material, it will use the lead times or operating times from the procedures/recipes, and if the material is an externally procured material, it will get the lead times or lead times for the material defined in the appropriate range. place in the tool/system. The planning of procurement proposals not only derives the capacity utilization of orders at the workplace, but also calculates the delivery dates of the components that would be required for production (delivery date = processing start date).
The MRP output suggests purchase proposals (planned orders or purchase requisitions) to guarantee material availability and at the same time plan purchase proposals using lead times for materials/components. Material Requirement Planning can be run for purchased materials or finished sales materials or subassemblies (semi-finished products) used in production.
Elevate your Career with SAP MM Course! Get free Demo Here!
What is MRP in SAP MM
MRP is a system designed for production planning. Identifies needed materials, estimates quantities, determines when the material will be needed to meet the production plan, and manages the timing of deliveries – to meet requirements and improve overall productivity.
Systems Applications and Products in Data Processing Material Requirement Planning(SAP MM) is used to produce the required amount of material on time for internal purposes. In manufacturing, the function of MRP is to ensure timely availability of material. The main goal is to plan the delivery based on the requirements and with regard to the current stock.
Advantages of SAP MRP
1: Accounting provides information on
The benefits of using SAP MRP are as follows:
- Improved Inventory Management: Systems Applications and Products in Data Processing (SAP) MRP provides enabling organizations to optimize inventory levels and reduce excess inventory, real-time visibility into inventory levels and demand forecasts . This leads to improved efficiency and significant cost savings.
- Better Production Planning: Using MRP, organizations can plan production more efficiently and ensure they have the right amount of raw materials and components on hand to meet production targets. This reduces the risk of stock outs and helps increase customer satisfaction.
- Streamlined Supply Chain Management: SAP MRP integrates with other key functions such as sourcing and inventory management to provide a holistic view of the supply chain. This enables organizations to optimize supply chain processes, reduce lead times and improve overall efficiency.
- Accurate Demand Forecasting: By analyzing current demand and historical data, SAP MRP helps organizations accurately forecast future demand. This allows them to plan production and purchasing activities more effectively, reducing the risk of oversupply or undersupply.
- Cost Savings: By optimizing inventory levels and improving production planning, SAP MRP helps organizations reduce costs associated with excess inventory, expedited purchasing and stock outs.
MRP versus ERP
You could say that ERP is a direct descendant of Material Requirement Planning (MRP) , or you could say that MRP is part of ERP.
For an explanation, let’s look to history. After its inception, further development of MRP involved the integration of the original MRP modules—sales, inventory, purchasing, bill of materials, and production control—and their combination with financial and accounting functions. The new set that was created was called MRP II. After that, the software set continued to grow and expand with new capabilities. To better describe its broader functionality, the term ERP – or Enterprise Resource Planning Software – was coined.
Today, the planning function includes much more than just materials, but even the latest incarnations of ERP can trace their roots directly to MRP. And in all ERPs, the original principle of Material Requirement Planning (MRP) is still intact: identify what is needed, when it is needed and how much is needed .
Also compared to MRP, ERP software contains much more functionality. There is an equally strong argument for the second statement: MRP is really only part of enterprise resource planning software.
Benefits of an MRP System
Why do companies that manufacture products need an MRP system? Because their success in the market largely depends on their material planning, production and inventory management capabilities.
Materials planning can be straightforward and relatively simple , but only when the number of products is limited, volumes are low, and each product contains only a few components.
Complex calculations are needed for complex products and higher production volumes. The ability to predict and plan for materials and components is critical to effectively managing finished goods production and inventory. The basic building block for the planning and scheduling of equipment and skilled personnel is planned production. Inventory is usually a major cost of doing business and one of the biggest factors in manufacturers’ profitability. Without material requirements planning, it is impossible to effectively manage inventory so that you have the right amount of the right item at the right time. Too much inventory is expensive, but not enough can lead to inventory outages, which are often a major cause of production interruptions, late deliveries, increased costs, and poor customer service.
How to run MRP for all Products
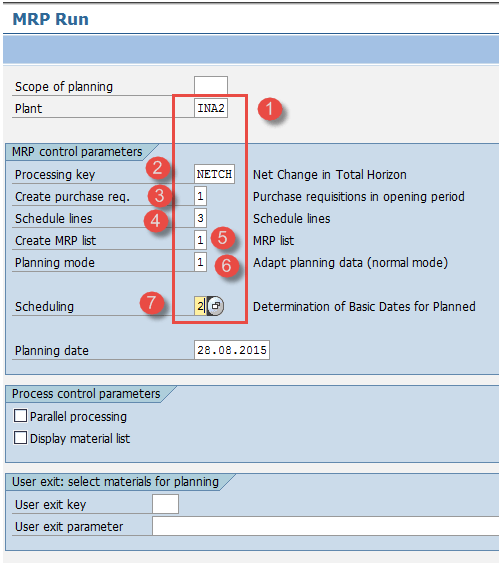
Step 1) On the SAP Easy Access screen, open transaction MD01 and we will run MRP at the plant level.
- Provide your manufacturing plant for which you want to run MRP.
- Enter processing key as “NETCH” (Net change in total horizon)
- Enter “1” in the Create Purchase Requisition field. This means that for externally procured materials, MRP will generate purchase requisitions instead of planned orders.
- Enter “3” for plan lines, which means that MRP will generate plan lines for raw materials that have a planning agreement.
- Enter “1” in the MRP list and the system will create an MRP list similar to the stock/requirement list for later analysis of the previous MRP run.
- Enter planning mode “3” as we delete and recreate all planning data for all materials.
- Enter a planning indicator of “2”, which means that MRP will perform lead time planning and consider routing times to calculate planned order dates.
in hand and cope with the shortage.
After filling the required fields, click![]() to go to the next screen.
to go to the next screen.
To ignore this message, press enter .
The system will nicely ask you to recheck your input parameter as the MRP run will reschedule and overwrite any existing data. Are you sure??? If so, press enter.
Are you really, really sure you want to continue??? If so, press enter again.
Step 2) The system will take some time to calculate the material requirement.
- A message will appear when the calculation is complete. Here it is possible to see how many materials were planned and what parameters were given during the run.
MRP Run for single material
Step 1) In transaction MD02 we run MRP for one material.Enter the material code for which you want to run MRP.
1.Enter the code of your manufacturing plant for which you want to run MRP.
2.Enter processing key as “NETCH” (Net change in total horizon)
3.Enter “1” in Create purchase requisition, which means that for externally procured materials, MRP will generate purchase requisitions instead of planned orders.
4.Enter “3” for plan lines, which means that MRP will generate plan lines for raw materials that have a planning agreement.
5. Enter “1” in the MRP list and the system will create an MRP list similar to the stock/requirement list for later analysis of the previous MRP run.
6.Enter planning mode “3” as we delete and recreate all planning data for all materials.
7.Enter a planning indicator of “2”, which means that MRP will perform lead time planning and consider routing times to calculate planned order dates.
After filling required data, click![]() to go to the next screen.
to go to the next screen.
The system will nicely ask you to recheck your input parameter as the MRP run will reschedule and overwrite any existing data. Are you sure??? If so, press enter.
Are you 100% sure you really want to continue??? If so, press enter again.
Step 2) The system will take some time to calculate the material requirement.
A message will appear when the calculation is complete. Here you can see how many materials have been scheduled.
Note : Since there are 22 materials available in the plant, only these 22 materials have been scheduled.
MRP evaluation – Stock/Requirement List
In this list, you will see requirements, current stock and planned receipts, i.e. material orders.
Step 1) On the SAP Easy Access screen, open transaction MD04
- Enter the material for which the stock/requirement list needs to be displayed.
- Enter the race code.
Step 2) After entering information in all the fields, click![]() to go to the next screen, and Stock/requirement list displayed.
to go to the next screen, and Stock/requirement list displayed.
-
Display stock/requirements list of the material is generated, where you can see
- BOM for material D13967476 was exploded and
- Purchase requisition of 50 (fixed lot size 50 maintained in material master code A01232589) was generated against the net requirement of – 41.606.
Step 2) After entering information in all the fields, click to go to the next screen and the inventory/requirement list will be displayed.
- A stock/material requisition list display will be generated where it can be seen
- The bill of material for material D13967476 was laid out and
- A purchase requisition of 50 (fixed lot size of 50 maintained in material master code A01232589) was generated against a net requisition of 41,606.
Troubleshooting
- There may be a case where the material master record does not exist. Before running MPS/MRPA, material master must be created for the material .
- Before running MRP, ensure that BOM and routing data are available to generate requirements-based purchase proposals at all BOM levels, otherwise planned orders would be generated without a BOM, causing problems in the subsequent consumption process.
Conclusion
Any Material Requirement Planning (MRP) report is a snapshot of a living organism. MRP has evolved from a relatively simple and straightforward calculation to a complex, intelligent and essential decision support system. It offers effective, efficient and responsive planning and control for any organization that turns components into products that meet customer requirements.
Entri online SAP MM training course with a focus on delivering world-class quality. This course equips you with knowledge and practical trading scenarios. This will also prepare you well for the job market and certification. Our SAP MM Training course is provided by a highly experienced and expert lecturer with many years of industry experience.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the difference between ERP and MRP?
MRP is the function or software module that calculates material acquisition plans – purchase and manufacturing orders – needed to meet production plans and customer demand. When combined with supporting applications like engineering, inventory, purchasing, and production control, the software suite is called manufacturing resource planning or MRP II. In the mid-1990s, MRP II was renamed enterprise resource planning (ERP) to reflect its broadened scope and distinguish newer, more capable versions from more limited predecessors. The ERP term is still the dominant name for these systems, although some authorities are using the more general term “enterprise systems.”
What is MRP II?
The original MRP function or module is the calculation of material requirements. When combined with supporting applications, such as customer orders, inventory, engineering, purchasing, production control, finance, and accounting, the suite is called manufacturing resource planning, or MRP II. MRP has been and remains the core planning approach in nearly all modern manufacturing information systems.
What is MRP planning?
MRP is the function or software module that calculates the need for materials and recommends production and purchasing activity (orders) to satisfy those demands. MRP planning is the process of exercising those calculations to develop a plan. MRP is a core part of nearly all integrated information management systems for manufacturers, called enterprise resource planning or ERP.